Three Ways Retailers Use Search Beyond the Ecommerce Store
March 29, 2023 | Updated: December 2, 2025
When consumers think of retail search, the first thing that comes to mind is typically the search bar of an ecommerce website. This is for a good reason: a Salesforce commerce study shows that 87% of shoppers begin their shopping journey in the search bar, and Forrester has found that as many as 68% of shoppers would not return to a site that provided a poor experience.
But retailers that exclusively focus on search capabilities in the context of ecommerce are missing out on huge benefits in customer experience and workforce efficiency. To drive fast application experiences, the querying and indexing of data sets is vitally important, and can be a game changer for easy performance optimization.
Let’s explore some of the innovative ways that retailers are using search indexes to super-power their application experiences.
Why search is important across retail organizations
Large retail data sets, like product and customer data, are used by both customer-facing ecommerce or loyalty applications and internal use cases: inventory management, stock management, customer care, purchasing, supplier and vendor management, marketing and more.
Customers using ecommerce search bars typically have an excellent “Google-like” experience with auto-complete, faceting, fuzzy matching, etc., but the retail workforce and back office staff often aren't given the same luxury. These internal teams are trying to work efficiently, but they are stuck using front ends powered by a traditional operational database with no search indexing capabilities.
These teams are missing out on a search engine that is optimized for unknown or unpredictable workloads. Search indexing will speed up queries where the input is user-defined or might be searching across multiple fields. Let’s look at a comparison:
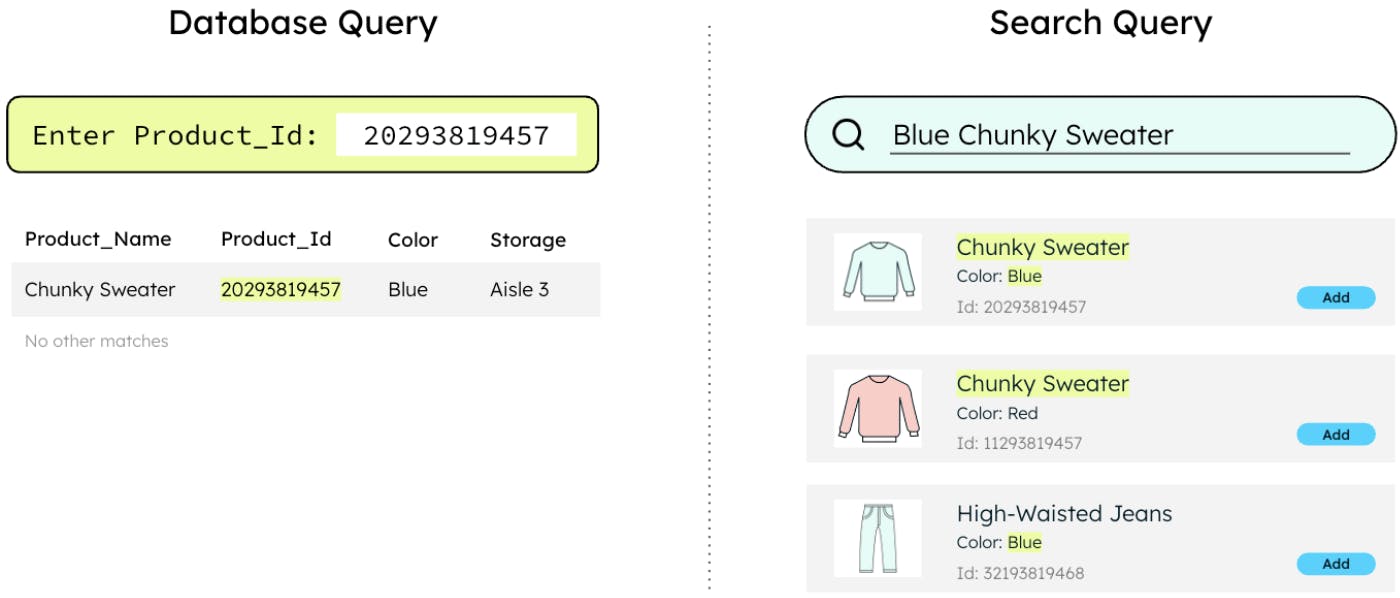
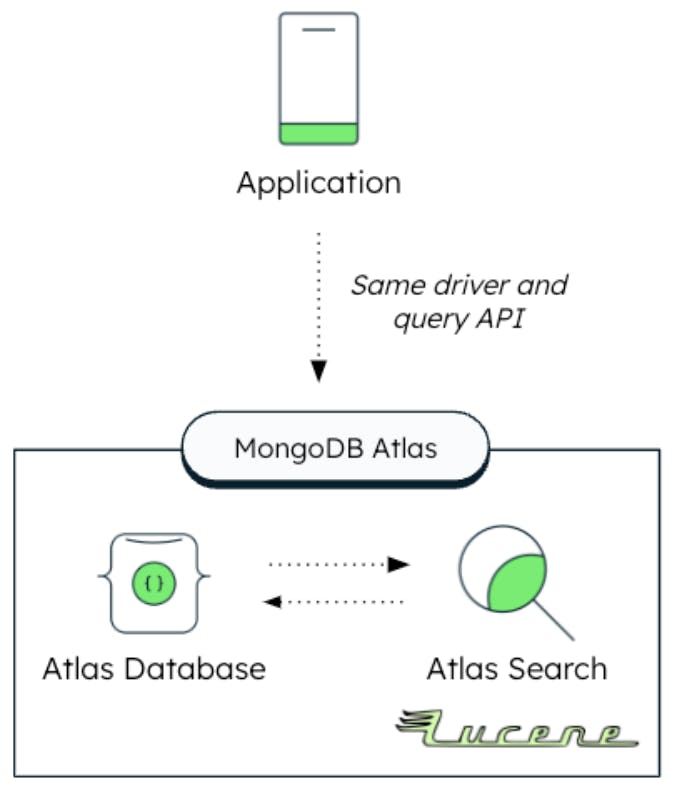
For these under-served and often overlooked use cases, retailers need a quick and cost-effective solution to adding search, like MongoDB Atlas Search. Adding a search index to an application can be done in minutes, without creating operational complexity. MongoDB manages the spin up and management of the backend Apache Lucene search engine, and the complex data and index synchronization activity.
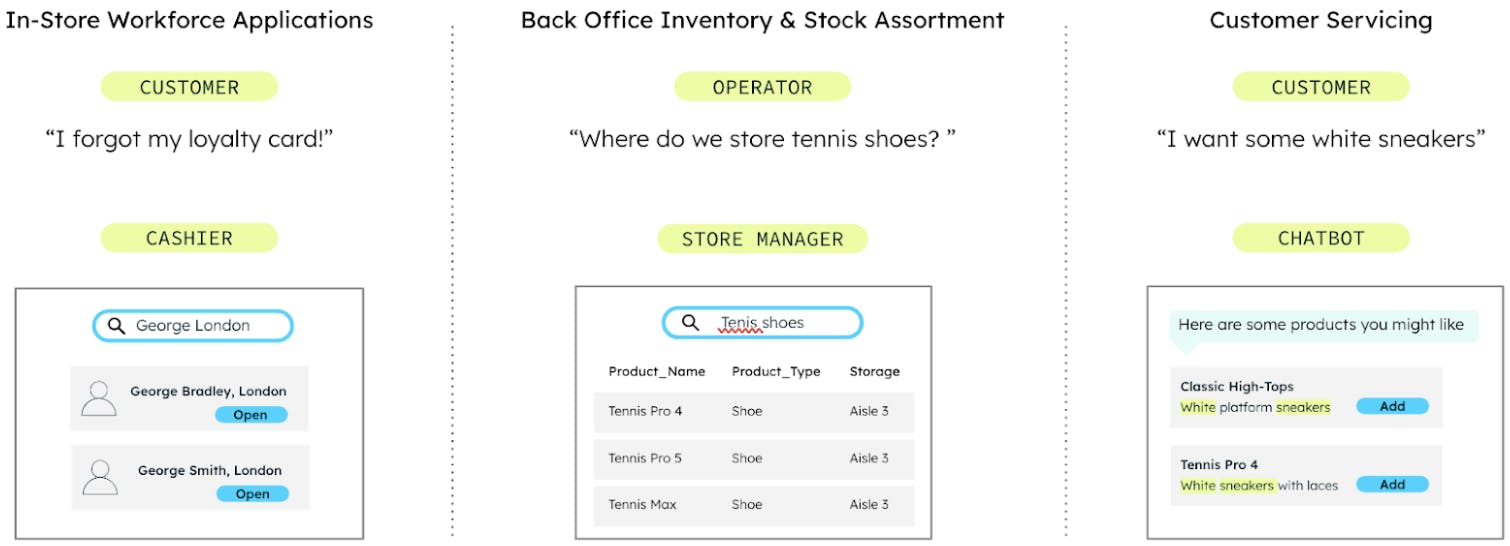
The three most common use cases for retail
The easy addition of search can optimize application performance and usability in the retail industry in three important areas:
-
In-store workforce applications
-
Back office inventory and assortment
-
Customer servicing
In-store workforce applications
Speed is important in workforce applications, because these interactions happen in real time. Think of an in-store customer spelling out a name in full at checkout for a grocery purchase to be added to a loyalty account. This could add five minutes to a checkout experience, disincentivizing the customer to engage with the loyalty program.
Now imagine that the same checkout attendant can identify the customer by any number of data points, not only loyalty number, but also name, first line of address, email, etc., with faster lookup through auto-complete and fuzzy matching. A retailer that MongoDB works with does this auto-lookup in store with Atlas Search in 200-300 milliseconds for optimum customer satisfaction.
Customers and staff also can have difficulty remembering or correctly identifying products. A DIY amateur or a new employee can’t be expected to know the exact name or product ID. This is a great use case for search indexing as we do not know the field in the document or the product attribute that we are querying against. MongoDB has customers that stock more than 150 million products. Strong typo tolerance makes life easier for everyone.
Back-office inventory and assortment
Flawless purchasing and stock management ensures brick and mortar and online stores get the right inventory at the right time to maximize sales and reduce wastage or deadstock.
An operator responsible for distributing products into categories will define in which store shelf a product needs to be and adjust this depending on customer behavior and contractual changes with the supplier. Inventory applications will be used on a daily basis by every operator.
These are small internal applications that can have a huge impact on the overall business, but are often overlooked by large IT programs for budget or have a smaller IT team. These teams are adopting Atlas Search because they can get it up and running in as few as three weeks and fully integrated into their application without taking on more operational overhead.
Customer servicing
Long call center or chat conversations wait times have high operational costs and cause customer churn. It is vital to identify the customer as quickly as possible by the data they provide: order or customer ID, phone number, store address, etc.
Retailers who have created a “Customer 360” across their customer relationship management and loyalty systems have created a large complex pool of data. The ability to run a single query to search across all available attributes makes it much faster to identify a customer.
Search can also be used to optimize speed and accuracy of results for chat applications and chat bots who have to answer a large volume and variety of questions. This is a perfect use case for search with unpredictable user inputs. If answers to the questions can be searched across the entire knowledge base, speed and relevancy can be improved.
MongoDB has retailer customers building chatbot applications for internal use cases like an IT team answering common questions, and external ones. For example, on the ecommerce homepage, a chatbot needs search functionality to be able to quickly do product lookup, customer identification, or make a suggestion. Quick and easy search implementation will add to the customer experience and reduce staff operations.
Where your company could add search functionality
It’s time to think beyond the ecommerce search bar.
-
What are the search workloads within your company’s retail estate?
-
Are there internal applications that have your frontline or back-office staff frustrated with inefficient lookups?
-
Is the reason you’re not implementing search today the fact that it's a heavy lift to add an additional technical component to your architecture?
These are the types of conversations that are driving adoption of Atlas Search across the retail industry, as businesses persevere in a tough macro-economic climate to do more with less. Adding vital functionality to applications without adding complexity is a win for the retailer, the workforce and the consumer.
Want to learn about how MongoDB has integrated Search into the Atlas Developer Data Platform? Head to the Search solution page to explore more technical and in-depth resources.