Your organization might be at a point where it’s ready to start exploring cloud options more thoroughly. You’re probably familiar with the top three cloud providers: Microsoft Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). But rather than just using pricing and the name of the companies behind those services, your organization might have some concerns about topics like availability, fault tolerance, and disaster recovery. After all, your organization has a lot on the line in the event of a problem.
Looking at Microsoft Azure in particular for this article, we’re going to take a look at some common topics around the cloud platform, such as what Azure regions are, how many regions there are in Azure, and how they relate to availability zones.
What are Azure regions?
An Azure region is a geographical area in which one or more physical Azure data centers reside. These data centers exist as part of a latency-defined perimeter to offer the best possible performance and security to users.
Azure has more than 60 announced regions, which is more than all other cloud providers to date.
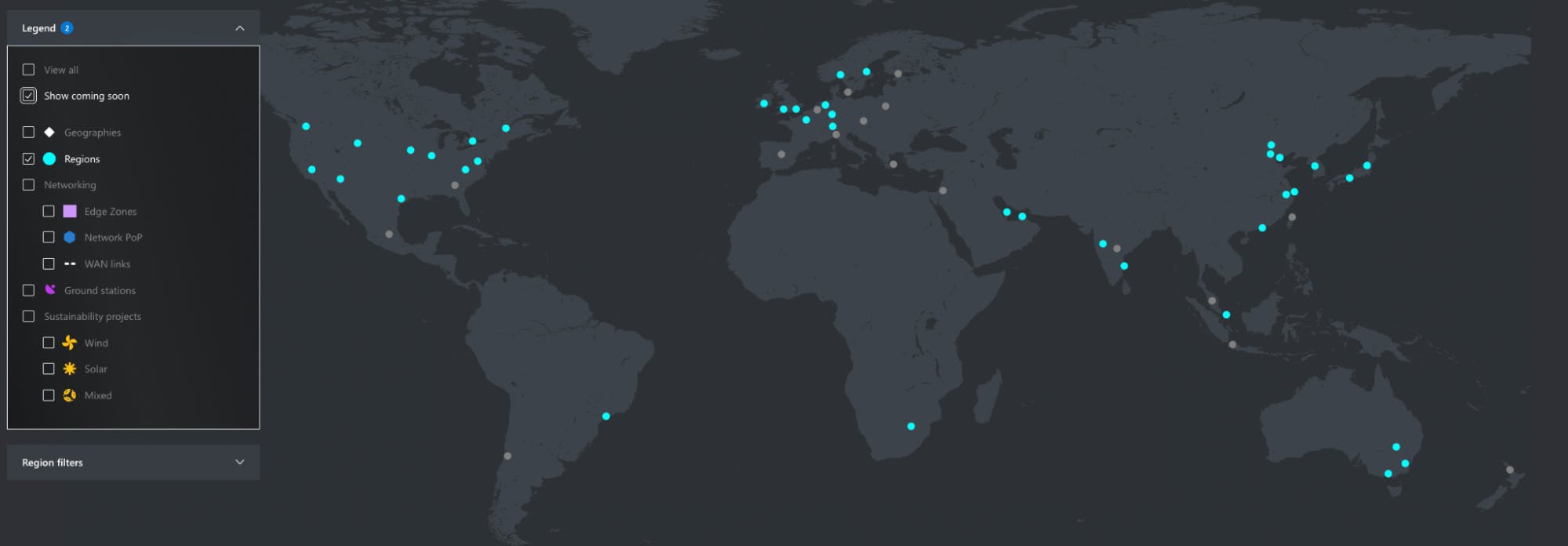
To handle failover and disaster recovery scenarios, Azure offers region pairs, which are two regions within the same geography. In the unfortunate scenario where one region becomes unresponsive, the other region in the Azure region pair will be used. As a result, your organization will experience high availability and a great user experience.
An Azure region only gives us a high-level view into the Azure cloud, more specifically around geographic locations. Digging deeper will lead to Azure availability zones.
Azure availability zones
An Azure availability zone is a physical data center location within a region. These physical data centers are separated within a region to provide tolerance from local failures that could be related to hardware or software problems and even natural disasters, such as earthquakes, fires, and floods.
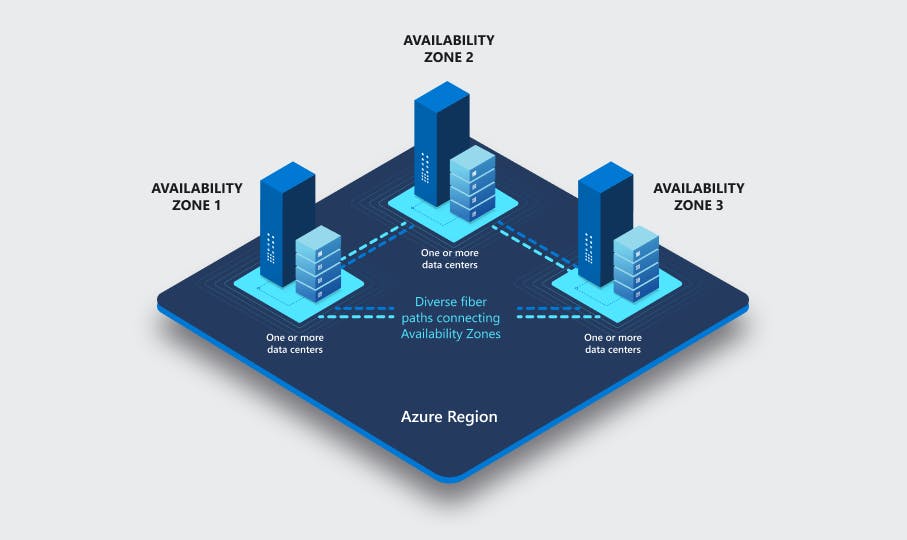 Image Sourced From: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/availability-zones/az-overview
Image Sourced From: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/availability-zones/az-overview
Azure availability zones are designed to be highly available, more fault-tolerant, and better at scaling than single data center architectures.
When choosing Azure as the cloud provider you use for your organization, you can be sure that you’ll have the performance and availability necessary to build amazing products.
FAQ
The following are some frequently asked questions around Azure regions, region pairs, and availability zones.
What are Azure regions and region pairs?
An Azure region is a collection of data centers deployed within a latency-defined perimeter. A region pair consists of two Azure regions within the same geographies for disaster recovery and failover scenarios.
What is the difference between a region and availability zone in Azure?
Azure availability zones are physical but separate locations within an Azure region.
Who has more regions, AWS or Azure?
As of right now, AWS has 27 geographic regions and Azure has more than 60 geographic regions as part of its global infrastructure.