Apple ID Authentication
Overview
The Apple ID authentication provider allows users to log in with their Apple ID credentials through Sign in with Apple. This authentication method uses the industry-standard OAuth 2.0 authorization protocol.
When a user successfully logs in through Sign in with Apple, Apple returns a credential object that includes a JSON Web Token that the Apple ID provider uses to authenticate the user. If the user has granted permissions to your app, the credential object may also include the user's name and email address.
For additional information on how to implement Sign in with Apple, check out:
The official Sign in with Apple documentation on Apple's Developer Portal
The Introducing Sign In with Apple session from WWDC 2019
The associated reference application.
Note
An iOS app that uses Apple ID authentication must target iOS 13 or newer.
The following diagram shows the OAuth logic flow:
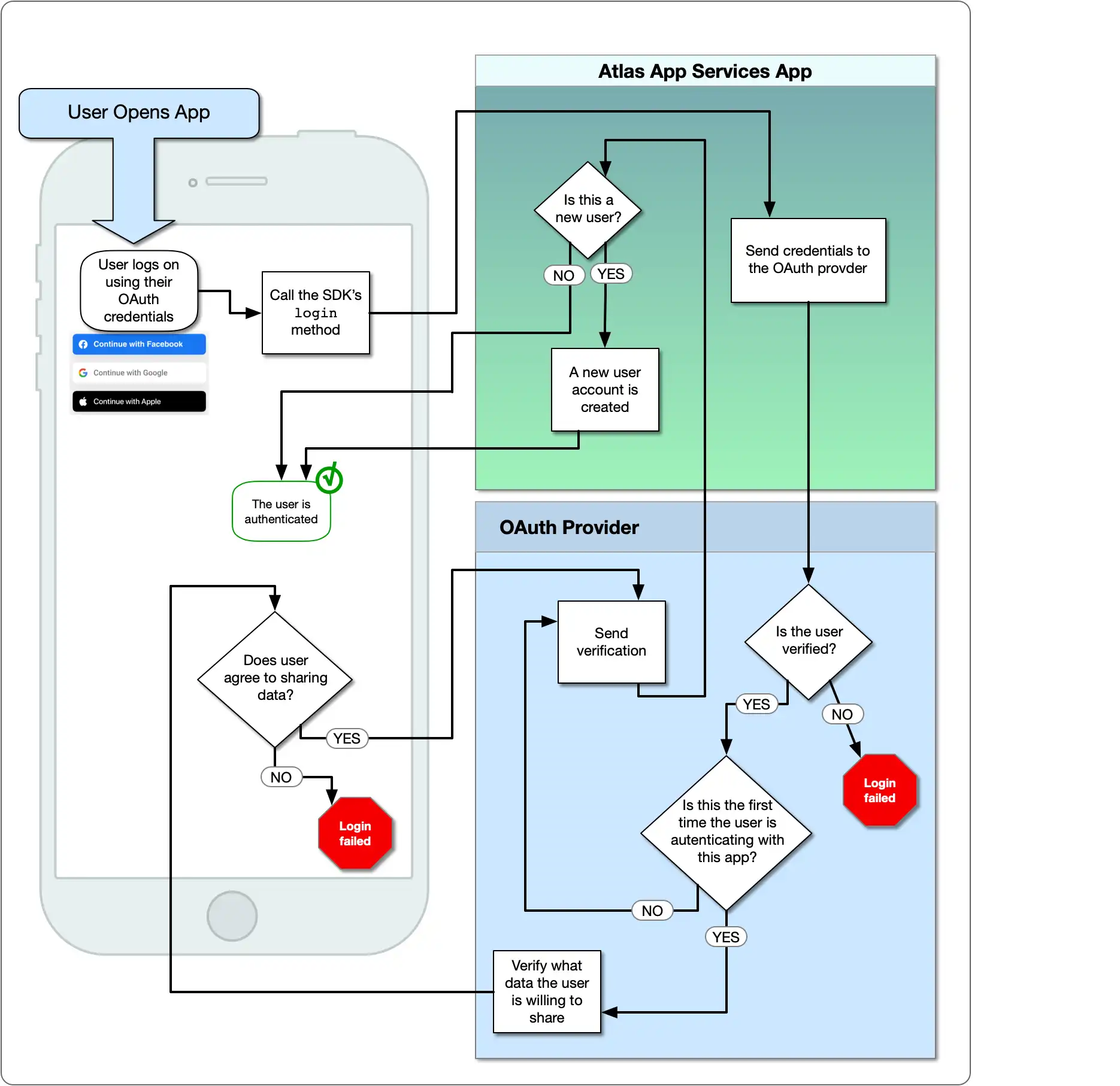
What You'll Need
Before you can implement Apple ID authentication you will need the following:
An active Apple Developer Program account.
Xcode 11 or newer.
Configure Apple ID Authentication
When using Sign-in with Apple with Atlas App Services, you can configure the Apple authentication provider for either a mobile application or a web application.
If you would like to use Sign in with Apple for both, you could set up your own manual Sign in with Apple flow for either the web or mobile app. Then, use the JWT that returns with the Custom JWT authentication provider. In the Realm SDKs, you can then link the user identities for each authentication provider to a single user.
To use Sign in with Apple exclusively with either a web or a mobile application, choose your application type and follow this guide.
Add Sign-in With Apple to Your App
Your app must have the Sign-in with Apple entitlement in order to use this capability.
Select your app target in Xcode.
Go to the Signing & Capabilities tab, and select + Capability.
Search for the Sign in with Apple capability, and select it.
Then, confirm it is enabled in the Apple Developer Portal.
Navigate to the Certificates, Identifiers and Profiles page of the Apple Developer Portal.
Select the identifier for your app from the dropdown. This takes you to your App ID Configuration pane.
Scroll down until you see the checkbox for Sign In with Apple. If that checkbox is not selected, select it. If you've made changes, press the Save button.
Note the Bundle ID of your app. You need the Bundle ID when you create a client secret and when you configure Sign in with Apple in App Services.
Create a Private Key
The client secret for Sign in with Apple is a JSON Web Token that you create and sign with a private key. You need to generate the private key through the Apple Developer Portal.
Click Keys in the left navigation menu.
Click the blue plus icon next to Keys.
On the Register a New Key page, enter a descriptive Key Name and then scroll down to find the Sign in with Apple row. Check the checkbox to enable Sign in with Apple and then click Configure.
On the Configure Key page, select the App ID for your app as the Primary App ID and then click Save.
Click Continue to review your key configuration. When you're sure that you've configured the key correctly, click Register.
Copy the Key ID value somewhere that you can access it later and then click Download to download the key as a
.p8text file. You will use these to generate the client secret.Important
Save the Key
You can only download the key one time. Make sure that you save the key somewhere safe in case you need it again. If you lose the key, you will need to generate a new one.
Create the Client Secret JWT
You can now create the client secret JWT for the Apple ID authentication provider. Make sure that you have the following information:
The Bundle ID of your app. You'll use this as the
client_idin the script below.The Key ID of the key that you created and the
.p8file that contains the key.Your Apple Team ID. You can find this in the top right of the Apple Developer Portal.
Once you've confirmed that you have all the required information, you can use a script to generate the JWT. You may define your own script or use the script in this step.
To generate the JWT, we'll use the jwt gem. To install it, run the following:
gem install jwt
Create a new file called generate_client_secret.rb and copy the following
code block into the file.
# Source: https://developer.okta.com/blog/2019/06/04/what-the-heck-is-sign-in-with-apple require 'jwt' # Update these values with your app's information team_id = '<Apple Team ID>' client_id = '<Bundle ID or Services ID>' key_id = '<Apple Key ID>' key_file = '<Key File Path>' # Define the JWT's headers and claims headers = { # The token must be signed with your key 'kid' => key_id } claims = { # The token is issued by your Apple team 'iss' => team_id, # The token applies to Apple ID authentication 'aud' => 'https://appleid.apple.com', # The token is scoped to your application 'sub' => client_id, # The token is valid immediately 'iat' => Time.now.to_i, # The token expires in 6 months (maximum allowed) 'exp' => Time.now.to_i + 86400*180, } # Read in the key and generate the JWT ecdsa_key = OpenSSL::PKey::EC.new IO.read key_file token = JWT.encode claims, ecdsa_key, 'ES256', headers # Print the JWT to stdout puts token
Update the values of team_id, client_id, key_id, and
key_file to match your application's information and then save
the file. When you're ready to generate the JWT, run the script in
your shell:
ruby generate_client_secret.rb >> client_secret.txt
Important
Save the JWT
The generate_client_secret.rb script outputs to stdout.
When we call it, we append stdout to a file called
client_secret.txt. You will need the JWT to configure
the Apple ID provider in App Services.
Configure the Provider in App Services
At this point you have configured an Apple application and generated the required OAuth 2.0 credentials. You can now configure the Apple ID authentication provider with the credentials to allow App Services client application users to log in.
Click Authentication in the left navigation menu and then click Apple ID.
Turn on the Provider Enabled toggle.
For the App Services Client ID, enter your application's Bundle ID.
For Client Secret, create a new secret with a descriptive name and set the Client Secret Value to the JWT string that you generated. Alternatively, you can select a pre-existing secret that contains the JWT.
Click Save to finish configuring the provider. To make the provider available to client applications, you need to deploy your changes. Click Review & Deploy Changes and then click Deploy.
To enable and configure the Apple authentication provider with
appservices, define a configuration
object for it in /auth/providers.json.
Apple provider configurations have the following form:
{ "oauth2-apple": { "name": "oauth2-apple", "type": "oauth2-apple", "disabled": <boolean>, "config": { "clientId": "<Bundle ID>" }, "secret_config": { "clientSecret": "<Secret Name>" }, "redirect_uris": ["<string>", ...] } }
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Client ID config.clientId | Required. Your application's Bundle ID. |
Client Secret secret_config.clientSecret | Required. The name of a Secret that stores the Client Secret JWT that you generated. |
Redirect URIs redirect_uris | Required for web applications. Not required for mobile applications. |
Once you've created the configuration file, you can make the Apple ID authentication provider available to client applications by deploying your application.
To deploy a draft application with App Services CLI:
appservices push
To deploy a draft application with automatic GitHub deployment:
git add ./auth/providers.json git commit -m "Configure and Enable Apple ID Authentication" git push origin <branch name>
Create an App ID
An Apple App ID represents your application and allows you to access services like Sign in with Apple. To configure the Apple ID provider, you must create a new App ID.
Navigate to the Certificates, Identifiers and Profiles page of the Apple Developer Portal.
Click Identifiers in the left navigation menu.
Click the blue plus icon next to Identifiers.
On the Register a New Identifier page, select App IDs and then click Continue.
On the Register an App ID page, select the Platform that your app runs on and then enter a brief Description and a reverse-dns notation Bundle ID.
Scroll down the Register an App ID page until you see the Sign in with Apple capability. Check the checkbox to enable the capability.
Press the Continue button at the top of the page. Complete any other setup steps that apply to your app, and then press the Register button.
Create a Services ID
An Apple Services ID represents a single application and allows you to configure an authorization callback URL and define a private key for the application.
Click Identifiers in the left navigation menu.
Click the blue plus icon next to Identifiers.
On the Register a New Identifier page, select Services IDs and then click Continue.
On the Register a Services ID page, enter a brief Description and a reverse-dns notation Identifier.
Important
Save the Identifier
The Identifier value of the Services ID is your application's Client ID. You will need this value later to configure the Apple ID provider in Atlas App Services.
Press the Continue button. Confirm the details, and then press Register.
Click into the service you just created. Check the checkbox to enable Sign in with Apple and then click Configure. Select the App ID that you created as the Primary App ID.
Enter your domains, subdomains, and return URLs for the Services ID. Press the Next button.
Click Continue and then click Save. Confirm that you have correctly configured the Services ID and then click Register.
Create a Private Key
The client secret for Sign in with Apple is a JSON Web Token that you create and sign with a private key. You need to generate the private key through the Apple Developer Portal.
Click Keys in the left navigation menu.
Click the blue plus icon next to Keys.
On the Register a New Key page, enter a descriptive Key Name and then scroll down to find the Sign in with Apple row. Check the checkbox to enable Sign in with Apple and then click Configure.
On the Configure Key page, select the App ID that you created as the Primary App ID and then click Save.
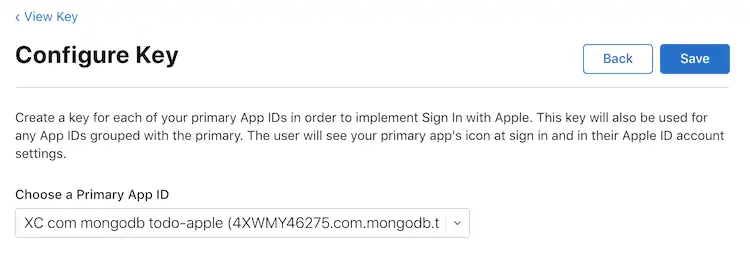
Click Continue to review your key configuration. When you're sure that you've configured the key correctly, click Register.
Copy the Key ID value somewhere that you can access it later and then click Download to download the key as a
.p8text file. You will use these to generate the client secret.Important
Save the Key
You can only download the key one time. Make sure that you save the key somewhere safe in case you need it again. If you lose the key, you will need to generate a new one.
Create the Client Secret JWT
You can now create the client secret JWT for the Apple ID authentication provider. Make sure that you have the following information:
The Services ID that you created. You'll use this as the
client_idin the script below.- The Key ID of the key that you created and the
.p8 - file that contains the key.
- The Key ID of the key that you created and the
- Your Apple Team ID. You can find this in the top right of the Apple
- Developer Portal.
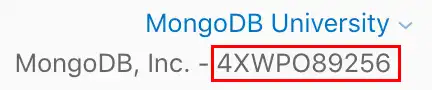
Once you've confirmed that you have all the required information, you can use a script to generate the JWT. You may define your own script or use the script in this step.
To generate the JWT, we'll use the jwt gem. To install it, run the following:
gem install jwt
Create a new file called generate_client_secret.rb and copy the following
code block into the file.
# Source: https://developer.okta.com/blog/2019/06/04/what-the-heck-is-sign-in-with-apple require 'jwt' # Update these values with your app's information team_id = '<Apple Team ID>' client_id = '<Bundle ID or Services ID>' key_id = '<Apple Key ID>' key_file = '<Key File Path>' # Define the JWT's headers and claims headers = { # The token must be signed with your key 'kid' => key_id } claims = { # The token is issued by your Apple team 'iss' => team_id, # The token applies to Apple ID authentication 'aud' => 'https://appleid.apple.com', # The token is scoped to your application 'sub' => client_id, # The token is valid immediately 'iat' => Time.now.to_i, # The token expires in 6 months (maximum allowed) 'exp' => Time.now.to_i + 86400*180, } # Read in the key and generate the JWT ecdsa_key = OpenSSL::PKey::EC.new IO.read key_file token = JWT.encode claims, ecdsa_key, 'ES256', headers # Print the JWT to stdout puts token
Update the values of team_id, client_id, key_id, and
key_file to match your application's information and then save
the file. When you're ready to generate the JWT, run the script in
your shell:
ruby generate_client_secret.rb >> client_secret.txt
Important
Save the JWT
The generate_client_secret.rb script outputs to stdout.
When we call it, we append stdout to a file called
client_secret.txt. You will need the JWT to configure
the Apple ID provider in App Services.
Configure the Provider in App Services
At this point you have configured an Apple application and generated the required OAuth 2.0 credentials. You can now configure the Apple ID authentication provider with the credentials to allow App Services client application users to log in.
Click Authentication in the left navigation menu and then click Apple ID.
Turn on the Provider Enabled toggle.
For the App Services Client ID, enter the Apple Services ID you got when you created a Services ID in step 2 above.
For Client Secret, create a new secret with a descriptive name and set the Client Secret Value to the JWT string that you generated. Alternatively, you can select a pre-existing secret that contains the JWT.
For Redirect URIs, click Add Redirect URI and enter the URL that App Services should redirect to once the OAuth process is complete. Provide a URL for a domain that you control and then use a universal link to redirect the user back to your app.
Click Save to finish configuring the provider. To make the provider available to client applications, you need to deploy your changes. Click Review & Deploy Changes and then click Deploy.
To enable and configure the Apple authentication provider with
appservices, define a configuration
object for it in /auth/providers.json.
Apple provider configurations have the following form:
{ "oauth2-apple": { "name": "oauth2-apple", "type": "oauth2-apple", "disabled": <boolean>, "config": { "clientId": "<Apple Services ID>" }, "secret_config": { "clientSecret": "<Secret Name>" }, "redirect_uris": ["<string>", ...] } }
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Client ID config.clientId | Required. The Apple Services ID that you created when you completed step 2 above. |
Client Secret secret_config.clientSecret | Required. The name of a Secret that stores the Client Secret JWT that you generated. |
Redirect URIs redirect_uris | Required for web applications. A list of allowed redirect URIs. Once a user completes the authentication process, App Services redirects them back to either a specified redirect URI or, if no redirect URI is specified, the URL that they initiated the authentication request from. App Services will only redirect a user to a URI that exactly matches an entry in this list, including the protocol and any trailing slashes. Provide a URL for a domain that you control and then use a universal link to redirect the user back to your app. |
Once you've created the configuration file, you can make the Apple ID authentication provider available to client applications by deploying your application.
To deploy a draft application with App Services CLI:
appservices push
To deploy a draft application with automatic GitHub deployment:
git add ./auth/providers.json git commit -m "Configure and Enable Apple ID Authentication" git push origin <branch name>
Examples
For code examples that demonstrate how to register and log in using Apple authentication, see the documentation for the Realm SDKs: