Indexes are special data structures that improve query performance. Indexes store a portion of a collection's data in an easy-to-traverse form. The index stores the value of a specific field or set of fields, ordered by the value of the field.
To improve query performance, build indexes on fields that appear often in queries and for all operations that sort by a field.
Queries on an indexed field can use the index to limit the number of documents that must be scanned to find matching documents.
Sort operations on an indexed field can return documents pre-sorted by the index.
To learn more about indexes, see Indexes.
Note
Considerations
Indexes have some negative performance impact on write operations. For collections with high write-to-read ratio, indexes are expensive since each insert must also update any indexes. For a detailed list of considerations for indexes, see Operational Considerations for Indexes.
Required Roles
To create, drop, or hide indexes, you must have access provided by at least one of the following roles:
Considerations
By default, you can have up to three concurrent index builds. To learn more, see Maximum Concurrent Index Builds.
Indexes Tab
The Indexes tab lists the existing indexes for a collection.
To access the Indexes tab for a collection:
In Atlas, go to the Data Explorer page for your project.
If it's not already displayed, select the organization that contains your project from the Organizations menu in the navigation bar.
If it's not already displayed, select your project from the Projects menu in the navigation bar.
In the sidebar, click Data Explorer under the Database heading.
The Data Explorer displays.
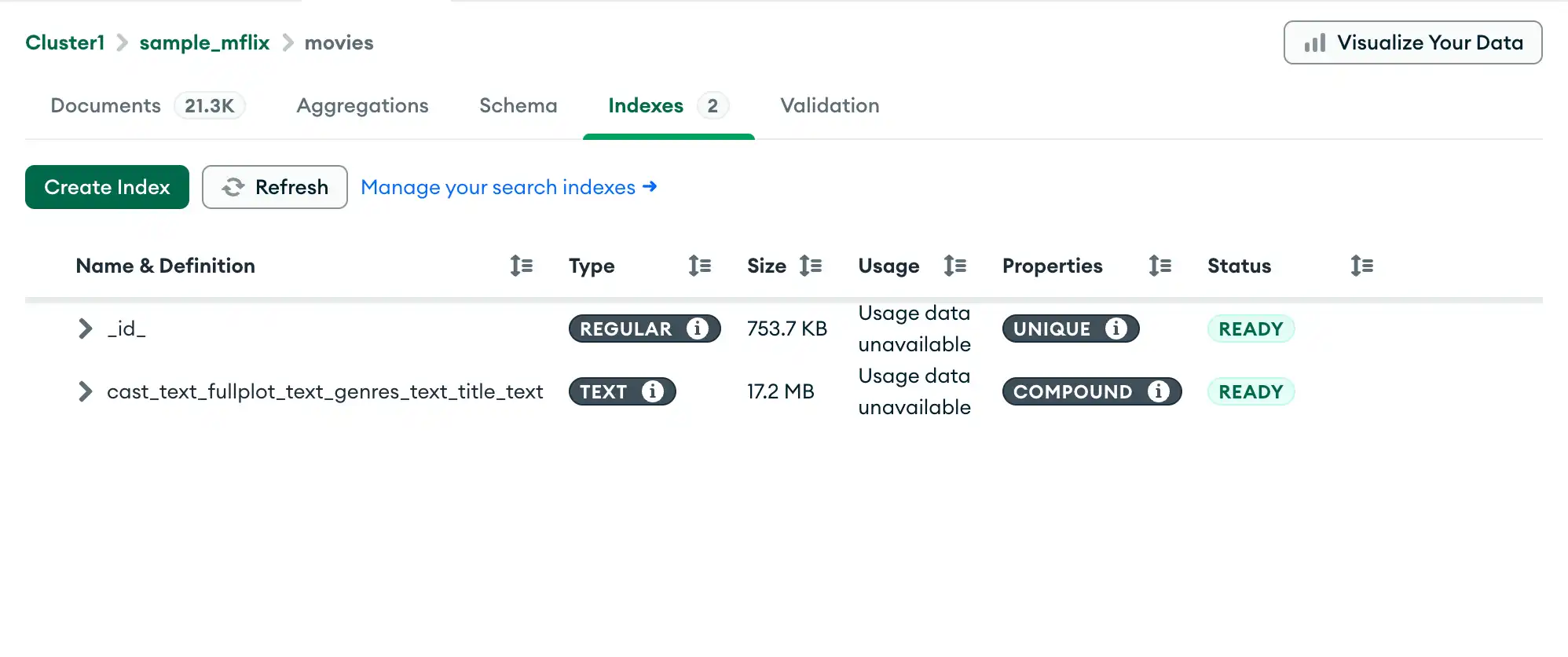
For each index, Atlas displays the following information:
Name and Definition | The name of the index and keys. |
Type | Regular, text, geospatial or hashed index. |
Size | How large the index is. |
Usage | Number of times the index has been used in a lookup since the time the index was created or the last server restart. WARNING: The Usage metrics show index usage statistics
only for the primary node and should only be used for informational
purposes. For more comprehensive index usage statistics, run the
|
Properties | Any special properties (such as uniqueness, partial) of the index. |
Create an Index
Open the index creation dialog
From the Indexes tab, click the Create Index button.
Add fields to the index
Specify an index key.
To specify an existing document field as an index key, select the field from the dropdown list.
To specify a field that does not exist in any document as an index key, enter the field name in the input box.
To create a compound index, click the plus icon next to the index type dropdown.
Use the dropdown to the right of each field name to specify the index type. You can specify one of the following types:
Ascending
Descending
2dsphere
Text
To learn how to specify a wildcard index, see Create a Wildcard Index.
Optional. Specify index options
Atlas supports the following index options:
Option | Description | More Information | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Create unique index | Ensure that the indexed fields do not store duplicate values. You cannot perform a rolling build for a unique index. If you enable
building indexes in a rolling fashion with the | |||||
Index name | Specify a name for the index. | |||||
Create a TTL index | Delete documents automatically after a specified number of seconds since the indexed field value. | |||||
Partial filter expression | Index only the documents which match the specified filter expression. For example: The following partial filter expression only indexes
documents where the | |||||
Wildcard projection | Support unknown or arbitrary fields which match the specified
projection in the index. To use a wildcard projection, set
your index field name to For example: Consider the following wildcard projection document: If your index field name is | |||||
Use custom collation | Create a custom collation for the index by typing or pasting the collation document in the text box. | |||||
Create sparse index | Index skips over any document that is missing the indexed field. | |||||
Build in rolling process | Can minimize the performance impact of index builds. IMPORTANT: Building an index in a rolling fashion reduces the resiliency of your cluster and increases index build times. We only recommend using rolling index builds when regular index builds do not meet your needs. WARNING: Avoid performing rolling index and replicated index build processes concurrently as it might lead to unexpected issues, such as broken builds and crash loops. You can only build rolling indexes on M10+ Clusters. During a rolling index build, Atlas takes each node out of the replica set, starts it in standalone mode to build the index, and then returns it to the replica set. This process repeats for each node in the cluster in a rolling sequence. Nodes may appear as down, while Atlas builds indexes offline. This is expected behavior, not an issue. |
MongoDB Vector Search and MongoDB Search Indexes
You can't create MongoDB Search or MongoDB Vector Search indexes in Data Explorer. To manage MongoDB Search and MongoDB Vector Search indexes for your collection, see:
Create a Wildcard Index
You can create wildcard indexes to
support queries against unknown or arbitrary fields. To create a
wildcard index in Atlas, manually type the wildcard index
field (<field>.$**) into the Select a field name
input.
Example
Consider a collection where documents contain a userMetadata
object. The fields within the userMetadata object may vary
between documents.
You can create a wildcard index on userMetadata to account for
all potential fields within the object. Type the following into
the Select a field name input:
userMetadata.$**
Specify a type (ascending or descending) for your wildcard
index, then click Create Index.
Atlas shows the type of your new index as Wildcard.
Hide or Unhide an Index
You can hide an index from the query planner to evaluate the potential impact of dropping an index without actually dropping the index.
Drop an Index
Click the trash can icon for the index to drop.
From the Indexes tab, to delete an index, click on the trash can icon for that index. A confirmation dialog appears.