Manage Customer Keys with Azure Key Vault
On this page
Note
This feature is not available for any of the following deployments:
M0Free clustersFlex clusters
Serverless instances (deprecated)
M2/M5Shared clusters (deprecated)
To learn more, see Limits.
You can use a customer-managed key (CMK) from Azure Key Vault (AKV) to further encrypt your data at rest in Atlas. You can also configure all traffic to your AKV to use Azure Private Link.
Atlas uses your Azure Key Vault CMK to encrypt and decrypt your MongoDB Master Keys. These MongoDB Master Keys are used to encrypt cluster database files and cloud providers snapshots. To learn more about how Atlas uses CMKs for encryption, see About Customer-Managed Keys with Azure Key Vault.
When you use your own cloud provider KMS, Atlas automatically rotates MongoDB Master Keys at least every 90 days. Your key rotation will begin during a maintenance window, if you have one configured. Deferring maintenance (either manually or automatically) may cause the key to be rotated past the 90-day mark. Keys are rotated on a rolling basis and the process does not require the data to be rewritten.
Important
Azure limits Client Secret lifetime for CMKs to two years. Atlas can't access a CMK once the Client Secret expires. Therefore, rotate your Client Secrets before its expiration to prevent loss of cluster availability.
This page covers configuring customer key management using AKV on your Atlas project. You can also use the Atlas Administration API to automatically set up Azure Private Link in your AKV to ensure that all traffic between Atlas and AKV take place over Azures private network interfaces.
You must configure customer key management for the Atlas project before enabling it on clusters in that project.
About Customer-Managed Keys with Azure Key Vault
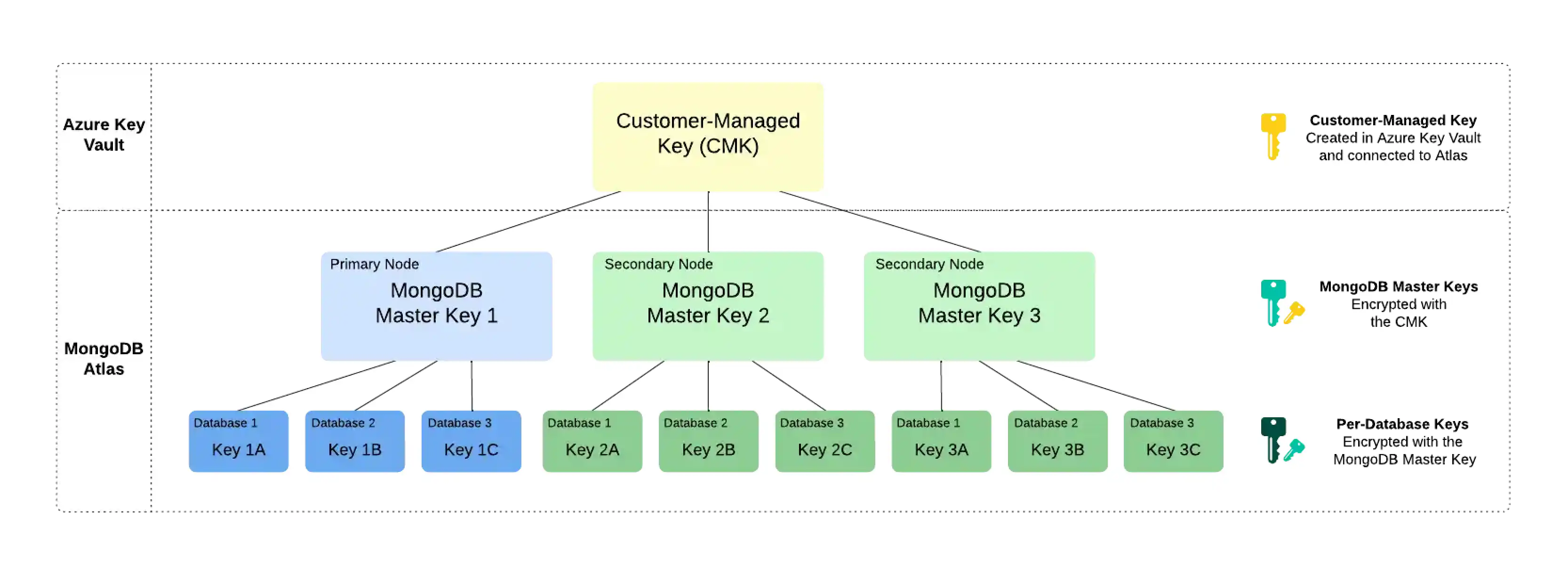
Customer key management in Atlas follows a process called envelope encryption. This process creates multiple layers of encryption by encrypting one key with another key. To enable customer key management, Atlas uses the following encryption keys:
Customer-Managed Key (CMK)Customer-managed keys are encryption keys that you create, own, and manage in Azure Key Vault. You create the CMK in Azure Key Vault and connect it to Atlas at the Project level. To learn more about the CMKs used in Azure Key Vault, see the Azure Documentation.
Atlas uses this key only to encrypt the MongoDB Master Keys.
MongoDB Master KeyEach node in your Atlas cluster creates a MongoDB Master Key. MongoDB Master Keys are encryption keys that a MongoDB Server uses to encrypt the per-database encryption keys. Atlas saves an encrypted copy of the key locally.
This key is encrypted with the CMK and encrypts the per-database encryption keys.
Per-Database Encryption KeyEach node in your Atlas cluster also creates an encryption key per database in your cluster. Atlas uses these keys to read and write data via WiredTiger, which also encrypts and stores these keys.
This key is encrypted with the MongoDB Master Key.
Example
Consider the following encryption hierarchy for a three-node replica set. Atlas uses the CMK from Azure Key Vault to encrypt a unique MongoDB Master Key for each node in the cluster. Each node also contains three databases, each of which is encrypted with a unique per-database encryption key. When the cluster starts up, Atlas decrypts the MongoDB Master Key by using the CMK from Azure Key Vault and supplies this to the MongoDB Server.
Note
If you revoke Atlas's access to the CMK, Atlas shuts down the nodes in your cluster and you can't access your data until you restore access to the CMK.
What You Need to Know
After configuring Atlas to use your AKV CMK, learn more About Rotating Your Azure Key Identifier and About Azure Key Vault Failover During an Outage.
About Rotating Your Azure Key Identifier
Note
This feature is not available for any of the following deployments:
M0Free clustersFlex clusters
Serverless instances (deprecated)
M2/M5Shared clusters (deprecated)
To learn more, see Limits.
MongoDB Master Key - MongoDB Responsibility
When you use your own cloud provider KMS, Atlas automatically rotates MongoDB Master Keys at least every 90 days. Your key rotation will begin during a maintenance window, if you have one configured. Deferring maintenance (either manually or automatically) may cause the key to be rotated past the 90-day mark. Keys are rotated on a rolling basis and the process does not require the data to be rewritten.
Rotate your Azure Key ID - Your Responsibility
Atlas does not automatically rotate the Key Identifier used for Azure Key Vault.
Atlas automatically creates an encryption key rotation alert to remind you to rotate your Azure Key Identifier every 90 days by
default when you enable Encryption at Rest
for an Atlas project.
You can rotate CMK stored in Azure Key Vault yourself or configure your Azure Key Vault to automatically rotate your keys. If you configure automatic rotation in Azure Key Vault, the default time period for rotation is approximately 365 days.
If you have already set up an automatic rotation in Azure Key Vault and don't want to receive the Atlas alert to rotate your Azure Key Identifier every 90 days, you can modify the default alert period to be greater than 365 days.
About Azure Key Vault Failover During an Outage
During a regional outage, your AKV region might become unavailable. If this happens, Azure automatically routes incoming Key Vault requests to a pre-assigned secondary region. To learn more, see Azure Key Vault Failover and Regional Pairings.
If both regions are down, you can manually migrate your key to a region outside of the regional pairing. To learn more, see Move a Key Vault across Regions.
Note
If you've enabled Encryption at Rest using Customer Key Management, you can perform encrypt and decrypt operations while at least one node is still available during the outage. Atlas won't shut down your clusters.
For certain regions, Azure doesn't support automatic failover. To learn more, see Azure documentation.
Required Access
To configure customer key management, you must have Project Owner
access to the project.
Users with Organization Owner access must add themselves to the
project as a Project Owner.
You must grant Atlas access to your AKV using a Permission Model. You can grant access by using a Key Vault Access Policy or Azure RBAC.
If you use access policies, do the following in the Azure UI to grant Atlas access to your AKV.
Under Access Control (IAM) settings, grant the
Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/readpermission to your application.In the Access Policies page, create an access policy with the following Key Permissions:
Grant this permission...To...Get
Read the metadata about the key stored in your AKV.
Encrypt
Use the keys in your AKV to encrypt data.
Decrypt
Use the keys in your AKV to decrypt data that has been previously encrypted with those keys.
Add the same app as the principal and configure the access policy.
If your AKV uses RBAC, you must do the following in the Azure UI Access Control (IAM) settings to grant Atlas access to your AKV.
Grant the the following
actionspermissions to the application.Grant this permission...To...Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/readRead the properties of a Key Vault
Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/readRead the metadata about the key stored in your AKV.
{ "permissions": [ { "actions": [ "Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/read" "Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/read" ] } ... ] } Grant the following
dataActionspermissions to the application.Grant this permission...To...Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/readRead the metadata about the key stored in your AKV.
Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/encrypt/actionUse the keys in your AKV to encrypt data.
Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/decrypt/actionUse the keys in your AKV to decrypt data previously encrypted with those keys.
{ "permissions": [ ... { "dataActions": [ "Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/read", "Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/encrypt/action", "Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/decrypt/action" ] } ] }
Next Steps
You can use a customer-managed key (CMK) from Azure Key Vault (AKV) over a public network or over Azure Private Endpoints. To learn more, see the following:
Manage Customer Keys with Azure Key Vault Over Private Endpoints
Manage Customer Keys with Azure Key Vault Over a Public Network
Note
If you've enabled Encryption at Rest using Customer Key Management, you can perform encrypt and decrypt operations while at least one node is still available during the outage.