Manage Indexes in Data Explorer
You can use the Data Explorer to manage indexes on your collections.
Access Data
To interact with your data in the Cloud Manager UI:
In MongoDB Cloud Manager, go to the Deployment page for your project.
If it is not already displayed, select the organization that contains your desired project from the Organizations menu in the navigation bar.
If it's not already displayed, select your desired project from the Projects menu in the navigation bar.
If the Deployment page is not already displayed, click Deployment in the sidebar.
The Deployment page displays.
Required Roles
To create or drop indexes, you must have access provided by at least one of the following roles:
Considerations
By default, you can have up to three concurrent non-rolling index builds. To learn more, see Maximum Concurrent Index Builds.
If you select to build indexes in a rolling fashion, you must ensure the following:
Request rolling index builds and non-rolling index builds sequentially and not simultaneously. Wait for a currently executing index build to complete before you request another index build.
If you need to request multiple rolling index builds, wait for the currently executing rolling index build to complete before you request another rolling index build.
To track rolling index builds, see the Activity Feed.
For aborted rolling index builds, you must run listIndexes
on each node to verify that the cancelled index no longer exists.
Otherwise, the cluster might remain in an inconsistent state.
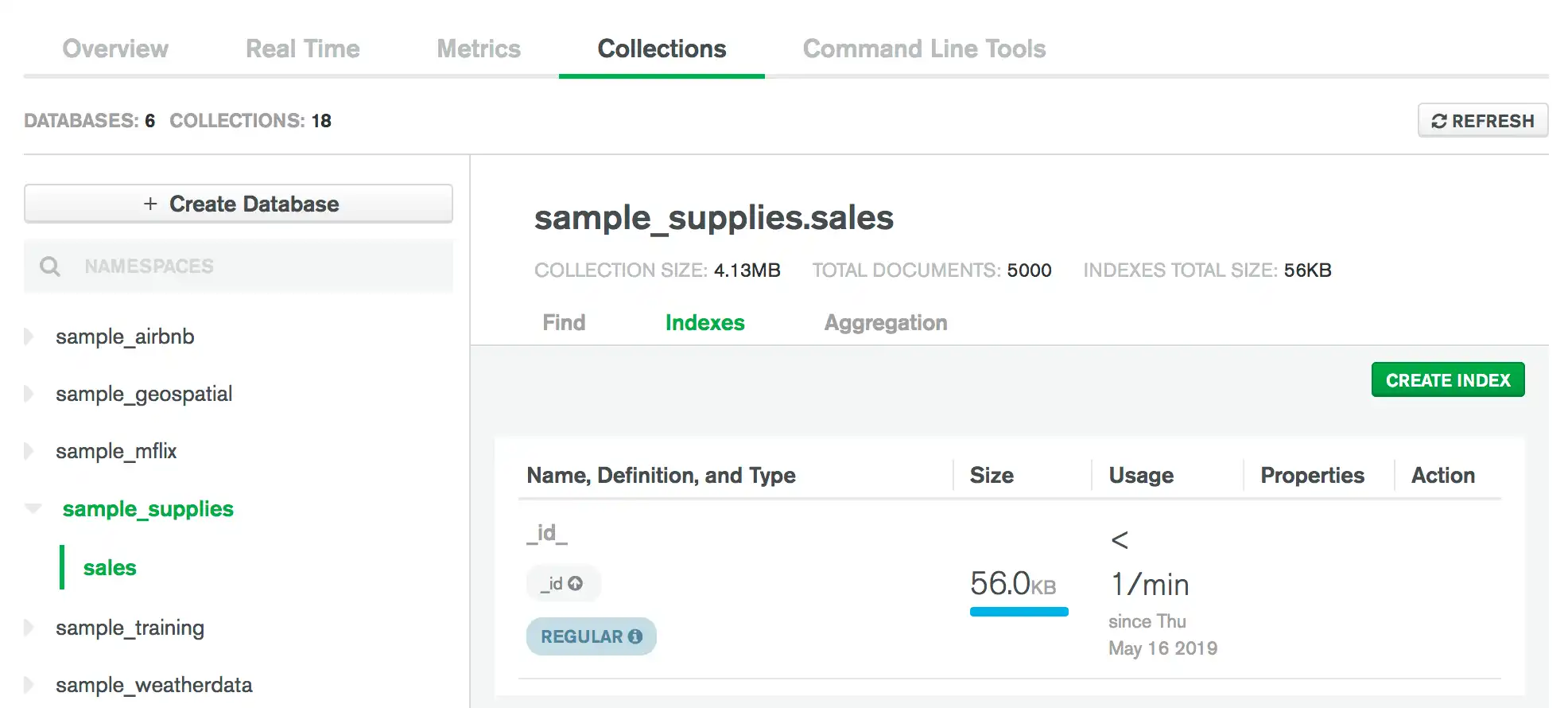
View Indexes
From the Collections tab, you can view index information for a collection. To view index information for a collection:
Create an Index
Tip
When you create indexes, keep the ratio of reads to writes on the target collection in mind. Indexes come with a performance cost, but are more than worth the cost for frequent queries on large data sets. To learn more about indexing strategies, see Indexing Strategies.
To create an index for a collection through the Data Explorer:
Click Create Index.
In the Create Index modal,
enter the index key specification
document in the Fields box:
{ <field1>: <index type>, ... }
Example
To create a compound index on the fields category
(ascending order) and score (descending order), specify the
index specification document:
{ category: 1, score: -1 }
For more information on indexes, see Indexes.
(Optional) Specify the index options.
{ <option1>: <value1>, ... }
Example
To set the unique option and a name for the new index,
enter this document:
{ unique: true, name: "myUniqueIndex" }
(Optional) Set the Collation options.
Use collation to specify language-specific rules for string comparison,
such as rules for lettercase and accent marks. The
collation document
contains a locale field which indicates the ICU Locale code, and may contain other
fields to define collation behavior.
Example
The following collation option document specifies a locale value
of fr for a French language collation:
{ "locale": "fr" }
To review the list of locales that MongoDB collation supports, see the list of languages and locales. To learn more about collation options, including which are enabled by default for each locale, see Collation in the MongoDB manual.
(Optional) Build indexes with rolling builds.
Warning
Due to critical issue SERVER-68925, Cloud Manager deployments using certain versions of the MongoDB Agent should not perform automated rolling index builds on clusters running the following MongoDB versions:
MongoDB 4.2.19-4.2.22
MongoDB 4.4.13-4.4.16
MongoDB 5.0.6-5.0.11
MongoDB 6.0.0-6.0.1
You can continue to perform manual rolling index builds safely on your clusters. To perform automated rolling index builds safely, upgrade the MongoDB Agent to 12.4.0.7703 or later or upgrade your clusters to:
MongoDB 4.2.23 or later
MongoDB 4.4.17 or later
MongoDB 5.0.12 or later
MongoDB 6.0.2 or later
Important
Rolling index builds succeed only when they meet certain conditions. To ensure your index build succeeds, avoid the following design patterns that commonly trigger a restart loop:
Index key exceeds the index key limit
Index name already exists
Index on more than one array field
Index on collection that has the maximum number of text indexes
Text index on collection that has the maximum number of text indexes
Note
Data Explorer doesn't support building indexes in a rolling fashion for standalone deployments.
Building indexes in a rolling fashion reduces the performance impact of building indexes on replica sets and sharded clusters. To maintain cluster availability, Cloud Manager removes one node from the cluster at a time starting with a secondary.
After you build an index in a rolling fashion, if your MongoDB database
runs with an FCV
less than 4.2, resync the head database to ensure that the head database takes the
new index into account.
Cloud Manager automatically cancels rolling index builds that don't succeed on all nodes. When a rolling index build completes on some nodes, but fails on others, Cloud Manager cancels the build and removes the index from any nodes that it was successfully built on.
In the event of a rolling index build cancellation, Cloud Manager generates an activity feed event and sends a notification email to the project owner with the following information:
Name of the cluster on which the rolling index build failed
Namespace on which the rolling index build failed
Project that contains the cluster and namespace
Organization that contains the project
Link to the activity feed event
To learn more about rebuilding indexes, see Build Indexes on Replica Sets.
Note
The following index options are incompatible with building indexes in a rolling fashion:
Cloud Manager ignores these options if you specify them in the Options pane.
Drop an Index
To drop an index from a collection through the Data Explorer:
Note
You cannot delete the _id index.