Overview
In this guide, you can learn how to update documents in MongoDB by using update operations.
Update operations change the fields that you specify while leaving other fields and values unchanged.
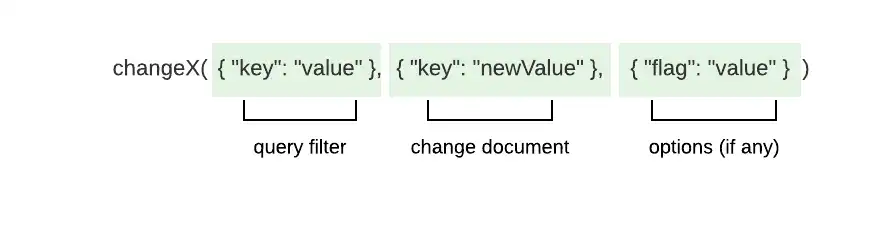
In MongoDB, all methods to modify documents follow the same pattern:
Note
Placeholder
changeX is a placeholder and not a real method.
The pattern expects you to:
Specify a query filter to match one or more documents to modify.
Specify the field and value changes.
Specify options, if you must modify the method behavior.
The driver provides the following methods to update documents:
UpdateByID(): Updates a single document based on its_id.UpdateOne(): Updates a single document.UpdateMany(): Updates multiple documents.
A Note About _id
Each document in a MongoDB collection has a unique and immutable _id
field. You cannot use update operations to change the
_id field. If you attempt to change this field, the update
methods return a WriteError.
Parameters
Each method takes an update document that includes at least one update operator. The update operator specifies the type of update to perform. The update document also includes the fields and values that describe the change. Update documents use the following format:
bson.D{{"<update operator>", bson.D{{"<field>", <value>}, {"<field>", <value>}, ... }}, {"<update operator>", ... }, ... }
See the MongoDB server manual for a complete list of update operators and descriptions.
Tip
UpdateOne() updates the first document that matches the query filter
you provide. To ensure that you update the correct document, you can use the sort
option to specify the order in which the operation finds documents. To learn more,
see the UpdateOneOptions API documentation.
Note
Aggregation Pipelines in Update Operations
You can use aggregation pipelines made up of a subset of aggregation stages in update operations. To learn more about the aggregation stages MongoDB supports in aggregation pipelines, see the tutorial on performing Updates with Aggregation Pipeline tutorial in the Server Manual.
Return Values
UpdateOne(), UpdateByID(), and UpdateMany() return an
UpdateResult type that contains information about the update
operation if the operation is successful. The UpdateResult type
contains the following properties:
Property | Description |
|---|---|
| The number of documents matched by the filter |
| The number of documents modified by the operation |
| The number of documents upserted by the operation |
| The |
If multiple documents match the query filter passed to UpdateOne(),
the method selects and updates the first matched document. If no
documents match the query filter, the update operation makes no
changes.
See the upsert guide to learn how to insert a new document if no documents match the query filter.
UpdateOne() Example
The following example uses the listingsAndReviews collection in the
sample_airbnb dataset from the Atlas sample datasets.
The following document describes an airbnb listing:
{ "_id": "10006546", "listing_url": "https://www.airbnb.com/rooms/10006546", "name": "Ribeira Charming Duplex", "summary": "Fantastic duplex apartment with three bedrooms, located in the historic area of Porto, Ribeira (Cube)...", ... "minimum_nights": "2", "maximum_nights": "30", ... "accommodates": 8, ... }
The following example uses the UpdateOne() method to:
Match the document where the
_idvalue is"10006546".Set the
namefield to"Ribiera River View Duplex".Increment the value of the
accommodatesfield by1.
filter := bson.D{{"_id", "10006546"}} update := bson.D{{"$set", bson.D{{"name", "Ribiera River View Duplex"}}}, {"$inc", bson.D{{"accomodates", 1}}}} result, err := collection.UpdateOne(context.TODO(), filter, update) fmt.Printf("Documents matched: %v\n", result.MatchedCount) fmt.Printf("Documents updated: %v\n", result.ModifiedCount)
Documents matched: 1 Documents updated: 1
The following shows the updated document resulting from the preceding update operation:
{ "_id": "10006546", "listing_url": "https://www.airbnb.com/rooms/10006546", "name": "Ribeira River View Duplex", "summary": "Fantastic duplex apartment with three bedrooms, located in the historic area of Porto, Ribeira (Cube)...", ... "minimum_nights": "2", "maximum_nights": "30", ... "accommodates": 9, ... }
UpdateOne() Example: Full File
Note
Example Setup
This example connects to an instance of MongoDB by using a
connection URI. To learn more about connecting to your MongoDB
instance, see the Create a MongoClient guide. This example
also uses the restaurants collection in the sample_restaurants database
included in the Atlas sample datasets. You
can load them into your database on the free tier of MongoDB Atlas
by following the Get Started with Atlas Guide.
The following example is a fully runnable file that performs the following
actions on the restaurants collection:
Finds a document with a specific
_idUpdates the
avg_ratingfield value of the matched document
// Updates the first document that matches a query filter by using the Go driver package main import ( "context" "fmt" "log" "os" "github.com/joho/godotenv" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/v2/bson" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/v2/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/v2/mongo/options" ) // Defines a Restaurant struct as a model for documents in the "restaurants" collection type Restaurant struct { ID bson.ObjectID `bson:"_id"` Name string `bson:"name"` AverageRating float64 `bson:"avg_rating,omitempty"` } func main() { if err := godotenv.Load(); err != nil { log.Println("No .env file found") } var uri string if uri = os.Getenv("MONGODB_URI"); uri == "" { log.Fatal("You must set your 'MONGODB_URI' environment variable. See\n\t https://www.mongodb.com/docs/drivers/go/current/connect/mongoclient/#environment-variable") } client, err := mongo.Connect(options.Client().ApplyURI(uri)) if err != nil { panic(err) } defer func() { if err = client.Disconnect(context.TODO()); err != nil { panic(err) } }() coll := client.Database("sample_restaurants").Collection("restaurants") id, _ := bson.ObjectIDFromHex("5eb3d668b31de5d588f4292b") filter := bson.D{{"_id", id}} // Creates instructions to add the "avg_rating" field to documents update := bson.D{{"$set", bson.D{{"avg_rating", 4.4}}}} // Updates the first document that has the specified "_id" value result, err := coll.UpdateOne(context.TODO(), filter, update) if err != nil { panic(err) } // Prints the number of updated documents fmt.Printf("Documents updated: %v\n", result.ModifiedCount) // When you run this file for the first time, it should print output similar to the following: // Documents updated: 1 }
Documents updated: 1
UpdateMany() Example: Full File
Note
Example Setup
This example connects to an instance of MongoDB by using a
connection URI. To learn more about connecting to your MongoDB
instance, see the Create a MongoClient guide. This example
also uses the restaurants collection in the sample_restaurants database
included in the Atlas sample datasets. You
can load them into your database on the free tier of MongoDB Atlas
by following the Get Started with Atlas Guide.
The following example is a fully runnable file that performs the following
actions on the restaurants collection:
Finds documents with the
cuisinefield value of"Pizza"and theboroughfield value of"Brooklyn"Updates the
avg_ratingfield value of the matched documents
// Updates documents that match a query filter by using the Go driver package main import ( "context" "fmt" "log" "os" "github.com/joho/godotenv" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/v2/bson" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/v2/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/v2/mongo/options" ) // Defines a Restaurant struct as a model for documents in the "restaurants" collection type Restaurant struct { ID bson.ObjectID `bson:"_id"` Name string `bson:"name"` Cuisine string `bson:"cuisine"` AverageRating float64 `bson:"avg_rating,omitempty"` } func main() { if err := godotenv.Load(); err != nil { log.Println("No .env file found") } var uri string if uri = os.Getenv("MONGODB_URI"); uri == "" { log.Fatal("You must set your 'MONGODB_URI' environment variable. See\n\t https://www.mongodb.com/docs/drivers/go/current/connect/mongoclient/#environment-variable") } client, err := mongo.Connect(options.Client().ApplyURI(uri)) if err != nil { panic(err) } defer func() { if err = client.Disconnect(context.TODO()); err != nil { panic(err) } }() coll := client.Database("sample_restaurants").Collection("restaurants") filter := bson.D{{"cuisine", "Pizza"}, {"borough", "Brooklyn"}} // Creates instructions to update the values of the "avg_rating" field update := bson.D{{"$set", bson.D{{"avg_rating", 4.5}}}} // Updates documents in which the value of the "Cuisine" // field is "Pizza" result, err := coll.UpdateMany(context.TODO(), filter, update) if err != nil { panic(err) } // Prints the number of updated documents fmt.Printf("Documents updated: %v\n", result.ModifiedCount) // end updatemany // When you run this file for the first time, it should print output similar to the following: // Documents updated: 296 }
Documents updated: 296
Additional Information
To learn more about the operations mentioned, see the following guides:
To learn more about updating array elements, see Update Arrays in a Document.
API Documentation
To learn more about any of the methods or types discussed in this guide, see the following API Documentation: