Overview
PyMongo is a Python package that you can use to connect to and communicate with MongoDB. This guide shows you how to create an application that uses PyMongo to connect to a MongoDB cluster hosted on MongoDB Atlas.
Tip
MongoDB Atlas is a fully managed cloud database service that hosts your MongoDB deployments. You can create your own free (no credit card required) MongoDB Atlas deployment by following the steps in this guide.
Follow this guide to connect a sample Python application to a MongoDB Atlas deployment. If you prefer to connect to MongoDB using a different driver or programming language, see our list of official drivers.
Download and Install
Note
Alternative Installation Methods
The following steps show you how to install PyMongo by using pip. To install PyMongo from source, see Install from Source in the API documentation.
Create a project directory
In your shell, run the following command to create a
directory called pymongo-quickstart for this project:
mkdir pymongo-quickstart
Select the tab corresponding to your operating system and run the following commands
to create a quickstart.py application file in the pymongo-quickstart directory:
cd pymongo-quickstart touch quickstart.py
cd pymongo-quickstart type nul > quickstart.py
Install PyMongo
Select the tab corresponding to your operating system and run the following commands to create and activate a virtual environment in which to install the driver:
python3 -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate
python3 -m venv venv . venv\Scripts\activate
With the virtual environment activated, run the following command to install the current version of PyMongo:
python3 -m pip install pymongo
After you complete these steps, you have a new project directory and the driver dependencies installed.
Create a MongoDB Deployment
You can create a free-tier MongoDB deployment on MongoDB Atlas to store and manage your data. MongoDB Atlas hosts and manages your MongoDB database in the cloud.
Create a free MongoDB deployment on Atlas
Complete the Get Started with Atlas guide to set up a new Atlas account and load sample data into a new free tier MongoDB deployment.
After you complete these steps, you have a new free tier MongoDB deployment on Atlas, database user credentials, and sample data loaded in your database.
Create a Connection String
You can connect to your MongoDB deployment by providing a connection URI, also called a connection string, which instructs the driver on how to connect to a MongoDB deployment and how to behave while connected.
The connection string includes the hostname or IP address and port of your deployment, the authentication mechanism, user credentials when applicable, and connection options.
To connect to an instance or deployment not hosted on Atlas, see Choose a Connection Target.
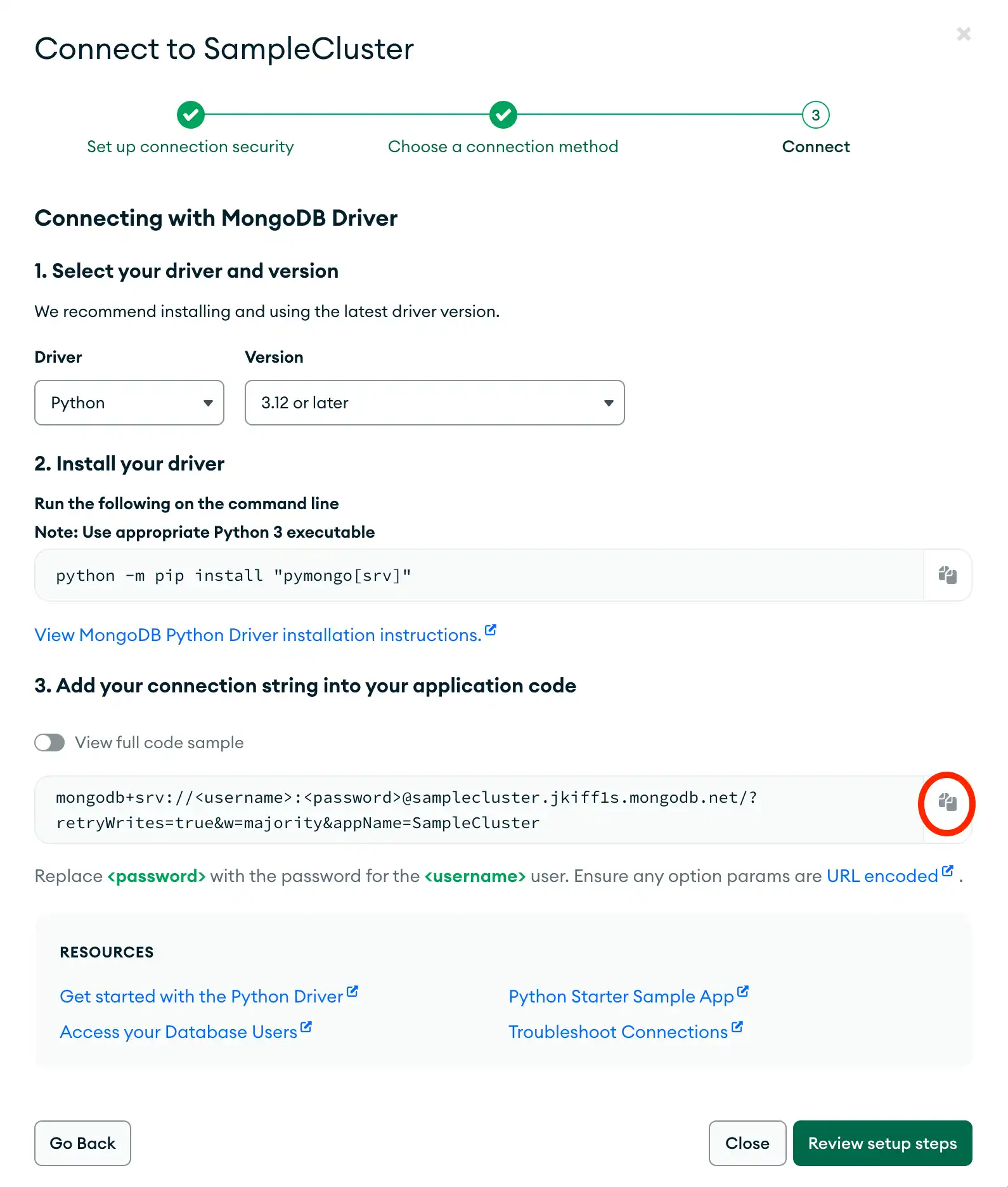
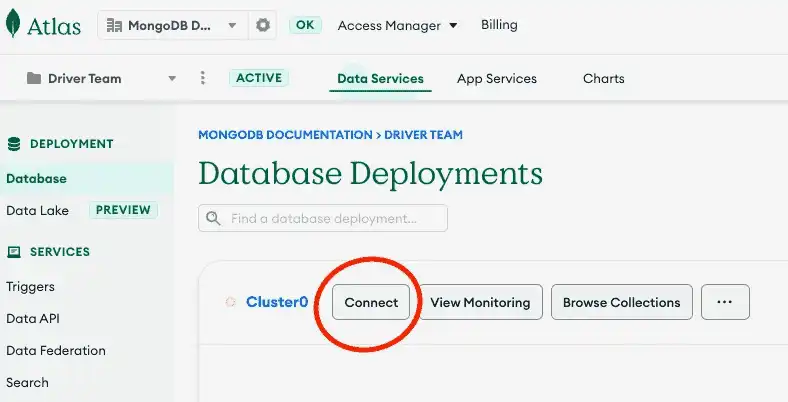
Find your MongoDB Atlas connection string
To retrieve your connection string for the deployment that you created in the previous step, log into your Atlas account and navigate to the Database section and click the Connect button for your new deployment.
Proceed to the Connect your application section and select "Python" from the Driver selection menu and the version that best matches the version you installed from the Version selection menu.
Select the Password (SCRAM) authentication mechanism.
Deselect the Include full driver code example option to view the connection string.
After completing these steps, you have a connection string that contains your database username and password.
Connect to MongoDB
Create your PyMongo application
Copy and paste the following code into the quickstart.py file in your application.
Select the Synchronous or Asynchronous tab to see the
corresponding code:
from pymongo import MongoClient uri = "<connection string URI>" client = MongoClient(uri) try: database = client.get_database("sample_mflix") movies = database.get_collection("movies") # Query for a movie that has the title 'Back to the Future' query = { "title": "Back to the Future" } movie = movies.find_one(query) print(movie) client.close() except Exception as e: raise Exception("Unable to find the document due to the following error: ", e)
import asyncio from pymongo import AsyncMongoClient async def main(): uri = "<connection string URI>" client = AsyncMongoClient(uri) try: database = client.get_database("sample_mflix") movies = database.get_collection("movies") # Query for a movie that has the title 'Back to the Future' query = { "title": "Back to the Future" } movie = await movies.find_one(query) print(movie) await client.close() except Exception as e: raise Exception("Unable to find the document due to the following error: ", e) # Run the async function asyncio.run(main())
Assign the connection string
Replace the <connection string URI> placeholder with the
connection string that you copied from the Create a Connection String
step of this guide.
Run your application
In your shell, run the following command to start this application:
python3 quickstart.py
The output includes details of the retrieved movie document:
{ _id: ..., plot: 'A young man is accidentally sent 30 years into the past...', genres: [ 'Adventure', 'Comedy', 'Sci-Fi' ], ... title: 'Back to the Future', ... }
Tip
If you encounter an error or see no output, check whether you specified the proper connection string, and that you loaded the sample data.
After you complete these steps, you have a working application that uses the driver to connect to your MongoDB deployment, runs a query on the sample data, and prints out the result.
Next Steps
Congratulations on completing the tutorial!
In this tutorial, you created a Python application that connects to a MongoDB deployment hosted on MongoDB Atlas and retrieves a document that matches a query.
Learn more about PyMongo from the following resources:
Learn how to insert documents in the Insert Documents section.
Learn how to find documents in the Query section.
Learn how to update documents in the Update Documents section.
Learn how to delete documents in the Delete Documents section.
Note
If you run into issues on this step, submit feedback by using the Rate this page tab on the right or bottom right side of this page.
You can find support for general questions by using the MongoDB Stack Overflow tag or the MongoDB Reddit community.