Overview
In this guide, you can learn how to store and retrieve large files in MongoDB by using GridFS. GridFS is a specification implemented by PyMongo that describes how to split files into chunks when storing them and reassemble them when retrieving them. The driver's implementation of GridFS is an abstraction that manages the operations and organization of the file storage.
You should use GridFS if the size of your files exceeds the BSON document size limit of 16MB. For more detailed information on whether GridFS is suitable for your use case, see GridFS in the MongoDB Server manual.
The following sections describe GridFS operations and how to perform them.
How GridFS Works
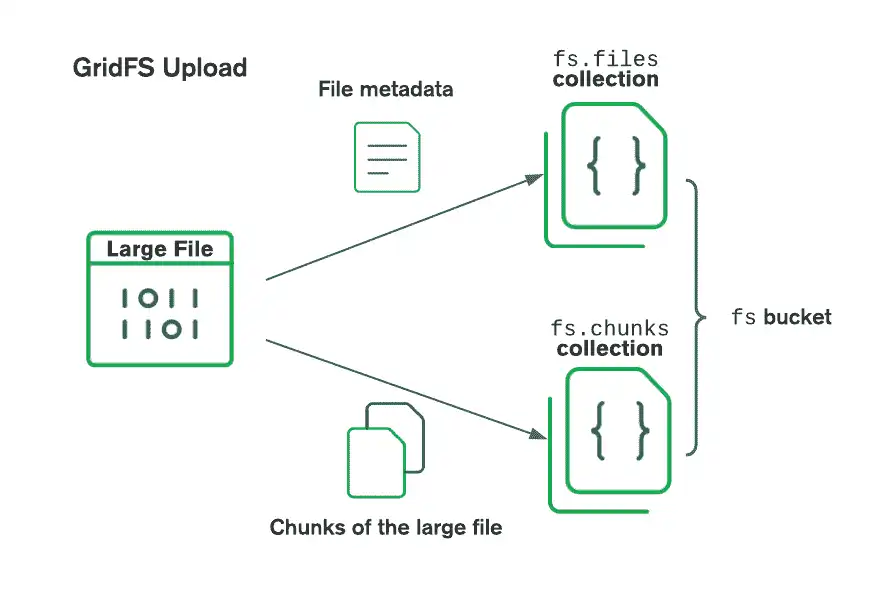
GridFS organizes files in a bucket, a group of MongoDB collections that contain the chunks of files and information describing them. The bucket contains the following collections, named using the convention defined in the GridFS specification:
The
chunkscollection stores the binary file chunks.The
filescollection stores the file metadata.
When you create a new GridFS bucket, the driver creates the preceding
collections, prefixed with the default bucket name fs, unless
you specify a different name. The driver also creates an index on each
collection to ensure efficient retrieval of the files and related
metadata. The driver creates the GridFS bucket, if it doesn't exist, only when the first write
operation is performed. The driver creates indexes only if they don't exist and when the
bucket is empty. For more information about
GridFS indexes, see GridFS Indexes
in the MongoDB Server manual.
When storing files with GridFS, the driver splits the files into smaller
chunks, each represented by a separate document in the chunks collection.
It also creates a document in the files collection that contains
a file ID, file name, and other file metadata. You can upload the file from
memory or from a stream. See the following diagram to see how GridFS splits
the files when uploaded to a bucket.
When retrieving files, GridFS fetches the metadata from the files
collection in the specified bucket and uses the information to reconstruct
the file from documents in the chunks collection. You can read the file
into memory or output it to a stream.
Create a GridFS Bucket
To store or retrieve files from GridFS, create a GridFS bucket by calling the
GridFSBucket() constructor and passing in a Database instance.
You can use the GridFSBucket instance to
call read and write operations on the files in your bucket. If you are working with an
asynchronous application, use the AsyncGridFSBucket() constructor instead.
Select the Synchronous or Asynchronous tab to see the corresponding code:
client = MongoClient("<connection string>") db = client["db"] bucket = gridfs.GridFSBucket(db)
client = AsyncMongoClient("<connection string>") db = client["db"] bucket = gridfs.AsyncGridFSBucket(db)
To create or reference a bucket with a custom name other than the default name
fs, pass your bucket name as the second parameter to the GridFSBucket()
constructor, as shown in the following example. Select the Synchronous or
Asynchronous tab to see the corresponding code:
custom_bucket = gridfs.GridFSBucket(db, bucket_name="myCustomBucket")
custom_bucket = gridfs.AsyncGridFSBucket(db, bucket_name="myCustomBucket")
Upload Files
Use the open_upload_stream() method from the GridFSBucket class to
create an upload stream for a given file name. The open_upload_stream()
method allows you to specify configuration information such as file chunk
size and other field/value pairs to store as metadata. Set these options
as parameters of open_upload_stream(), as shown in the following code
example. Select the Synchronous or Asynchronous tab to see the
corresponding code:
with bucket.open_upload_stream( "my_file", chunk_size_bytes=1048576, metadata={"contentType": "text/plain"} ) as grid_in: grid_in.write("data to store")
async with bucket.open_upload_stream( "my_file", chunk_size_bytes=1048576, metadata={"contentType": "text/plain"} ) as grid_in: await grid_in.write("data to store")
Retrieve File Information
In this section, you can learn how to retrieve file metadata stored in the
files collection of the GridFS bucket. The metadata contains information
about the file it refers to, including:
The
_idof the fileThe name of the file
The length/size of the file
The upload date and time
A
metadatadocument in which you can store any other information
To retrieve files from a GridFS bucket, call the find() method on the GridFSBucket
instance. The method returns a Cursor instance
from which you can access the results. To learn more about Cursor objects in
PyMongo, see Access Data From a Cursor.
The following code example shows you how to retrieve and print file metadata
from all your files in a GridFS bucket. It uses the for...in syntax to traverse the
Cursor iterable and display the results. Select the Synchronous or
Asynchronous tab to see the corresponding code:
for file_doc in bucket.find({}): print(file_doc)
async for file_doc in bucket.find({}): print(file_doc)
The find() method accepts various query specifications. You can use
its parameters to specify the sort order, maximum number of documents to return,
and the number of documents to skip before returning. To learn more about querying
MongoDB, see Find Documents.
Download Files
You can download files from your MongoDB database by using the
open_download_stream_by_name() method from GridFSBucket to create a
download stream.
The following example shows you how to download a file referenced
by the file name, "my_file", and read its contents. Select the Synchronous
or Asynchronous tab to see the corresponding code:
file = bucket.open_download_stream_by_name("my_file") contents = file.read()
file = await bucket.open_download_stream_by_name("my_file") contents = await file.read()
Note
If there are multiple documents with the same filename value,
GridFS will stream the most recent file with the given name (as
determined by the uploadDate field).
Alternatively, you can use the open_download_stream()
method, which takes the _id field of a file as a parameter. Select the Synchronous
or Asynchronous tab to see the corresponding code:
file = bucket.open_download_stream(ObjectId("66b3c86e672a17b6c8a4a4a9")) contents = file.read()
file = await bucket.open_download_stream(ObjectId("66b3c86e672a17b6c8a4a4a9")) contents = await file.read()
Note
The GridFS streaming API cannot load partial chunks. When a download stream needs to pull a chunk from MongoDB, it pulls the entire chunk into memory. The 255-kilobyte default chunk size is usually sufficient, but you can reduce the chunk size to reduce memory overhead.
Rename Files
Use the rename() method to update the name of a GridFS file in your
bucket. You must specify the file to rename by its _id field
rather than its file name.
The following example shows how to update the filename field to
"new_file_name" by referencing a document's _id field. Select the Synchronous
or Asynchronous tab to see the corresponding code:
bucket.rename(ObjectId("66b3c86e672a17b6c8a4a4a9"), "new_file_name")
await bucket.rename(ObjectId("66b3c86e672a17b6c8a4a4a9"), "new_file_name")
Note
The rename() method supports updating the name of only one file at
a time. To rename multiple files, retrieve a list of files matching the
file name from the bucket, extract the _id field from the files you
want to rename, and pass each value in separate calls to the rename()
method.
Delete Files
Use the delete() method to remove a file's collection document and associated
chunks from your bucket. This effectively deletes the file. You must
specify the file by its _id field rather than its file name.
The following example shows you how to delete a file by referencing its _id field.
Select the Synchronous or Asynchronous tab to see the
corresponding code:
bucket.delete(ObjectId("66b3c86e672a17b6c8a4a4a9"))
await bucket.delete(ObjectId("66b3c86e672a17b6c8a4a4a9"))
Note
The delete() method supports deleting only one file at a time. To
delete multiple files, retrieve the files from the bucket, extract
the _id field from the files you want to delete, and pass each value
in separate calls to the delete() method.
API Documentation
To learn more about using PyMongo to store and retrieve large files, see the following API documentation: