Welcome to MongoDB Shell (mongosh)
The MongoDB Shell, mongosh, is a JavaScript and Node.js REPL
environment for interacting with MongoDB deployments in
Atlas , locally,
or on another remote host. Use the MongoDB Shell to test queries and
interact with the data in your MongoDB database.
_Spot.webp)
Access MongoDB From Your Shell
Find Your Connection String
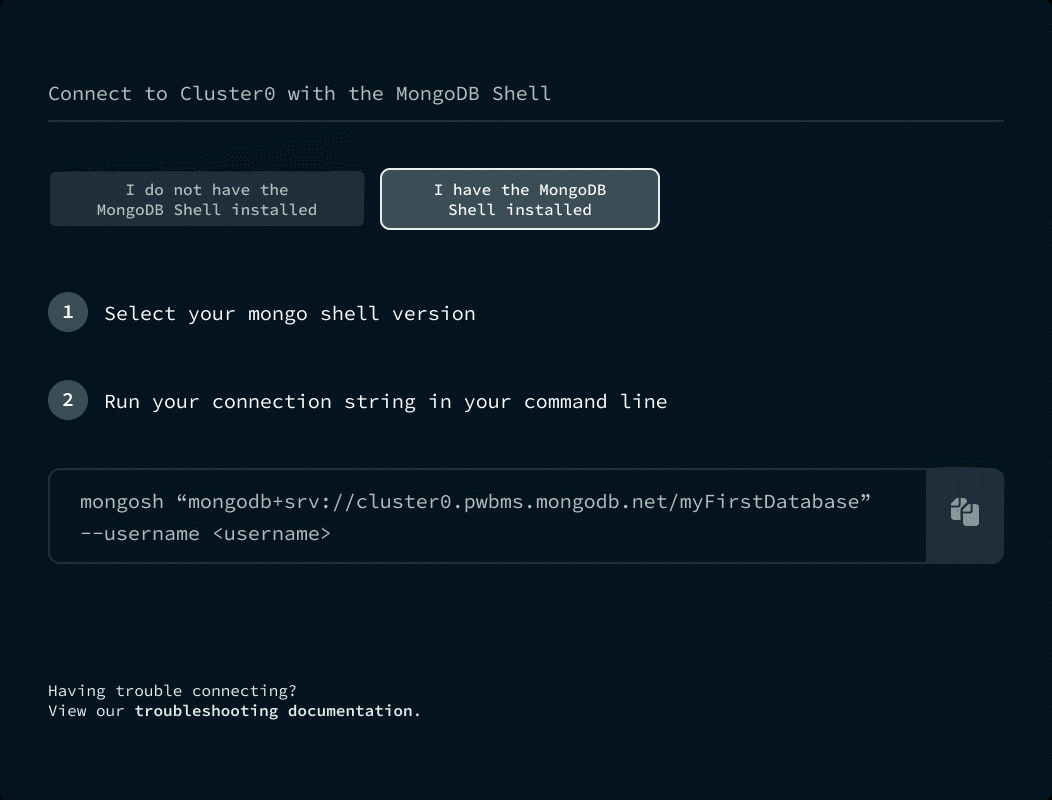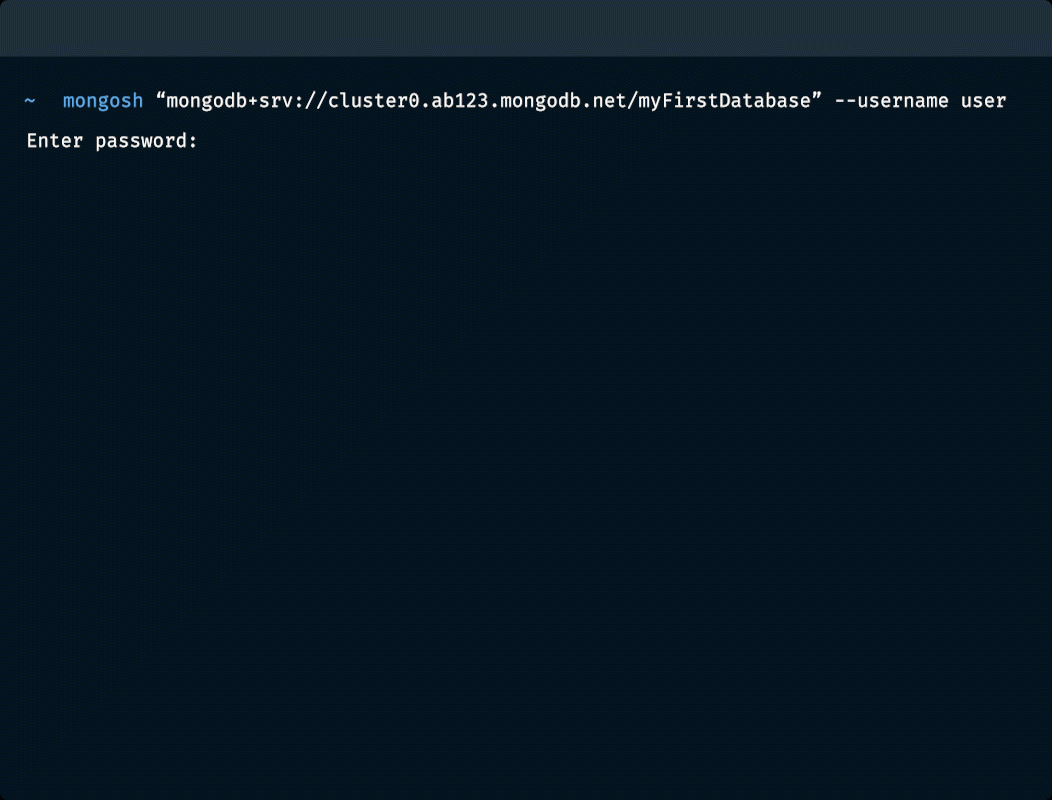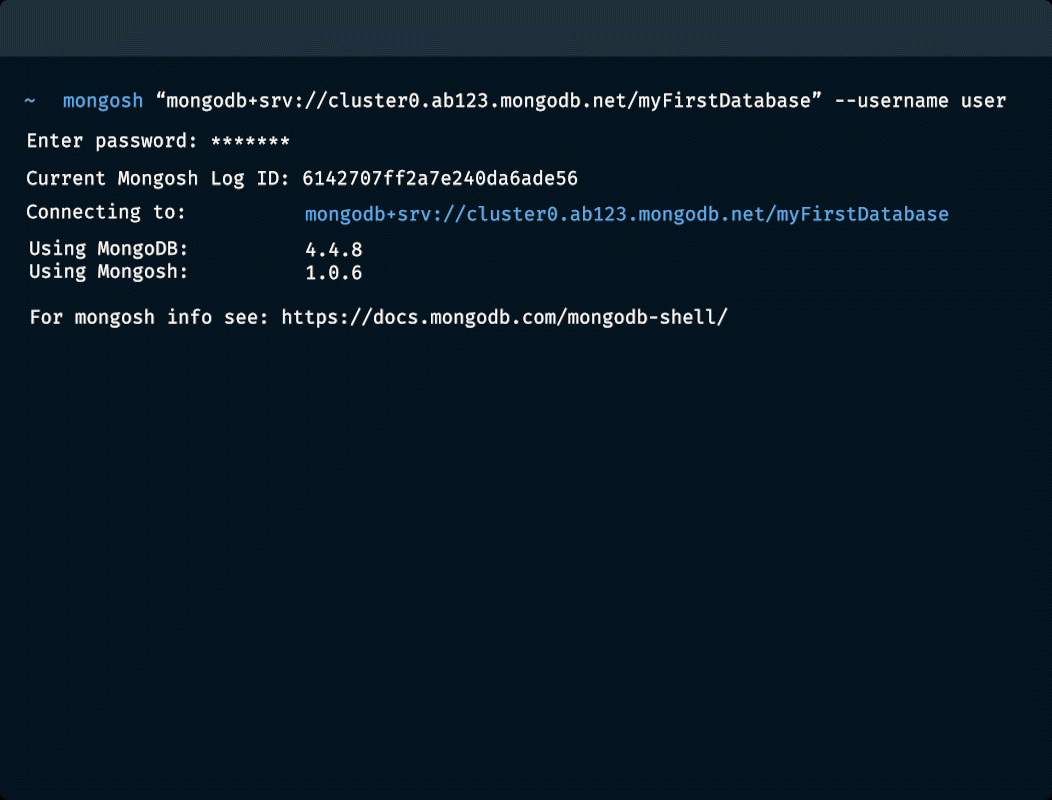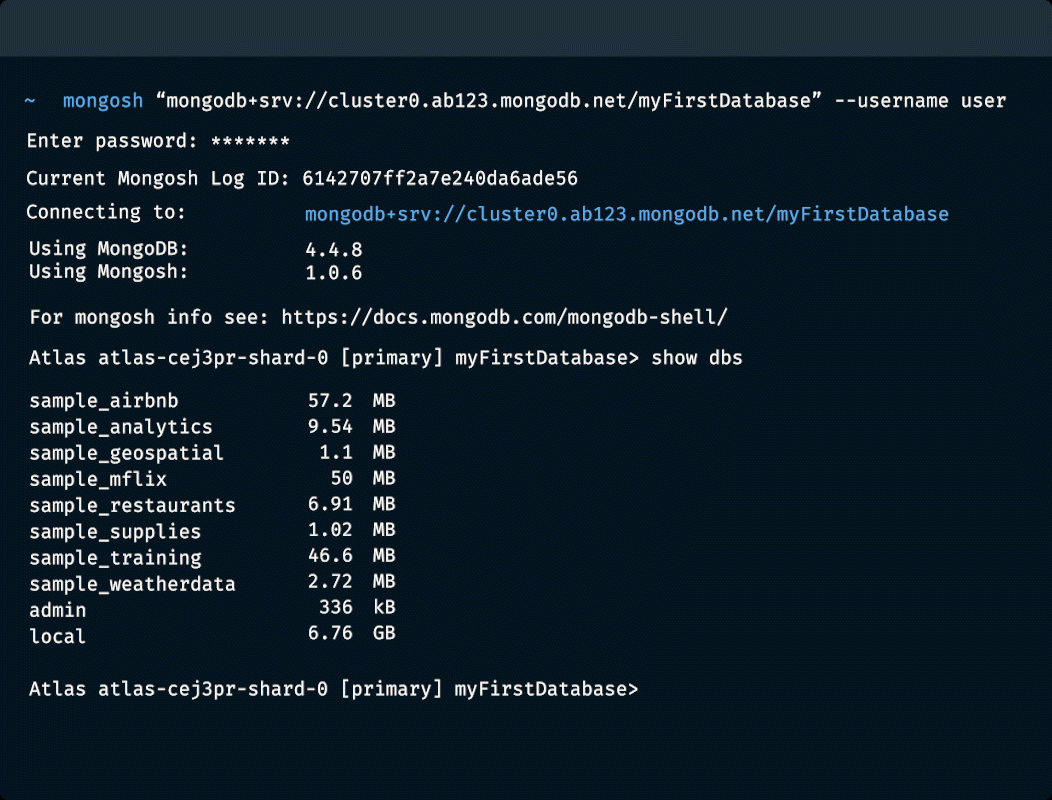
Find your connection string. The connection string varies depending on the type of deployment you're connecting to.
Learn how to find your connection string for Atlas.
Or connect to a self-hosted deployment.
Interact with Your Data
Use your chosen connection type to view your data, import documents, and run queries.
For more information, refer to Perform CRUD Operations.
Insert Documents
mongosh supports common insert opererations,
including:
For more information and examples, refer to Insert Documents.
Read Documents
Use the db.collection.find() method to query documents
in a collection. For more information and examples, refer to
Query Documents.
Update Documents
mongosh supports common update operations,
including:
For more information and examples, refer to Update Documents.
Delete Documents
mongosh supports common delete operations,
including:
For more information and examples, refer to Delete Documents.
Run Aggregation Pipelines
You can run aggregation pipelines in mongosh
using the db.collection.aggregate() method.
Aggregation pipelines transform your documents into
aggregated results based on the stages you specify. For more
information and examples, refer to Run Aggregation Pipelines.
Manage Databases and Collections
View information about databases, create collections or views, or drop databases - all from your shell. See all Database Methods.
Perform collection operations, create or delete indexes, or explain queries with Collection Methods.
Administer Servers
Manage replication or sharding conveniently in your shell.
Check server status with a variety of Server Status Methods.
Manage Users and Roles
Create or update roles, define and update privileges, or drop roles using Role Management Methods.
Create and update users, authenticate users, and manage user roles with User Management Methods.
_Spot.webp)
Run Scripts for CRUD or Administrative Tasks
Write scripts to run with the MongoDB Shell that perform CRUD or administrative operations in MongoDB.
For example, if you have a JS file that seeds synthetic or mock data into MongoDB in your development or staging environment, run the file with:
mongosh YOUR_JS_FILENAME.js
Explore a tutorial that uses the MongoDB Shell with JavaScript to access MongoDB: Write Scripts.
Create Custom Helper Functions with .mongoshrc
Repeatedly writing large helper functions in the Shell? Store
them in a .mongoshrc config file. For
example, if you often find yourself converting date strings to
ISO format for queries, create a function in .mongoshrc to
handle it:
function toISO(dateString) { return new Date(dateString).toISOString(); }
Then, call the function in mongosh:
db.clientConnections.find( { connectTime: toISO("06/07/2017") } )
For more information, refer to Execute Code From a Configuration File.
Use or Publish Snippets
Pull existing snippets into your codebase for convenient reuse. Or create and share snippets for your custom use case.
For example, you might have a snippet that validates the data you import daily as a cron job. You can publish this snippet, so your development team can access it. Publish to a community registry or configure a private registry.
For more information, refer to Registries and Registry Configuration.
_Spot.webp)
Other Powerful Features
Use an external or built-in editor to work with multiline
functions. Go beyond the line-oriented mongosh
default console.
Access session logs for any session within the last 30 days. Find the command syntax you can't quite remember, or look for common commands you can script.
Find out which methods mongosh supports. Get example
syntax and parameter details for supported methods.