Send Trigger Events to AWS EventBridge
On this page
Overview
MongoDB offers an AWS Eventbridge partner event source that lets you send Atlas Trigger events to an event bus instead of calling an Atlas Function. You can configure any Trigger type to send events to EventBridge. Database Triggers also support custom error handling, to reduce trigger suspensions due to non-critical errors.
All you need to send Trigger events to EventBridge is an AWS account ID. This guide walks through finding your account ID, configuring the Trigger, associating the Trigger event source with an event bus, and setting up custom error handling.
Note
Official AWS Partner Event Source Guide
This guide is based on Amazon's Receiving Events from a SaaS Partner documentation.
Procedure
Note
The AWS put entry for an EventBridge trigger event must be smaller than 256 KB.
Learn how to reduce the size of your PutEvents entry in the Performance Optimization section.
Set Up the MongoDB Partner Event Source
To send trigger events to AWS EventBridge, you need the AWS account ID of the account that should receive the events. Open the Amazon EventBridge console and click Partner event sources in the navigation menu. Search for the MongoDB partner event source and then click Set up.
On the MongoDB partner event source page, click Copy to copy your AWS account ID to the clipboard.
Configure the Trigger
Once you have the AWS account ID, you can configure a trigger to send events to EventBridge.
In the App Services UI, create and configure a new database trigger, authentication trigger, or scheduled trigger and select the EventBridge event type.
Paste in the AWS Account ID that you copied from EventBridge and select an AWS Region to send the trigger events to.
Optionally, you can configure a function for handling trigger errors. Custom error handling is only valid for database triggers. For more details, refer to the Custom Error Handling section on this page.
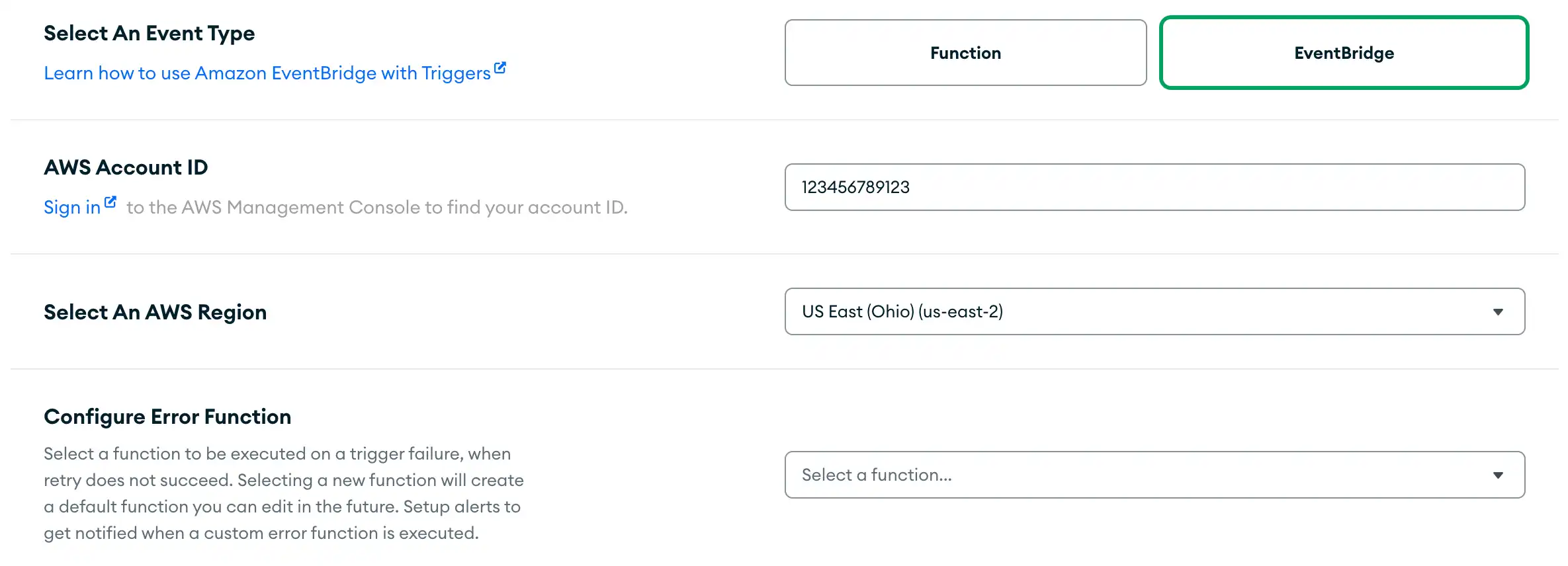
By default, triggers convert the BSON types in event objects into standard JSON types. To preserve BSON type information, you can serialize event objects into Extended JSON format instead. Extended JSON preserves type information at the expense of readability and interoperability.
To enable Extended JSON, click the Enable Extended JSON toggle in the Advanced (Optional) section.
Create a trigger configuration file
in the /triggers directory. Omit the function_name field
and define an AWS_EVENTBRIDGE event processor.
Set the account_id field to the AWS Account ID
that you copied from EventBridge and set the region field to
an AWS Region.
By default, triggers convert the BSON types in event objects into standard JSON types. To preserve BSON type information, you can serialize event objects into Extended JSON format instead. Extended JSON preserves type information at the expense of readability and interoperability.
To enable Extended JSON, set the extended_json_enabled field to true.
Optionally, you can configure a function for handling trigger errors. Custom error handling is only valid for database triggers. For more details, refer to the Custom Error Handling section on this page.
The trigger configuration file should resemble the following:
{ "name": "...", "type": "...", "event_processors": { "AWS_EVENTBRIDGE": { "config": { "account_id": "<AWS Account ID>", "region": "<AWS Region>", "extended_json_enabled": <boolean> } } } }
Note
Supported AWS Regions
For a full list of supported AWS regions, refer to Amazon's Receiving Events from a SaaS Partner guide.
Associate the Trigger Event Source with an Event Bus
Go back to the EventBridge console and choose Partner event sources in the navigation pane. In the Partner event sources table, find and select the Pending trigger source and then click Associate with event bus.
On the Associate with event bus screen, define any required access permissions for other accounts and organizations and then click Associate.
Once confirmed, the status of the trigger event source changes from Pending to Active, and the name of the event bus updates to match the event source name. You can now start creating rules that trigger on events from that partner event source. For more information, see Creating a Rule That Triggers on a SaaS Partner Event.
Custom Error Handling
Note
Only Database Triggers Support Custom Error Handlers
Currently, only database triggers support custom error handling. Authentication triggers and scheduled triggers do not support custom error handling at this time.
You can create an error handler to be executed on a trigger failure, when retry does not succeed. Custom error handling allows you to determine whether an error from AWS EventBridge is critical enough to suspend the Trigger, or if it is acceptable to ignore the error and continue processing other events. For more information on suspended database triggers, refer to Suspended Triggers.
Create a New Custom Error Handler
You can create the new function directly in the Create a Trigger page, as below, or from the Functions tab. For more information on how to define functions in App Services, refer to Define a Function.
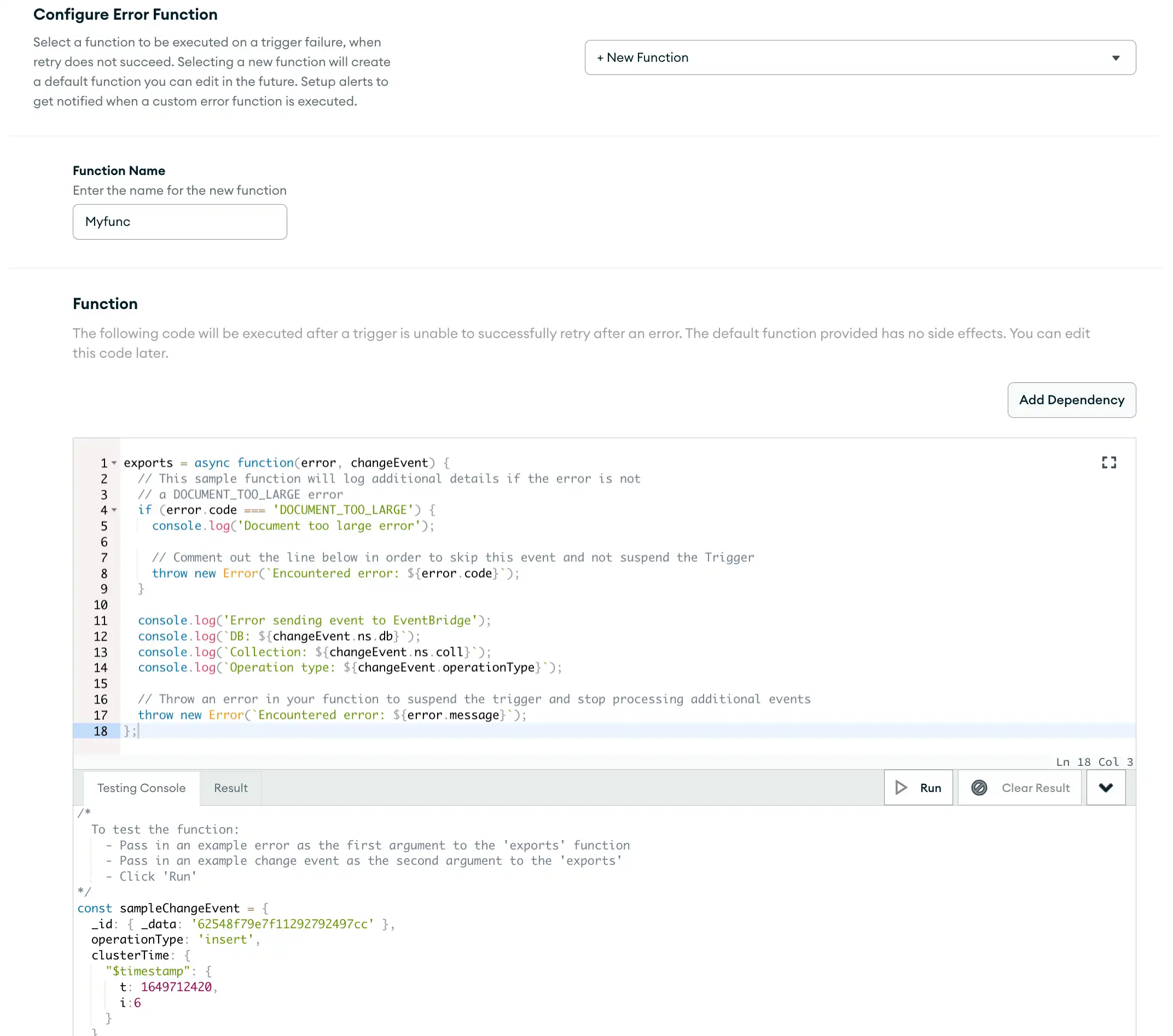
Write the Function Code
In the Function section, write the JavaScript code directly in the function editor. The function editor contains a default function that you can edit as needed. For more information on creating functions, refer to the Functions documentation.
Test the Function
In the Testing Console tab beneath the function editor, you can
test the function by passing in example values to the error and
changeEvent parameters, as shown in the comments of the testing console.
For more information on these paramaters, refer to the Error Handler Parameters section on this page.
Click Run to run the test.
In order to update your trigger's configuration with an error handler, follow these steps to Update an App. When you update your configuration files in Step 3, do the following:
Write the Error Handler
Follow the steps in Define a Function to write your error handler source code and configuration file.
For the error handler source code, see the following template error handler:
exports = async function(error, changeEvent) { // This sample function will log additional details if the error is not // a DOCUMENT_TOO_LARGE error if (error.code === 'DOCUMENT_TOO_LARGE') { console.log('Document too large error'); // Comment out the line below in order to skip this event and not suspend the Trigger throw new Error(`Encountered error: ${error.code}`); } console.log('Error sending event to EventBridge'); console.log(`DB: ${changeEvent.ns.db}`); console.log(`Collection: ${changeEvent.ns.coll}`); console.log(`Operation type: ${changeEvent.operationType}`); // Throw an error in your function to suspend the trigger and stop processing additional events throw new Error(`Encountered error: ${error.message}`); };
Add an Error Handler to Your Trigger Configuration
Add an error_handler attribute to your trigger configuration file
in the Triggers folder. The trigger configuration file should
resemble the following:
{ "name": "...", "type": "DATABASE", "event_processors": { "AWS_EVENTBRIDGE": { "config": { "account_id": "<AWS Account ID>", "region": "<AWS Region>", "extended_json_enabled": <boolean> } } }, "error_handler": { "config": { "enabled": <boolean>, "function_name": "<Error Handler Function Name>" } } }
For more information on trigger configuration files, see Trigger Configuration Files.
Authenticate a MongoDB Atlas User
Call the admin user authentication endpoint with your MongoDB Atlas API key pair:
curl -X POST \ https://services.cloud.mongodb.com/api/admin/v3.0/auth/providers/mongodb-cloud/login \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -H 'Accept: application/json' \ -d '{ "username": "<Public API Key>", "apiKey": "<Private API Key>" }'
If authentication succeeds, the response body contains a JSON object
with an access_token value:
{ "access_token": "<access_token>", "refresh_token": "<refresh_token>", "user_id": "<user_id>", "device_id": "<device_id>" }
The access_token grants access to the App Services Admin API. You
must include it as a Bearer token in the Authorization header for
all Admin API requests.
Create a Deployment Draft (Optional)
A draft represents a group of application changes that you can deploy or discard as a single unit. If you don't create a draft, updates automatically deploy individually.
To create a draft, send a POST request with no body to
the Create a Deployment Draft endpoint:
curl -X POST 'https://services.cloud.mongodb.com/api/admin/v3.0/groups/{groupId}/apps/{appId}/drafts' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>'
Create the Error Handler Function
Create the function to handle errors for a failed AWS
EventBridge trigger via a POST request to the
Create a new
Function endpoint.
curl -X POST \ https://services.cloud.mongodb.com/api/admin/v3.0/groups/{groupId}/apps/{appId}/functions \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>' \ -d '{ "name": "string", "private": true, "source": "string", "run_as_system": true }'
Create the AWS EventBridge Trigger
Create the AWS EventBridge Trigger with error handling
enabled via a POST request to the
Create a Trigger endpoint.
curl -X POST \ https://services.cloud.mongodb.com/api/admin/v3.0/groups/{groupId}/apps/{appId}/triggers \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>' \ -d '{ "name": "string", "type": "DATABASE", "config": { "service_id": "string", "database": "string", "collection": "string", "operation_types": { "string" }, "match": , "full_document": false, "full_document_before_change": false, "unordered": true }, "event_processors": { "AWS_EVENTBRIDGE": { "account_id": "string", "region": "string", "extended_json_enabled": false }, }, "error_handler": { "enabled": true, "function_id": "string" } }'
Deploy the Draft
If you created a draft, you can deploy all changes in
the draft by sending a POST request with no body to the
Deploy a deployment draft endpoint.
If you did not create a draft as a first step, the
individual function and trigger requests deployed automatically.
curl -X POST \ 'https://services.cloud.mongodb.com/api/admin/v3.0/groups/{groupId}/apps/{appId}/drafts/{draftId}/deployment' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --header 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>' \
Error Handler Parameters
The default error handler has two parameters: error and changeEvent.
error
Has the following two attributes:
code: The code for the errored EventBridge put request. For a list of error codes used by the error handler, see the below section.message: The unfiltered error message from an errored EventBridge put request.
changeEvent
The requested change to your data made by EventBridge. For more information on types of change events and their configurations, see Change Event Types.
Error Codes
If an error was recevied from EventBridge, the event processor will parse the
error as either DOCUMENT_TOO_LARGE or OTHER. This parsed error is passed
to the error handler function through the error parameter.
DOCUMENT_TOO_LARGE
If the put entry for an EventBridge trigger event is larger than 256 KB, EventBridge will throw an error. The error will contain either:
status code: 400 and
total size of the entries in the request is over the limit.status code: 413, which indicates a too large payload.
For more information on reducing put entry size, see the below Performance Optimization section.
OTHER
The default bucket for all other errors.
Tip
Optimize Error Handling for Errors with OTHER Code
You can make special error handling cases for
your most common error messages to optimize your error handling for
errors with an OTHER code. To determine which errors need
special cases, we recommended keeping track of
the most common error messages you receive in error.message.
Error Handler Logs
You can view Trigger Error Handler logs for your EventBridge Trigger error handler in the application logs.
Click
Logsin the left navigation of the App Services UI.Click the Filter by Type dropdown and select Triggers Error Handlers to view all error handler logs for the App.
Pass the trigger_error_handler value to the --type flag to
view all error handler logs for the App.
appservices logs list --type=trigger_error_handler
Retrieve TRIGGER_ERROR_HANDLER type logs via a GET request to
the Retreive App Services Logs endpoint:
curl -X GET 'https://services.cloud.mongodb.com/api/admin/v3.0/groups/{groupId}/apps/{appId}/logs' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer <access_token>' -d '{ "type": "TRIGGER_ERROR_HANDLER" }'
To learn more about viewing application logs, see View Application Logs.
Example Event
The following object configures a trigger to send events to AWS Eventbridge and handle errors:
"event_processors": { "AWS_EVENTBRIDGE": { "config": { "account_id": "012345678901", "region": "us-east-1" } } }, "error_handler": { "config": { "enabled": true, "function_name": "myErrorHandler.js" } }
Performance Optimization
The AWS put entry for an EventBridge trigger event must be smaller than 256 KB.
For more information, see the AWS Documentation to calculate Amazon PutEvents event entry size.
When using Database Triggers, the Project Expression can be useful reduce the document size before sending messages to EventBridge. This expression lets you include only specified fields, reducing document size.
Learn more in the Database Trigger Project Expression documentation.