マルチユーザー アプリケーション - Node.js SDK
Realm SDK を使用すると、複数のユーザーが特定のデバイスで同時にアプリにログインできます。 Realm クライアント アプリケーションは、複数のユーザーが同時にログインしている場合でも、単一のアクティブ ユーザーのコンテキストで実行されます。 再度ログインする必要なく、認証されたユーザー間ですばやく切り替えることができます。
重要
ログインしたユーザーは、再認証を行わずに アクティブ ユーザー になる場合があります。 アプリによっては、セキュリティ上の脆弱性がある場合があります。 たとえば、共有デバイス上のユーザーは、認証情報を提供したり明示的な許可を必要とせずに、同僚のログイン アカウントに切り替えることができます。 アプリケーションでより厳格な認証が必要な場合は、ユーザー間の切り替えを避け、別のユーザーを認証する前にアクティブなユーザーを明示的にログアウトすることをおすすめします。
ユーザー アカウントの状態
ユーザーが特定のデバイスまたはブラウザで Realm SDK を介して初めてログインすると、SDK はユーザーの情報を保存し、デバイス上のユーザーの状態を追跡します。 ログアウトした場合でも、ユーザーをアクティブに削除しない限り、ユーザーのデータはデバイス上に残ります。
次の状態では、ある時点でデバイス上のユーザーを記述します。
認証済み:デバイスにログイン済みで、ログアウトしたことがない、またはセッションが取り消されているユーザー。
アクティブ: 特定のデバイスで現在アプリを使用している単一の認証済みユーザー。 SDK はこのユーザーを送信リクエストに関連付け、Atlas App Services はデータアクセス権限を評価し、このユーザーのコンテキストで関数を実行します。 詳細については、アクティブ ユーザーを参照してください。
非アクティブ: 現在アクティブなユーザーではない、すべての認証済みユーザー。 現在非アクティブなユーザーにいつでもアクティブなユーザーを切り替えることができます。
ログアウト:デバイスで認証されたが、ログアウトされたユーザーまたはセッションが取り消されたユーザー。
以下の図は、特定のイベントが発生したときに App Services クライアント アプリ内のユーザーが状態間でどのように移行するかを示しています。
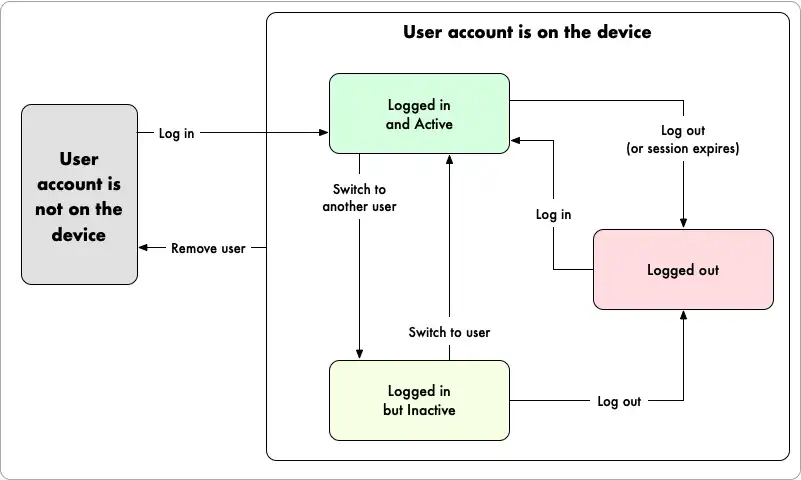
デバイスへの新しいユーザーの追加
Realm SDK は、ユーザーがそのデバイスに初めてログインするときに、そのデバイスにユーザーを自動的に追加します。 ユーザーはログインすると、すぐにアプリケーションのアクティブ ユーザー になります。
例
以下の例では、メールが joe@example.comのユーザーがログインして アクティブ ユーザーになります。 その後、メールemma@example.comのユーザーがログインしてアクティブ ユーザーになります。
const app = new Realm.App({ id: "myapp-abcde" }); // Log in as Joe const joeCredentials = Realm.Credentials.emailPassword("joe@example.com", "passw0rd") const joe = await app.logIn(joeCredentials); // The active user is now Joe assert(joe.id === app.currentUser.id); // Log in as Emma const emmaCredentials = Realm.Credentials.emailPassword("emma@example.com", "pa55word") const emma = await app.logIn(emmaCredentials); // The active user is now Emma, but Joe is still logged in assert(emma.id === app.currentUser.id);
const app = new Realm.App({ id: "myapp-abcde" }); // Log in as Joe const joeCredentials = Realm.Credentials.emailPassword("joe@example.com", "passw0rd") const joe = await app.logIn(joeCredentials); // The active user is now Joe assert(joe.id === app.currentUser.id); // Log in as Emma const emmaCredentials = Realm.Credentials.emailPassword("emma@example.com", "pa55word") const emma = await app.logIn(emmaCredentials); // The active user is now Emma, but Joe is still logged in assert(emma.id === app.currentUser.id);
デバイス上のすべてのユーザーを一覧表示
デバイス上のすべてのユーザー アカウントのリストにアクセスできます。 このリストには、特定のデバイス上のクライアント アプリにログインしたすべてのユーザーが含まれます。
例
以下の例では、開発者はRealm.App.allUsers をループ処理して、デバイス上のすべてのログイン ユーザーを出力します。
// Get a list of all Users app.allUsers.forEach(user => { console.log(`User with id ${user.id} is ${user.isLoggedIn ? "logged in" : "logged out"}`); });
// Get a list of all Users app.allUsers.forEach((user: Realm.User) => { console.log(`User with id ${user.id} is ${user.isLoggedIn ? "logged in" : "logged out"}`); });
デバイスからユーザーを削除
デバイスからユーザーに関するすべての情報を削除し、ユーザーを自動的にログアウトできます。
例
以下の例では、現在のユーザーはRealm.App.removeUser() メソッドを使用してデバイスから削除されています 使用して複数のドキュメントを挿入できます。
// Remove the current user from the device const user = app.currentUser; await app.removeUser(user); // The user is no longer the active user if(app.currentUser) { // The active user is now the logged in user (if there still is one) that was // most recently active assert(user.id !== app.currentUser.id) } // The user is no longer on the device assert(app.allUsers.find(({ id }) => id === user.id) === undefined);
// Remove the current user from the device const user = app.currentUser; await app.removeUser(user); // The user is no longer the active user // The active user is now the logged in user (if there still is one) that was // most recently active assert(user.id !== app.currentUser?.id) // The removed user is no longer on the device assert(app.allUsers.find(({ id }) => id === user.id) === undefined);
アクティブなユーザーの変更
アプリのアクティブ ユーザーを別のログイン ユーザーにいつでもすばやく切り替えることができます。
例
以下の例では、アクティブなユーザーはRealm.App.switchUser() メソッドを使用して最初にuser1に切り替えられます。 使用して複数のドキュメントを挿入できます。 その後、アクティブなユーザーはuser2に切り替えられます。
// Get some logged-in users const authenticatedUsers = app.allUsers.filter(user => user.isLoggedIn); const user1 = authenticatedUsers[0]; const user2 = authenticatedUsers[1]; // Switch to user1 app.switchUser(user1); // The active user is now user1 assert(app.currentUser.id === user1.id); // Switch to user2 app.switchUser(user2); // The active user is now user2 assert(app.currentUser.id === user2.id);
// Get some logged-in users const authenticatedUsers = app.allUsers.filter(user => user.isLoggedIn); const user1 = authenticatedUsers[0]; const user2 = authenticatedUsers[1]; // Switch to user1 app.switchUser(user1); // The active user is now user1 assert(app.currentUser.id === user1.id); // Switch to user2 app.switchUser(user2); // The active user is now user2 assert(app.currentUser.id === user2.id);