ドキュメントをクエリするには、返すドキュメントを示すクエリ述語を指定します。 空のクエリ述語( { } )を指定すると、クエリはコレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを返します。
次の方法を使用して、MongoDB 内のドキュメントをクエリできます。
プログラミング言語のドライバー。
MongoDB Atlas UI 。詳しくは、「MongoDB Atlas を使用したドキュメントのクエリ」を参照してください。
➤ 右上の [言語選択] ドロップダウンメニューを使用して、以下の例の言語を設定するか、MongoDB Compass を選択します。
このページでは、db.collection.find() メソッドを使用した、mongosh. でのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、MongoDB Compass. を使用したクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、mongoc_collection_find_with_opts を使用したクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、MongoCollection.Find() メソッドを使用した MongoDB C# ドライバーでのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、Collection.Find 関数を使用した、MongoDB Go ドライバーでのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、com.mongodb.reactivestreams.client.MongoCollection.find メソッドを使用した、MongoDB Java Reactive Streams ドライバーでのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、 com.mongodb を使用したクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。 MongoDB Java同期ドライバー のクライアント.MongoCollection.find メソッド。
Tip
ドライバーが提供する com.mongodb.client.model.Filters ヘルパー メソッドを使用すると、フィルター ドキュメントの作成が簡単になります。このページでは、これらのメソッドを使用してフィルター ドキュメントを作成する例を紹介します。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、MongoCollection.find()MongoDB Kotlinコルーチン ドライバー で実行されるクエリ操作の例を取りあげます。
Tip
ドライバーが提供する com.mongodb.client.model.Filters ヘルパー メソッドを使用すると、フィルター ドキュメントの作成が簡単になります。このページでは、これらのメソッドを使用してフィルター ドキュメントを作成する例を紹介します。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
2025 年 5 月 14 日現在、Motor は非推奨となり、PyMongo ライブラリの PyMongo 非同期 API の GA リリースが推奨されています。Motor に新しい機能を追加することはなく、2026 年 5 月14 日までバグ修正のみを提供します。その後、2027 年 5 月 14日に、最終サポートが終了するまで、重大なバグのみを修正します。Motor がまだサポートされている間に、PyMongo 非同期 API への移行を強くお勧めします。
移行の詳細については、PyMongo ドキュメントの「PyMongo 非同期への移行」ガイドを参照してください。
このページでは、pymongo.asynchronous.collection.AsyncCollection.find メソッドを使用した PyMongo Async APIでのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、 Collection.find()メソッドを使用した、 MongoDB Node.jsドライバー でのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、MongoDB\\Collection::find() メソッドを使用した、MongoDB PHP ライブラリでのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、pymongo.collection.Collection.find メソッドを使用した PyMongo Python ドライバーでのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、Mongo::Collection#find() メソッドを使用したMongoDB Ruby ドライバーでのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
このページでは、collection.find() メソッドを使用した、配列フィールドにおける MongoDB Scala ドライバーでのクエリ操作の例を取り上げます。
このページの例では、inventory コレクションを使用しています。MongoDB インスタンスのテスト データベースに接続し、inventory コレクションを作成します。
db.inventory.insertMany([ { item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }, { item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" }, { item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" }, { item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" }, { item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" } ]);
[ { "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": { "h": 14, "w": 21, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "A" }, { "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "status": "A" }, { "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "status": "D" }, { "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": { "h": 22.85, "w": 30, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "D" }, { "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": { "h": 10, "w": 15.25, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "A" } ]
MongoDB Compass でドキュメントを挿入する手順については、「ドキュメントの挿入」を参照してください。
mongoc_collection_t *collection; mongoc_bulk_operation_t *bulk; bson_t *doc; bool r; bson_error_t error; bson_t reply; collection = mongoc_database_get_collection (db, "inventory"); bulk = mongoc_collection_create_bulk_operation_with_opts (collection, NULL); doc = BCON_NEW ( "item", BCON_UTF8 ("journal"), "qty", BCON_INT64 (25), "size", "{", "h", BCON_DOUBLE (14), "w", BCON_DOUBLE (21), "uom", BCON_UTF8 ("cm"), "}", "status", BCON_UTF8 ("A")); r = mongoc_bulk_operation_insert_with_opts (bulk, doc, NULL, &error); bson_destroy (doc); if (!r) { MONGOC_ERROR ("%s\n", error.message); goto done; } doc = BCON_NEW ( "item", BCON_UTF8 ("notebook"), "qty", BCON_INT64 (50), "size", "{", "h", BCON_DOUBLE (8.5), "w", BCON_DOUBLE (11), "uom", BCON_UTF8 ("in"), "}", "status", BCON_UTF8 ("A")); r = mongoc_bulk_operation_insert_with_opts (bulk, doc, NULL, &error); bson_destroy (doc); if (!r) { MONGOC_ERROR ("%s\n", error.message); goto done; } doc = BCON_NEW ( "item", BCON_UTF8 ("paper"), "qty", BCON_INT64 (100), "size", "{", "h", BCON_DOUBLE (8.5), "w", BCON_DOUBLE (11), "uom", BCON_UTF8 ("in"), "}", "status", BCON_UTF8 ("D")); r = mongoc_bulk_operation_insert_with_opts (bulk, doc, NULL, &error); bson_destroy (doc); if (!r) { MONGOC_ERROR ("%s\n", error.message); goto done; } doc = BCON_NEW ( "item", BCON_UTF8 ("planner"), "qty", BCON_INT64 (75), "size", "{", "h", BCON_DOUBLE (22.85), "w", BCON_DOUBLE (30), "uom", BCON_UTF8 ("cm"), "}", "status", BCON_UTF8 ("D")); r = mongoc_bulk_operation_insert_with_opts (bulk, doc, NULL, &error); bson_destroy (doc); if (!r) { MONGOC_ERROR ("%s\n", error.message); goto done; } doc = BCON_NEW ( "item", BCON_UTF8 ("postcard"), "qty", BCON_INT64 (45), "size", "{", "h", BCON_DOUBLE (10), "w", BCON_DOUBLE (15.25), "uom", BCON_UTF8 ("cm"), "}", "status", BCON_UTF8 ("A")); r = mongoc_bulk_operation_insert_with_opts (bulk, doc, NULL, &error); bson_destroy (doc); if (!r) { MONGOC_ERROR ("%s\n", error.message); goto done; } /* "reply" is initialized on success or error */ r = (bool) mongoc_bulk_operation_execute (bulk, &reply, &error); if (!r) { MONGOC_ERROR ("%s\n", error.message); }
var documents = new BsonDocument[] { new BsonDocument { { "item", "journal" }, { "qty", 25 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 14 }, { "w", 21 }, { "uom", "cm"} } }, { "status", "A" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "notebook" }, { "qty", 50 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 8.5 }, { "w", 11 }, { "uom", "in"} } }, { "status", "A" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "paper" }, { "qty", 100 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 8.5 }, { "w", 11 }, { "uom", "in"} } }, { "status", "D" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "planner" }, { "qty", 75 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 22.85 }, { "w", 30 }, { "uom", "cm"} } }, { "status", "D" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "postcard" }, { "qty", 45 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 10 }, { "w", 15.25 }, { "uom", "cm"} } }, { "status", "A" } }, }; collection.InsertMany(documents);
docs := []any{ bson.D{ {"item", "journal"}, {"qty", 25}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 14}, {"w", 21}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, {"status", "A"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "notebook"}, {"qty", 50}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 8.5}, {"w", 11}, {"uom", "in"}, }}, {"status", "A"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "paper"}, {"qty", 100}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 8.5}, {"w", 11}, {"uom", "in"}, }}, {"status", "D"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "planner"}, {"qty", 75}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 22.85}, {"w", 30}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, {"status", "D"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "postcard"}, {"qty", 45}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 10}, {"w", 15.25}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, {"status", "A"}, }, } result, err := coll.InsertMany(context.TODO(), docs)
Publisher<Success> insertManyPublisher = collection.insertMany(asList( Document.parse("{ item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }") ));
collection.insertMany(asList( Document.parse("{ item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }") ));
collection.insertMany( listOf( Document("item", "journal") .append("qty", 25) .append("size", Document("h", 14) .append("w", 21) .append("uom", "cm") ) .append("status", "A"), Document("item", "notebook") .append("qty", 50) .append("size", Document("h", 8.5) .append("w", 11) .append("uom", "in") ) .append("status", "A"), Document("item", "paper") .append("qty", 100) .append("size", Document("h", 8.5) .append("w", 11) .append("uom", "in") ) .append("status", "D"), Document("item", "planner") .append("qty", 75) .append("size", Document("h", 22.85) .append("w", 30) .append("uom", "cm") ) .append("status", "D"), Document("item", "postcard") .append("qty", 45) .append("size", Document("h", 10) .append("w", 15.25) .append("uom", "cm") ) .append("status", "A"), ) )
await db.inventory.insert_many( [ { "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": {"h": 14, "w": 21, "uom": "cm"}, "status": "A", }, { "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": {"h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in"}, "status": "A", }, { "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": {"h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in"}, "status": "D", }, { "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": {"h": 22.85, "w": 30, "uom": "cm"}, "status": "D", }, { "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": {"h": 10, "w": 15.25, "uom": "cm"}, "status": "A", }, ] )
await db.collection('inventory').insertMany([ { item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' } ]);
$insertManyResult = $db->inventory->insertMany([ [ 'item' => 'journal', 'qty' => 25, 'size' => ['h' => 14, 'w' => 21, 'uom' => 'cm'], 'status' => 'A', ], [ 'item' => 'notebook', 'qty' => 50, 'size' => ['h' => 8.5, 'w' => 11, 'uom' => 'in'], 'status' => 'A', ], [ 'item' => 'paper', 'qty' => 100, 'size' => ['h' => 8.5, 'w' => 11, 'uom' => 'in'], 'status' => 'D', ], [ 'item' => 'planner', 'qty' => 75, 'size' => ['h' => 22.85, 'w' => 30, 'uom' => 'cm'], 'status' => 'D', ], [ 'item' => 'postcard', 'qty' => 45, 'size' => ['h' => 10, 'w' => 15.25, 'uom' => 'cm'], 'status' => 'A', ], ]);
db.inventory.insert_many( [ { "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": {"h": 14, "w": 21, "uom": "cm"}, "status": "A", }, { "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": {"h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in"}, "status": "A", }, { "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": {"h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in"}, "status": "D", }, { "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": {"h": 22.85, "w": 30, "uom": "cm"}, "status": "D", }, { "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": {"h": 10, "w": 15.25, "uom": "cm"}, "status": "A", }, ] )
client[:inventory].insert_many([{ item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' } ])
collection.insertMany(Seq( Document("""{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }"""), Document("""{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" }"""), Document("""{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" }"""), Document("""{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" }"""), Document("""{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }""") )).execute()
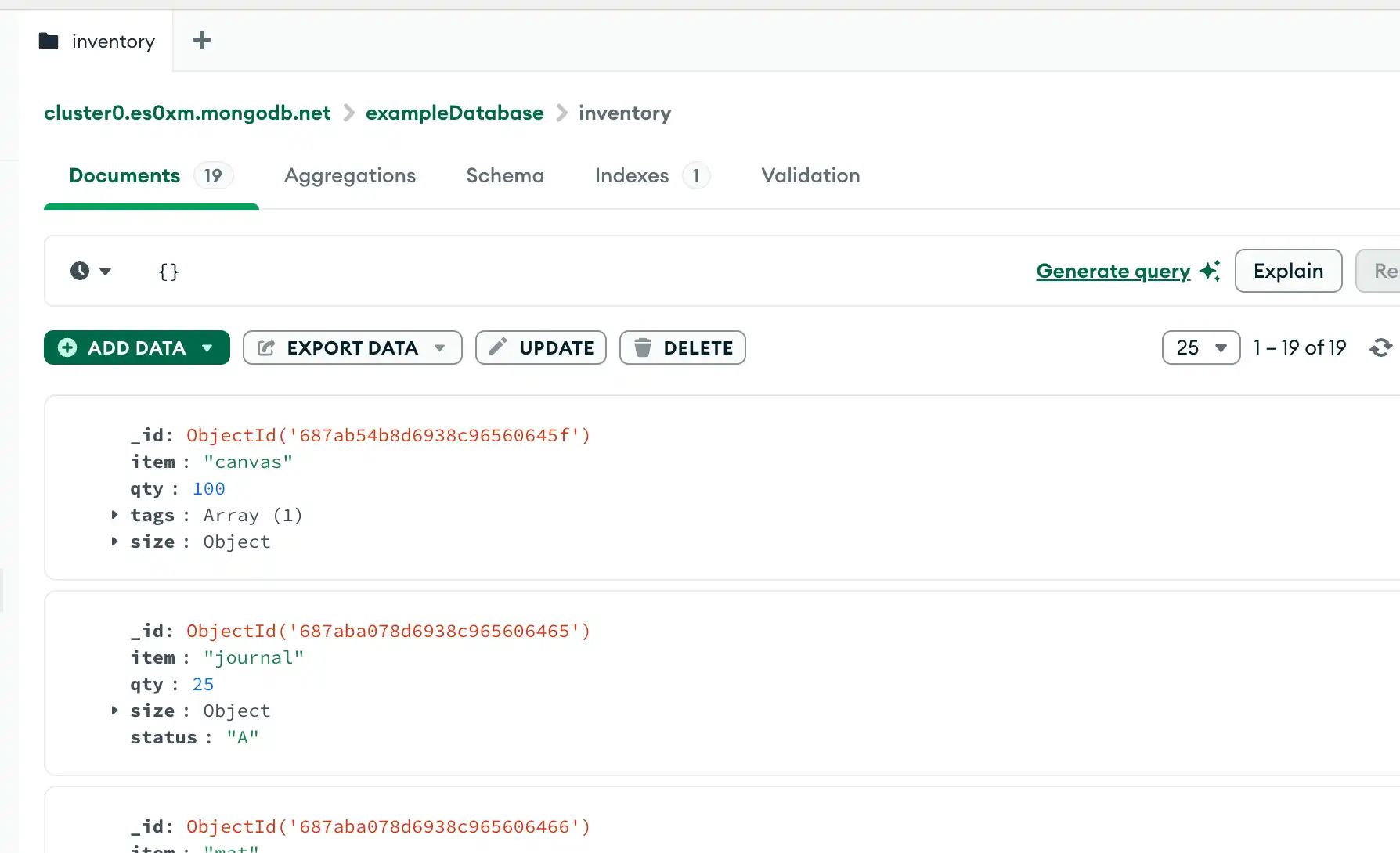
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとしてクエリ バーに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメーターによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
コレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択するには、空のドキュメントをクエリフィルター パラメーターとして find メソッドに渡します。クエリフィルター パラメータによって選択基準が決定されます。
db.inventory.find( {} )
mongoc_collection_t *collection; bson_t *filter; mongoc_cursor_t *cursor; collection = mongoc_database_get_collection (db, "inventory"); filter = BCON_NEW (NULL); cursor = mongoc_collection_find_with_opts (collection, filter, NULL, NULL);
必要に応じて、次のメソッドを呼び出して、開いているリソースをクリーンアップします。
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Empty; var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{}, )
FindPublisher<Document> findPublisher = collection.find(new Document());
FindIterable<Document> findIterable = collection.find(new Document());
val flowInsertMany = collection .find(empty())
cursor = db.inventory.find({})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({});
$cursor = $db->inventory->find([]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({})
client[:inventory].find({})
var findObservable = collection.find(Document())
この操作では、次の SQL ステートメントに対応する{}のクエリ述語が使用されます。
SELECT * FROM inventory
メソッドの構文の詳細については、「find()」を参照してください。
MongoDB Compass クエリ バーの詳細については、「クエリ バー」を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、mongoc_collection_find_with_opts を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、Find() を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、コレクション.Find を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、com.mongodb.reactivestreams.client.MongoCollection.find を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection.find を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、MongoCollection.find() を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、 find を参照してください。
find() メソッドでサポートされているオプションを確認するには、find(). を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、「find()」を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、 find を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、find() を参照してください。
メソッドの構文の詳細については、collection.find() を参照してください。
等価条件を指定
等価条件を指定するには、クエリフィルター ドキュメントで <field>:<value> 式を使用します。
{ <field1>: <value1>, ... }
等価条件を指定するには、クエリフィルター ドキュメントで <field>:<value> 式を使用します。
{ <field1>: <value1>, ... }
等価条件を指定するには、クエリフィルター ドキュメントで <field>:<value> 式を使用します。
{ <field1>: <value1>, ... }
等価条件を指定するには、Eq メソッドを使用してフィルターを構築します:
Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq(<field>, <value>);
等価条件を指定するには、bson.D タイプを使用してフィルタードキュメントを作成します。
filter := bson.D{{"<field>", <value>}}
等価条件を指定するには、 com.mongodb を使用します。クライアント.model.Filters.eq メソッドを使用して、クエリフィルタードキュメントを作成します。
and(eq(<field1>, <value1>), eq(<field2>, <value2>) ...)
等価条件を指定するには、com.mongodb.client.model.Filters.eq_ メソッドを使用してクエリフィルター ドキュメントを作成します。
and(eq(<field1>, <value1>), eq(<field2>, <value2>) ...)
等価条件を指定するには、Filters.eq()クエリフィルタードキュメントを作成する方法
and(eq(<field1>, <value1>), eq(<field2>, <value2>) ...)
等価条件を指定するには、クエリフィルター ドキュメントで <field>:<value> 式を使用します。
{ <field1>: <value1>, ... }
等価条件を指定するには、クエリフィルター ドキュメントで <field>:<value> 式を使用します。
{ <field1>: <value1>, ... }
等価条件を指定するには、クエリフィルター ドキュメントで <field> => <value> 式を使用します。
[ <field1> => <value1>, ... ]
等価条件を指定するには、クエリフィルター ドキュメントで <field>:<value> 式を使用します。
{ <field1>: <value1>, ... }
等価条件を指定するには、クエリフィルター ドキュメントで <field> => <value> 式を使用します。
{ <field1> => <value1>, ... }
等価条件を指定するには、com.mongodb.client.model.Filters.eq_ メソッドを使用してクエリフィルター ドキュメントを作成します。
and(equal(<field1>, <value1>), equal(<field2>, <value2>) ...)
次の例では、inventory コレクションから、status が "D"と等しいすべてのドキュメントを選択します。
db.inventory.find( { status: "D" } )
次のフィルターを Compass のクエリバーにコピーし、[Find] ボタンをクリックします。
{ status: "D" }
注意
MongoDB Compass クエリ バーは、埋め込まれたサブドキュメント内のキーを含め、コレクションのドキュメント内のキーに基づいて現在のクエリを自動補完します。
mongoc_collection_t *collection; bson_t *filter; mongoc_cursor_t *cursor; collection = mongoc_database_get_collection (db, "inventory"); filter = BCON_NEW ("status", BCON_UTF8 ("D")); cursor = mongoc_collection_find_with_opts (collection, filter, NULL, NULL);
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("status", "D"); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{{"status", "D"}}, )
findPublisher = collection.find(eq("status", "D"));
findIterable = collection.find(eq("status", "D"));
val findFlow = collection .find(eq("status", "D"))
cursor = db.inventory.find({"status": "D"})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ status: 'D' });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['status' => 'D']);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"status": "D"})
client[:inventory].find(status: 'D')
findObservable = collection.find(equal("status", "D"))
この操作では、次の SQL ステートメントに対応する{ status: "D" }のクエリ述語が使用されます。
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "D"
クエリ演算子を使用して条件を指定
クエリフィルター ドキュメントでは、クエリ演算子を使用して次の形式で条件を指定できます。
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
クエリフィルター ドキュメントでは、クエリ演算子を使用して次の形式で条件を指定できます。
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
クエリフィルター ドキュメントでは、クエリ演算子を使用して次の形式で条件を指定できます。
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
等価フィルターに加えて、MongoDB はフィルター条件を指定するためのさまざまなクエリ演算子を提供します。フィルタードキュメントを作成するには、FilterDefinitionBuilder メソッドを使用します。以下に例を挙げます。
var builder = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter; builder.And(builder.Eq(<field1>, <value1>), builder.Lt(<field2>, <value2>));
等価フィルターに加えて、 MongoDB はフィルター条件を指定するためのさまざまな クエリ演算子 を提供します。BSONパッケージを使用して、フィルター ドキュメントのクエリ演算子を作成します。 (例: )。
filter := bson.D{ {"$and", bson.A{ bson.D{{"field1", bson.D{{"$eq", value1}}}}, bson.D{{"field2", bson.D{{"$lt", value2}}}}, }}, }
等価条件に加えて、 MongoDB はフィルター条件を指定するためのさまざまな クエリ演算子 を提供します。com.mongodb を使用します。クライアント.model.Filtersヘルパーメソッドを使用すると、フィルター ドキュメントの作成が簡単になります。(例: )。
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), eq(<field3>, <value3>))
等価条件に加えて、 MongoDB はフィルター条件を指定するためのさまざまな クエリ演算子 を提供します。com.mongodb を使用します。クライアント.model.Filtersヘルパーメソッドを使用すると、フィルター ドキュメントの作成が簡単になります。(例: )。
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), eq(<field3>, <value3>))
等価条件に加えて、 MongoDB はフィルター条件を指定するためのさまざまな クエリ演算子 を提供します。com.mongodb を使用します。クライアント.model.Filtersヘルパーメソッドを使用すると、フィルター ドキュメントの作成が簡単になります。(例: )。
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), eq(<field3>, <value3>))
クエリフィルター ドキュメントでは、クエリ演算子を使用して次の形式で条件を指定できます。
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
クエリフィルター ドキュメントでは、クエリ演算子を使用して次の形式で条件を指定できます。
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
クエリフィルター ドキュメントでは、クエリ演算子を使用して次の形式で条件を指定できます。
[ <field1> => [ <operator1> => <value1> ], ... ]
クエリフィルター ドキュメントでは、クエリ演算子を使用して次の形式で条件を指定できます。
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
クエリフィルター ドキュメントでは、クエリ演算子を使用して次の形式で条件を指定できます。
{ <field1> => { <operator1> => <value1> }, ... }
MongoDB には等価条件に加え、フィルター条件を指定するためのさまざまなクエリ演算子が付属します。フィルター ドキュメントの作成を容易にするには、com.mongodb.client.model.Filters_ ヘルパー メソッドを使用します。以下に例を挙げます。
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), equal(<field3>, <value3>))
次の例では、inventory コレクションから、status が "A" または "D" に等しいすべてのドキュメントを検索します。
db.inventory.find( { status: { $in: [ "A", "D" ] } } )
次のフィルターを Compass のクエリ バーにコピーし、[Find] をクリックします。
{ status: { $in: [ "A", "D" ] } }
mongoc_collection_t *collection; bson_t *filter; mongoc_cursor_t *cursor; collection = mongoc_database_get_collection (db, "inventory"); filter = BCON_NEW ( "status", "{", "$in", "[", BCON_UTF8 ("A"), BCON_UTF8 ("D"), "]", "}"); cursor = mongoc_collection_find_with_opts (collection, filter, NULL, NULL);
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.In("status", new[] { "A", "D" }); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{{"status", bson.D{{"$in", bson.A{"A", "D"}}}}})
findPublisher = collection.find(in("status", "A", "D"));
findIterable = collection.find(in("status", "A", "D"));
val findFlow = collection .find(`in`("status", "A", "D"))
cursor = db.inventory.find({"status": {"$in": ["A", "D"]}})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ status: { $in: ['A', 'D'] } });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['status' => ['$in' => ['A', 'D']]]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"status": {"$in": ["A", "D"]}})
client[:inventory].find(status: { '$in' => [ 'A', 'D' ]})
findObservable = collection.find(in("status", "A", "D"))
この操作では、次の SQL ステートメントに対応する{ status: { $in: [ "A", "D" ] } }のクエリ述語が使用されます。
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status in ("A", "D")
MongoDBクエリ演算子の完全なリストについては、クエリ述語を参照してください。
AND 条件を指定
複合クエリは、コレクション内のドキュメントの複数のフィールドに条件を指定することができます。暗黙的に、論理的な AND 結合が複合クエリの各条件句を接続し、すべての条件に一致するドキュメントがコレクションから選択されます。
次の例では、inventory コレクション内で、status が "A" に等しく、かつ qty が($lt)30 より小さいすべてのドキュメントを検索します。
db.inventory.find( { status: "A", qty: { $lt: 30 } } )
次のフィルターを Compass のクエリ バーにコピーし、[Find] をクリックします。
{ status: "A", qty: { $lt: 30 } }
mongoc_collection_t *collection; bson_t *filter; mongoc_cursor_t *cursor; collection = mongoc_database_get_collection (db, "inventory"); filter = BCON_NEW ( "status", BCON_UTF8 ("A"), "qty", "{", "$lt", BCON_INT64 (30), "}"); cursor = mongoc_collection_find_with_opts (collection, filter, NULL, NULL);
var builder = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter; var filter = builder.And(builder.Eq("status", "A"), builder.Lt("qty", 30)); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"status", "A"}, {"qty", bson.D{{"$lt", 30}}}, })
findPublisher = collection.find(and(eq("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)));
findIterable = collection.find(and(eq("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)));
val findFlow = collection .find(and(eq("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)))
cursor = db.inventory.find({"status": "A", "qty": {"$lt": 30}})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ status: 'A', qty: { $lt: 30 } });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find([ 'status' => 'A', 'qty' => ['$lt' => 30], ]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"status": "A", "qty": {"$lt": 30}})
client[:inventory].find(status: 'A', qty: { '$lt' => 30 })
findObservable = collection.find(and(equal("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)))
この操作では、次の SQL ステートメントに対応する{ status: "A", qty: { $lt: 30 } }のクエリ述語が使用されます。
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" AND qty < 30
その他の MongoDB 比較演算子については、「比較演算子」を参照してください。
OR 条件を指定
$or 演算子を使用すると、各条件句を論理的な OR 結合で結合する複合クエリを指定できます。これにより、クエリは、少なくとも 1 つの条件に一致するドキュメントをコレクションから選択します。
次の例では、コレクション内で status が "A" に等しい、または qty が($lt) 30 より小さいすべてのドキュメントを検索します。
db.inventory.find( { $or: [ { status: "A" }, { qty: { $lt: 30 } } ] } )
次のフィルターを Compass のクエリ バーにコピーし、[Find] をクリックします。
{ $or: [ { status: "A" }, { qty: { $lt: 30 } } ] }
mongoc_collection_t *collection; bson_t *filter; mongoc_cursor_t *cursor; collection = mongoc_database_get_collection (db, "inventory"); filter = BCON_NEW ( "$or", "[", "{", "status", BCON_UTF8 ("A"), "}","{", "qty", "{", "$lt", BCON_INT64 (30), "}", "}", "]"); cursor = mongoc_collection_find_with_opts (collection, filter, NULL, NULL);
var builder = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter; var filter = builder.Or(builder.Eq("status", "A"), builder.Lt("qty", 30)); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ { "$or", bson.A{ bson.D{{"status", "A"}}, bson.D{{"qty", bson.D{{"$lt", 30}}}}, }, }, })
findPublisher = collection.find(or(eq("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)));
findIterable = collection.find(or(eq("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)));
val findFlow = collection .find(or(eq("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)))
cursor = db.inventory.find({"$or": [{"status": "A"}, {"qty": {"$lt": 30}}]})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ $or: [{ status: 'A' }, { qty: { $lt: 30 } }] });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find([ '$or' => [ ['status' => 'A'], ['qty' => ['$lt' => 30]], ], ]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"$or": [{"status": "A"}, {"qty": {"$lt": 30}}]})
client[:inventory].find('$or' => [{ status: 'A' }, { qty: { '$lt' => 30 } } ])
findObservable = collection.find(or(equal("status", "A"), lt("qty", 30)))
この操作では、次の SQL ステートメントに対応する{ $or: [ { status: 'A' }, { qty: { $lt: 30 } } ] }のクエリ述語が使用されます。
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" OR qty < 30
AND と OR 条件を指定
次の例では、複合クエリ ドキュメントは、status が"A" と等しく、かつqty が($lt)30 より小さいか、または item が p の文字で始まる いずれかの条件が満たされるコレクション内のすべてのドキュメントを選択します。
db.inventory.find( { status: "A", $or: [ { qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: /^p/ } ] } )
次のフィルターを Compass のクエリ バーにコピーし、[Find] をクリックします。
{ status: "A", $or: [ { qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: /^p/ } ] }
mongoc_collection_t *collection; bson_t *filter; mongoc_cursor_t *cursor; collection = mongoc_database_get_collection (db, "inventory"); filter = BCON_NEW ( "status", BCON_UTF8 ("A"), "$or", "[", "{", "qty", "{", "$lt", BCON_INT64 (30), "}", "}","{", "item", BCON_REGEX ("^p", ""), "}", "]"); cursor = mongoc_collection_find_with_opts (collection, filter, NULL, NULL);
var builder = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter; var filter = builder.And( builder.Eq("status", "A"), builder.Or(builder.Lt("qty", 30), builder.Regex("item", new BsonRegularExpression("^p")))); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"status", "A"}, {"$or", bson.A{ bson.D{{"qty", bson.D{{"$lt", 30}}}}, bson.D{{"item", bson.Regex{Pattern: "^p", Options: ""}}}, }}, })
findPublisher = collection.find( and(eq("status", "A"), or(lt("qty", 30), regex("item", "^p"))) );
findIterable = collection.find( and(eq("status", "A"), or(lt("qty", 30), regex("item", "^p"))) );
val findFlow = collection .find( and(eq("status", "A"), or(lt("qty", 30), regex("item", "^p"))) )
cursor = db.inventory.find( {"status": "A", "$or": [{"qty": {"$lt": 30}}, {"item": {"$regex": "^p"}}]} )
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ status: 'A', $or: [{ qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: { $regex: '^p' } }] });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find([ 'status' => 'A', '$or' => [ ['qty' => ['$lt' => 30]], // Alternatively: ['item' => new \MongoDB\BSON\Regex('^p')] ['item' => ['$regex' => '^p']], ], ]);
cursor = db.inventory.find( {"status": "A", "$or": [{"qty": {"$lt": 30}}, {"item": {"$regex": "^p"}}]} )
client[:inventory].find(status: 'A', '$or' => [{ qty: { '$lt' => 30 } }, { item: { '$regex' => BSON::Regexp::Raw.new('^p') } } ])
findObservable = collection.find(and( equal("status", "A"), or(lt("qty", 30), regex("item", "^p"))) )
この操作では、次のクエリ述語を使用します。
{ status: 'A', $or: [ { qty: { $lt: 30 } }, { item: { $regex: '^p' } } ] }
これは、次の SQL ステートメントに対応します。
SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE status = "A" AND ( qty < 30 OR item LIKE "p%")
注意
MongoDB は、文字列パターンの一致を実行するための正規表現 $regex のクエリをサポートしています。
MongoDB Atlas でドキュメントをクエリする
このセクションの例では、映画データセットのサンプルを使用します。サンプル データセットを MongoDB Atlas 配置にロードする方法について詳しくは、「サンプル データのロード」を参照してください。
MongoDB Atlas でクエリから返されるフィールドをプロジェクトするには、次の手順に従います。
MongoDB Atlas UI で、プロジェクトの Clusters ページに移動します。
まだ表示されていない場合は、希望するプロジェクトを含む組織を選択しますナビゲーション バーのOrganizationsメニュー
まだ表示されていない場合は、ナビゲーション バーの Projects メニューからプロジェクトを選択します。
サイドバーで、 Database見出しの下のClustersをクリックします。
[ Clusters (クラスター) ] ページが表示されます。
Filterフィールドを指定します
Filter フィールドにクエリフィルター ドキュメントを指定します。クエリフィルター ドキュメントは、クエリ演算子を使用して検索条件を指定します。
次のクエリフィルター ドキュメントを Filter 検索バーにコピーします。
{ year: 1924 }
その他のクエリに関するチュートリアル
その他のクエリの例については、以下を参照してください。
動作
Cursor
db.collection.find() メソッドは、一致するドキュメントにカーソルを返します。
MongoDB Compass の Find 操作では、検索クエリに基づいてコレクションの一致するドキュメントへのカーソルを開くことができます。
MongoDB Compass でのサンプリングの詳細については、「Compass FAQ」を参照してください。
mongoc_collection_find_with_opts メソッドは、一致するドキュメントに カーソル を返します。
MongoCollection.Find() メソッドは、一致するドキュメントへの カーソル を返します。カーソルの反復処理については、MongoDB C#ドライバーのドキュメントを参照してください。
Collection.Find 関数は、一致するドキュメントに カーソル を返します。詳細については、 カーソル のドキュメントを参照してください。
MongoCollection.find() メソッドは、 FindFlowクラスのインスタンスを返します。
pymongo.asynchronous.collection.AsyncCollection.find メソッドは、一致するドキュメントに カーソル を返します。
Collection.find() メソッドは、 カーソル を返します。
MongoDB\\Collection::find()メソッドは、一致するドキュメントにカーソルを返します。カーソルの反復処理については、MongoDB PHP ライブラリのドキュメントを参照してください。
pymongo.collection.Collection.find メソッドは、一致するドキュメントに カーソル を返します。カーソルの反復処理については、PyMongo のドキュメントを参照してください。
Mongo::Collection#find() メソッドからは Enumerable である CollectionView が返されます。カーソルは、View が列挙されると作成されます。例えば、#to_a() または #each() を呼び出した場合です。View で#to_enum() を呼び出すことで、Enumerator を取得することもできます。カーソルの反復処理については、Ruby ドライバー API ドキュメントを参照してください。
コレクションの.find() メソッドからは find Observable が返されます。
カーソル使用中の同時更新
カーソルによってドキュメントが返されると、読み取り保証 (read concern)のレベルによっては、バックグラウンドで他の操作が実行され、結果に影響が出る可能性があります。 詳細については、「 読み取り分離、整合性、最新性について 」を参照してください。
読み取りの分離
レプリカセットおよびレプリカセット シャードへの読み取りの場合、読み取り保証 (read concern) により、クライアントは読み取りの分離レベルを選択できます。詳細については、「読み取り保証 (read concern)」を参照してください。
クエリ結果の形式
MongoDB ドライバーまたは mongosh を使用して検索操作を実行すると、コマンドはクエリ結果を管理するカーソルを返します。クエリ結果はドキュメントの配列として返されません。
カーソル内でドキュメントを反復処理する方法については、 「ドライバーのドキュメント」を参照してください。 mongoshを使用している場合は、「 mongoshでのカーソルの反復処理 」を参照してください。
その他のメソッドとオプション
次の例でもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
注意
db.collection.findOne()メソッドは、 1の制限でdb.collection.find()メソッドと同じ操作を実行します。
次のメソッドでもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
次の例でもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
集計パイプラインでは、
$matchのパイプライン ステージで MongoDB クエリへのアクセスが提供されます。MongoDB C# ドライバーのLINQ ドキュメントを参照してください。
注意
MongoCollection.FindOne() メソッドは、1 の制限で MongoCollection.Find() メソッドと同じ操作を実行します。
次の例でもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
集計パイプラインでは、
$matchパイプラインステージがMongoDBクエリにアクセスできます。詳細は、Collection.Aggregate を参照してください。
集計パイプラインでは、$matchパイプラインステージはMongoDBクエリにアクセスでき、コレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。Java非同期ドライバー集計の例 を参照してください
次の例でもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
集計パイプラインでは、
$matchパイプラインステージがMongoDBクエリにアクセスできます。Java同期ドライバーの集計例 を参照してください
次のメソッドでもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
集計パイプラインでは、
$matchパイプライン ステージを使用して MongoDB クエリを実行できます。 詳しくは、「 Kotlin コルーチン ドライバー検索操作の例」を参照してください。
次のメソッドでもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
注意
pymongo.asynchronous.collection.AsyncCollection.find_one メソッドは、pymongo.asynchronous.collection.AsyncCollection.find メソッドと同じ操作を1 の制限で実行します。
次の例でもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
注意
Collection.findOne() メソッドは、 Collection.find() メソッドと同じ操作を実行します。メソッドとして、1 の制限を持つものです。
次の例でもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
注意
MongoDB\\Collection::findOne()メソッドは、 1の制限でMongoDB\\Collection::find()メソッドと同じ操作を実行します。
次の例でもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
集計パイプラインでは、
$matchパイプラインステージがMongoDBクエリにアクセスできます。詳細は、PyMongo Aggregation の例 を参照してください。
注意
pymongo.collection.Collection.find_one メソッドは、pymongo.collection.Collection.find メソッドと同じ操作を1 の制限で実行します。
次の例でもコレクションからドキュメントを読み取ることができます。
集計パイプラインでは、
$matchパイプラインステージがMongoDBクエリにアクセスできます。詳細については、 MongoDB Scalaドライバーの「 集計メソッド 」を参照してください。