Query on Embedded/Nested Documents
➤ Use the Select your language drop-down menu in the upper-right to set the language of the following examples.
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the
db.collection.find() method in mongosh.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using MongoDB Compass.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the MongoCollection.Find() method in the MongoDB C# Driver.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the Collection.Find function in the MongoDB Go Driver.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the com.mongodb.reactivestreams.client.MongoCollection.find method in the MongoDB Java Reactive Streams Driver.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection.find method in the MongoDB Java Synchronous Driver.
Tip
The driver provides com.mongodb.client.model.Filters helper methods to facilitate the creation of filter documents. The examples on this page use these methods to create the filter documents.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the
motor.motor_asyncio.AsyncIOMotorCollection.find
method in the Motor
driver.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the Collection.find() method in the MongoDB Node.js Driver.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the MongoDB::Collection::find() method in the MongoDB Perl Driver.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the
MongoDB\\Collection::find()
method in the
MongoDB PHP Library.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the
pymongo.collection.Collection.find method in the
PyMongo
Python driver.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the Mongo::Collection#find() method in the MongoDB Ruby Driver.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
This page provides examples of query operations on embedded/nested documents using the collection.find() method in the MongoDB Scala Driver.
The examples on this page use the inventory collection. Connect to a
test database in your MongoDB instance then create the inventory
collection:
db.inventory.insertMany( [ { item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }, { item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" }, { item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" }, { item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" }, { item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" } ]);
[ { "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": { "h": 14, "w": 21, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "A" }, { "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "status": "A" }, { "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "status": "D" }, { "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": { "h": 22.85, "w": 30, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "D" }, { "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": { "h": 10, "w": 15.25, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "A" } ]
For instructions on inserting documents in MongoDB Compass, see Insert Documents.
var documents = new[] { new BsonDocument { { "item", "journal" }, { "qty", 25 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 14 }, { "w", 21 }, { "uom", "cm" } } }, { "status", "A" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "notebook" }, { "qty", 50 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 8.5 }, { "w", 11 }, { "uom", "in" } } }, { "status", "A" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "paper" }, { "qty", 100 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 8.5 }, { "w", 11 }, { "uom", "in" } } }, { "status", "D" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "planner" }, { "qty", 75 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 22.85 }, { "w", 30 }, { "uom", "cm" } } }, { "status", "D" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "postcard" }, { "qty", 45 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 10 }, { "w", 15.25 }, { "uom", "cm" } } }, { "status", "A" } }, }; collection.InsertMany(documents);
docs := []interface{}{ bson.D{ {"item", "journal"}, {"qty", 25}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 14}, {"w", 21}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, {"status", "A"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "notebook"}, {"qty", 50}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 8.5}, {"w", 11}, {"uom", "in"}, }}, {"status", "A"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "paper"}, {"qty", 100}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 8.5}, {"w", 11}, {"uom", "in"}, }}, {"status", "D"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "planner"}, {"qty", 75}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 22.85}, {"w", 30}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, {"status", "D"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "postcard"}, {"qty", 45}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 10}, {"w", 15.25}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, {"status", "A"}, }, } result, err := coll.InsertMany(context.TODO(), docs)
Publisher<Success> insertManyPublisher = collection.insertMany(asList( Document.parse("{ item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }") ));
collection.insertMany(asList( Document.parse("{ item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }") ));
# Subdocument key order matters in a few of these examples so we have # to use bson.son.SON instead of a Python dict. from bson.son import SON await db.inventory.insert_many( [ { "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": SON([("h", 14), ("w", 21), ("uom", "cm")]), "status": "A", }, { "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": SON([("h", 8.5), ("w", 11), ("uom", "in")]), "status": "A", }, { "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": SON([("h", 8.5), ("w", 11), ("uom", "in")]), "status": "D", }, { "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": SON([("h", 22.85), ("w", 30), ("uom", "cm")]), "status": "D", }, { "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": SON([("h", 10), ("w", 15.25), ("uom", "cm")]), "status": "A", }, ] )
await db.collection('inventory').insertMany([ { item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' } ]);
# Subdocument key order matters in this example so we have # to use Tie::IxHash instead of a regular, unordered Perl hash. $db->coll("inventory")->insert_many( [ { item => "journal", qty => 25, size => Tie::IxHash->new( h => 14, w => 21, uom => "cm" ), status => "A" }, { item => "notebook", qty => 50, size => Tie::IxHash->new( h => 8.5, w => 11, uom => "in" ), status => "A" }, { item => "paper", qty => 100, size => Tie::IxHash->new( h => 8.5, w => 11, uom => "in" ), status => "D" }, { item => "planner", qty => 75, size => Tie::IxHash->new( h => 22.85, w => 30, uom => "cm" ), status => "D" }, { item => "postcard", qty => 45, size => Tie::IxHash->new( h => 10, w => 15.25, uom => "cm" ), status => "A" } ] );
$insertManyResult = $db->inventory->insertMany([ [ 'item' => 'journal', 'qty' => 25, 'size' => ['h' => 14, 'w' => 21, 'uom' => 'cm'], 'status' => 'A', ], [ 'item' => 'notebook', 'qty' => 50, 'size' => ['h' => 8.5, 'w' => 11, 'uom' => 'in'], 'status' => 'A', ], [ 'item' => 'paper', 'qty' => 100, 'size' => ['h' => 8.5, 'w' => 11, 'uom' => 'in'], 'status' => 'D', ], [ 'item' => 'planner', 'qty' => 75, 'size' => ['h' => 22.85, 'w' => 30, 'uom' => 'cm'], 'status' => 'D', ], [ 'item' => 'postcard', 'qty' => 45, 'size' => ['h' => 10, 'w' => 15.25, 'uom' => 'cm'], 'status' => 'A', ], ]);
# Subdocument key order matters in a few of these examples so we have # to use bson.son.SON instead of a Python dict. from bson.son import SON db.inventory.insert_many( [ { "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": SON([("h", 14), ("w", 21), ("uom", "cm")]), "status": "A", }, { "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": SON([("h", 8.5), ("w", 11), ("uom", "in")]), "status": "A", }, { "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": SON([("h", 8.5), ("w", 11), ("uom", "in")]), "status": "D", }, { "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": SON([("h", 22.85), ("w", 30), ("uom", "cm")]), "status": "D", }, { "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": SON([("h", 10), ("w", 15.25), ("uom", "cm")]), "status": "A", }, ] )
client[:inventory].insert_many([ { item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' } ])
collection.insertMany(Seq( Document("""{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }"""), Document("""{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" }"""), Document("""{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" }"""), Document("""{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" }"""), Document("""{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }""") )).execute()
Match an Embedded/Nested Document
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the
query filter document
{ <field>: <value> } where <value> is the document
to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the
query filter document
{ <field>: <value> } where <value> is the document
to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an embedded/nested document, construct a filter using the Eq method:
Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq(<field>, <value>)
<value> is the document to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the filter document
eq( <field1>, <value>) where <value> is the document
to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the filter document
eq( <field1>, <value>) where <value> is the document
to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the
query filter document
{ <field>: <value> } where <value> is the document
to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the
query filter document
{ <field>: <value> } where <value> is the document
to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the
query filter document
[ <field> => <value> ] where <value> is the document
to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the
query filter document
{ <field>: <value> } where <value> is the document
to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the
query filter document
{ <field> => <value> } where <value> is the document
to match.
To specify an equality condition on a field that is an
embedded/nested document, use the filter document
equal( <field1>, <value> ) where <value> is the document
to match.
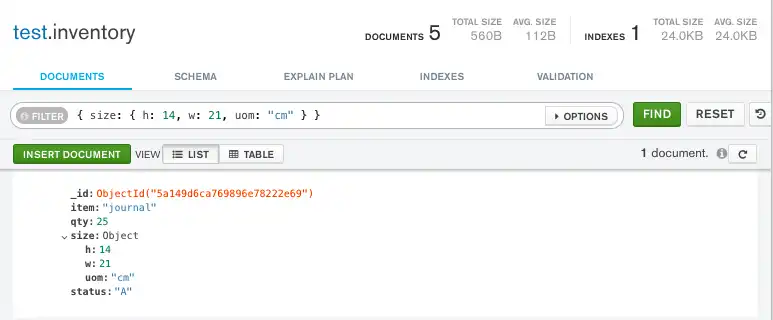
For example, the following query selects all documents where the field
size equals the document { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }:
db.inventory.find( { size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } } )
Copy the following filter into the Compass query bar and click Find:
{ size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } }
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 14 }, { "w", 21 }, { "uom", "cm" } }); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 14}, {"w", 21}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, })
FindPublisher<Document> findPublisher = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }")));
FindIterable<Document> findIterable = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }")));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size": SON([("h", 14), ("w", 21), ("uom", "cm")])})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' } });
# Subdocument key order matters in this example so we have # to use Tie::IxHash instead of a regular, unordered Perl hash. $cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( { size => Tie::IxHash->new( h => 14, w => 21, uom => "cm" ) } );
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size' => ['h' => 14, 'w' => 21, 'uom' => 'cm']]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size": SON([("h", 14), ("w", 21), ("uom", "cm")])})
client[:inventory].find(size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' })
var findObservable = collection.find(equal("size", Document("h" -> 14, "w" -> 21, "uom" -> "cm")))
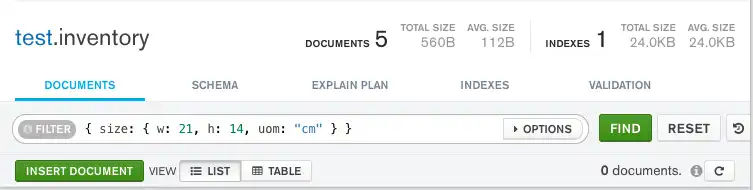
Equality matches on the whole embedded document require an exact
match of the specified <value> document, including the field order.
For example, the following query does not match any documents in the
inventory collection:
db.inventory.find( { size: { w: 21, h: 14, uom: "cm" } } )
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("size", new BsonDocument { { "w", 21 }, { "h", 14 }, { "uom", "cm" } }); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"size", bson.D{ {"w", 21}, {"h", 14}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, })
findPublisher = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ w: 21, h: 14, uom: 'cm' }")));
findIterable = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ w: 21, h: 14, uom: 'cm' }")));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size": SON([("w", 21), ("h", 14), ("uom", "cm")])})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ size: { w: 21, h: 14, uom: 'cm' } });
# Subdocument key order matters in this example so we have # to use Tie::IxHash instead of a regular, unordered Perl hash. $cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( { size => Tie::IxHash->new( w => 21, h => 14, uom => "cm" ) } );
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size' => ['w' => 21, 'h' => 14, 'uom' => 'cm']]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size": SON([("w", 21), ("h", 14), ("uom", "cm")])})
client[:inventory].find(size: { h: 21, w: 14, uom: 'cm' })
findObservable = collection.find(equal("size", Document("w" -> 21, "h" -> 14, "uom" -> "cm")))
Query on Nested Field
To specify a query condition on fields in an embedded/nested document,
use dot notation ("field.nestedField").
Note
When querying using dot notation, the field and nested field must be inside quotation marks.
Specify Equality Match on a Nested Field
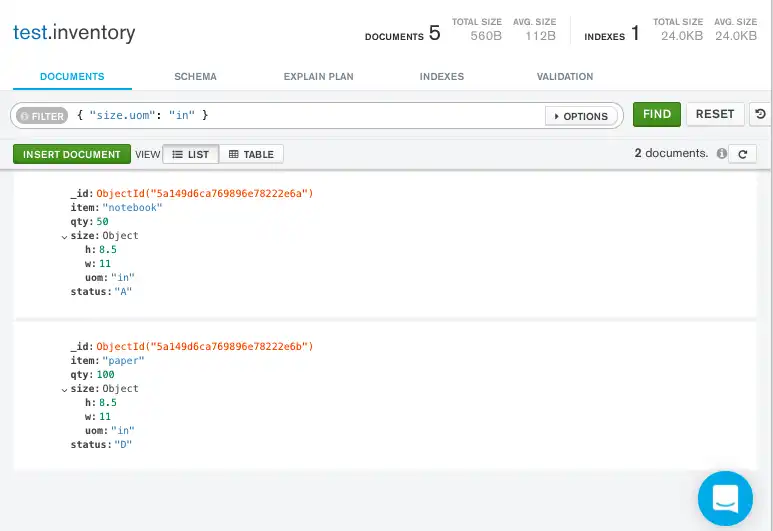
The following example selects all documents where the field uom
nested in the size field equals "in":
db.inventory.find( { "size.uom": "in" } )
Copy the following filter into the Compass query bar and click Find:
{ "size.uom": "in" }
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("size.uom", "in"); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{{"size.uom", "in"}}, )
findPublisher = collection.find(eq("size.uom", "in"));
findIterable = collection.find(eq("size.uom", "in"));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.uom": "in"})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ 'size.uom': 'in' });
$cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( { "size.uom" => "in" } );
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size.uom' => 'in']);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.uom": "in"})
client[:inventory].find('size.uom' => 'in')
findObservable = collection.find(equal("size.uom", "in"))
Specify Match using Query Operator
A query filter document can use the query operators to specify conditions in the following form:
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
A query filter document can use the query operators to specify conditions in the following form:
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
In addition to the equality filter, MongoDB provides various query operators to specify filter conditions. Use the FilterDefinitionBuilder methods to create a filter document. For example:
var builder = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter; builder.And(builder.Eq(<field1>, <value1>), builder.Lt(<field2>, <value2>));
In addition to the equality condition, MongoDB provides various query operators to specify filter conditions. Use the com.mongodb.client.model.Filters helper methods to facilitate the creation of filter documents. For example:
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), eq(<field3>, <value3>))
In addition to the equality condition, MongoDB provides various query operators to specify filter conditions. Use the com.mongodb.client.model.Filters helper methods to facilitate the creation of filter documents. For example:
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), eq(<field3>, <value3>))
A query filter document can use the query operators to specify conditions in the following form:
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
A query filter document can use the query operators to specify conditions in the following form:
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
A query filter document can use the query operators to specify conditions in the following form:
{ <field1> => { <operator1> => <value1> }, ... }
A query filter document can use the query operators to specify conditions in the following form:
[ <field1> => [ <operator1> => <value1> ], ... ]
A query filter document can use the query operators to specify conditions in the following form:
{ <field1>: { <operator1>: <value1> }, ... }
A query filter document can use the query operators to specify conditions in the following form:
{ <field1> => { <operator1> => <value1> }, ... }
In addition to the equality condition, MongoDB provides
various query operators to specify
filter conditions. Use the
com.mongodb.client.model.Filters_ helper methods to
facilitate the creation of filter documents. For example:
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), equal(<field3>, <value3>))
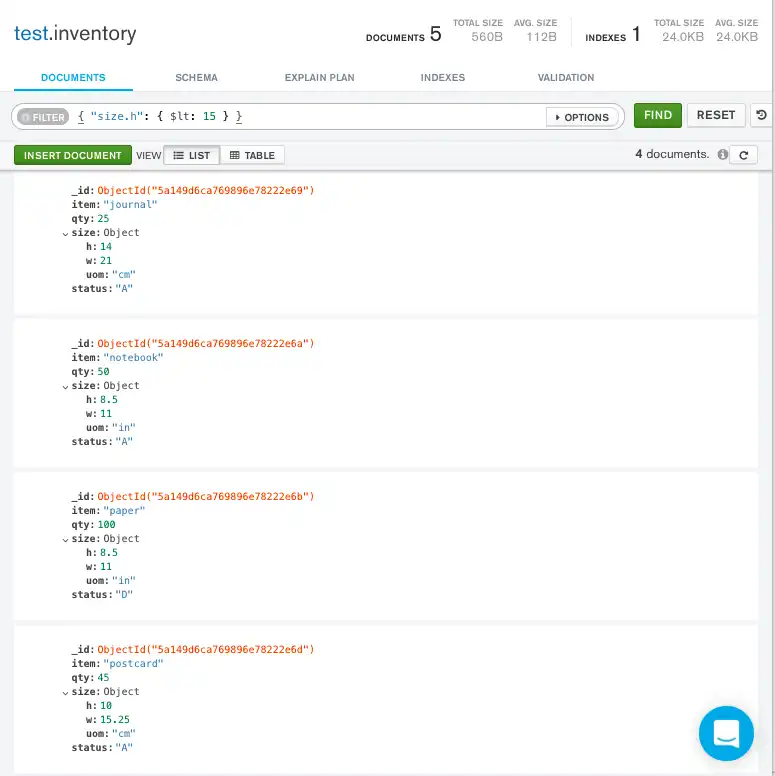
The following query uses the less than operator ($lt) on
the field h embedded in the size field:
db.inventory.find( { "size.h": { $lt: 15 } } )
Copy the following filter into the Compass query bar and click Find:
{ "size.h": { $lt: 15 } }
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Lt("size.h", 15); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"size.h", bson.D{ {"$lt", 15}, }}, })
findPublisher = collection.find(lt("size.h", 15));
findIterable = collection.find(lt("size.h", 15));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.h": {"$lt": 15}})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ 'size.h': { $lt: 15 } });
$cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( { "size.h" => { '$lt' => 15 } } );
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size.h' => ['$lt' => 15]]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.h": {"$lt": 15}})
client[:inventory].find('size.h' => { '$lt' => 15 })
findObservable = collection.find(lt("size.h", 15))
Specify AND Condition
The following query selects all documents where the nested field h
is less than 15, the nested field uom equals "in", and the
status field equals "D":
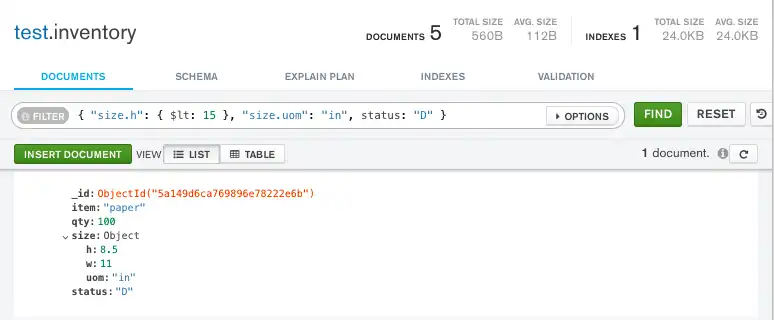
db.inventory.find( { "size.h": { $lt: 15 }, "size.uom": "in", status: "D" } )
Copy the following filter into the Compass query bar and click Find:
{ "size.h": { $lt: 15 }, "size.uom": "in", status: "D" }
var builder = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter; var filter = builder.And(builder.Lt("size.h", 15), builder.Eq("size.uom", "in"), builder.Eq("status", "D")); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"size.h", bson.D{ {"$lt", 15}, }}, {"size.uom", "in"}, {"status", "D"}, })
findPublisher = collection.find(and( lt("size.h", 15), eq("size.uom", "in"), eq("status", "D") ));
findIterable = collection.find(and( lt("size.h", 15), eq("size.uom", "in"), eq("status", "D") ));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.h": {"$lt": 15}, "size.uom": "in", "status": "D"})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ 'size.h': { $lt: 15 }, 'size.uom': 'in', status: 'D' });
$cursor = $db->coll("inventory")->find( { "size.h" => { '$lt' => 15 }, "size.uom" => "in", status => "D" } );
$cursor = $db->inventory->find([ 'size.h' => ['$lt' => 15], 'size.uom' => 'in', 'status' => 'D', ]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.h": {"$lt": 15}, "size.uom": "in", "status": "D"})
client[:inventory].find('size.h' => { '$lt' => 15 }, 'size.uom' => 'in', 'status' => 'D')
findObservable = collection.find(and( lt("size.h", 15), equal("size.uom", "in"), equal("status", "D") ))
Additional Query Tutorials
For additional query examples, see: