계획 결과 설명 해석
이 페이지의 내용
결과 설명을 사용하여 쿼리에 대한 다음 정보를 확인할 수 있습니다.
쿼리를 완료하는 데 걸린 시간
쿼리가 인덱스를 사용했는지 여부
쿼리를 수행하기 위해 스캔한 문서 및 인덱스 키의 수
참고
쿼리에 대한 계획 결과 설명은 MongoDB 버전에 따라 변경될 수 있습니다.
cursor.explain("executionStats") 및 db.collection.explain("executionStats") 메서드는 쿼리 성능에 대한 통계를 제공합니다. 이러한 통계는 쿼리에서 인덱스를 사용하는지 여부와 방법을 측정하는 데 유용할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 db.collection.explain()을 참조하세요.
MongoDB Compass는 쿼리 성능에 대한 통계를 표시하는 설명 계획 탭을 제공합니다. 이러한 통계는 쿼리에서 인덱스를 사용하는지 여부와 방법을 측정하는 데 유용할 수 있습니다.
쿼리 성능 평가
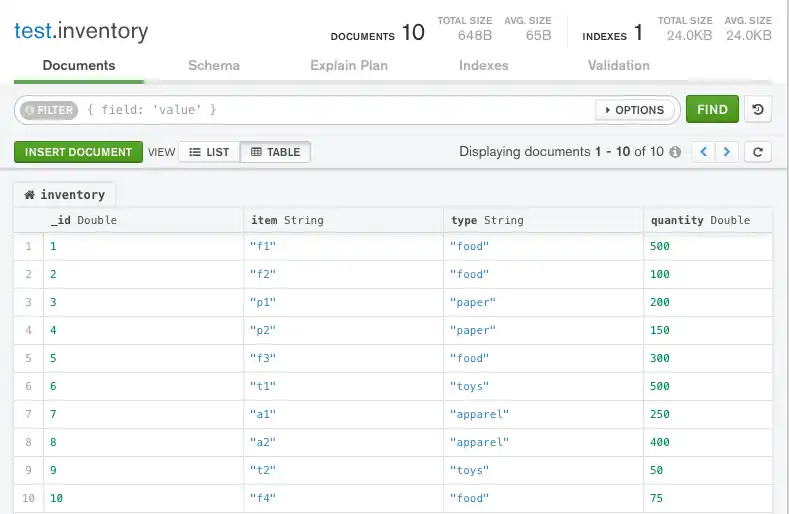
다음 문서가 포함된 inventory 컬렉션을 생각해 보세요.
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "f1", type: "food", quantity: 500 } { "_id" : 2, "item" : "f2", type: "food", quantity: 100 } { "_id" : 3, "item" : "p1", type: "paper", quantity: 200 } { "_id" : 4, "item" : "p2", type: "paper", quantity: 150 } { "_id" : 5, "item" : "f3", type: "food", quantity: 300 } { "_id" : 6, "item" : "t1", type: "toys", quantity: 500 } { "_id" : 7, "item" : "a1", type: "apparel", quantity: 250 } { "_id" : 8, "item" : "a2", type: "apparel", quantity: 400 } { "_id" : 9, "item" : "t2", type: "toys", quantity: 50 } { "_id" : 10, "item" : "f4", type: "food", quantity: 75 }
해당 문서는 MongoDB Compass에 다음과 같이 나타납니다.
인덱스가 없는 쿼리
다음 쿼리는 quantity 필드의 값이 100 ~ 200 사이인 문서를 검색합니다.
db.inventory.find( { quantity: { $gte: 100, $lte: 200 } } )
이 쿼리는 다음 문서를 반환합니다.
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "f2", "type" : "food", "quantity" : 100 } { "_id" : 3, "item" : "p1", "type" : "paper", "quantity" : 200 } { "_id" : 4, "item" : "p2", "type" : "paper", "quantity" : 150 }
선택한 쿼리 계획을 보려면 cursor.explain("executionStats") 커서 메서드를 find 명령의 끝에 연결합니다.
db.inventory.find( { quantity: { $gte: 100, $lte: 200 } } ).explain("executionStats")
explain() 이에 따라 다음과 같은 결과를 반환합니다:
{ queryPlanner: { ... winningPlan: { queryPlan: { stage: 'COLLSCAN', ... } } }, executionStats: { executionSuccess: true, nReturned: 3, executionTimeMillis: 0, totalKeysExamined: 0, totalDocsExamined: 10, executionStages: { stage: 'COLLSCAN', ... }, ... }, ... }
컬렉션 스캔을 나타내기 위해
queryPlanner.winningPlan.queryPlan.stage에서COLLSCAN을 표시합니다.컬렉션 스캔은
mongod가 결과를 식별하기 위해 전체 컬렉션 문서를 문서별로 스캔해야 함을 나타냅니다. 이 작업은 일반적으로 비용이 많이 드는 작업이며 쿼리 속도가 느려질 수 있습니다.executionStats.nReturned은(는)3을(를) 표시하여 우승한 쿼리 계획이 3개의 문서를 반환한다는 것을 나타냅니다.executionStats.totalKeysExamined가0을 표시하여 이 쿼리가 인덱스를 사용하지 않음을 나타냅니다.executionStats.totalDocsExamined가10을 표시하여 MongoDB가 일치하는 3개의 문서를 찾기 위해 10개의 문서(즉, 컬렉션의 모든 문서 스캔)를 스캔해야 함을 나타냅니다.
다음 쿼리는 quantity 필드의 값이 100 ~ 200 사이인 문서를 검색합니다.
다음 필터를 Compass 쿼리 표시줄에 복사하고 Find를 클릭합니다.
{ quantity: { $gte: 100, $lte: 200 } }
이 쿼리는 다음 문서를 반환합니다.
선택한 쿼리 계획을 보려면 다음을 수행하세요.
test.inventorycollection의 Explain Plan 탭을 클릭합니다.Explain를 클릭합니다.
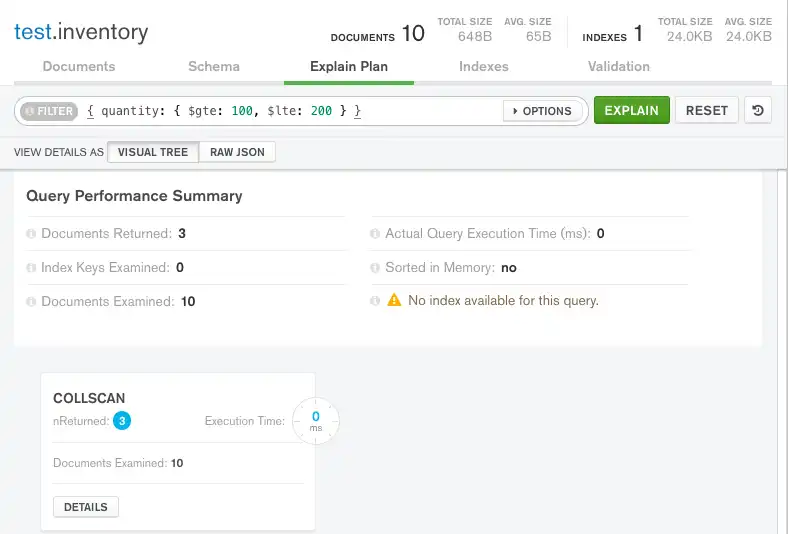
MongoDB Compass는 다음과 같이 쿼리 계획을 표시합니다.
참고
이 튜토리얼에서는 매우 작은 데이터 세트를 사용하기 때문에 인덱스를 사용하지 않더라도 Actual Query Execution Time은 0초를 표시합니다.
더 큰 데이터 세트에서는 인덱싱된 쿼리와 인덱싱되지 않은 쿼리 간의 쿼리 실행 시간 차이가 훨씬 클 것입니다.
시각적 트리
Query Performance Summary은(는) 쿼리의 실행 통계를 보여줍니다.
Documents Returned 성공적인 쿼리 계획이 세 개의 문서를 반환한다는 것을 나타내기 위해
3을 표시합니다.Index Keys Examined
0을 표시하여 이 쿼리가 인덱스를 사용하지 않음을 나타냅니다.Documents Examined 은
10을 표시합니다. 이는 MongoDB가 세 개의 일치하는 문서를 찾기 위해 컬렉션의 모든 문서인 열 개의 문서를 스캔해야 했음을 나타냅니다.
Query Performance Summary 아래에 MongoDB Compass는
COLLSCAN쿼리 단계를 표시하여 이 쿼리에 컬렉션 스캔이 사용되었음을 나타냅니다.컬렉션 스캔은
mongod가 결과를 식별하기 위해 전체 컬렉션 문서를 문서별로 스캔해야 함을 나타냅니다. 이 작업은 일반적으로 비용이 많이 드는 작업이며 쿼리 속도가 느려질 수 있습니다.
Raw JSON
쿼리 표시줄 아래의 Raw JSON을 클릭하여 원시 JSON 형식으로 설명 세부 정보를 볼 수도 있습니다.
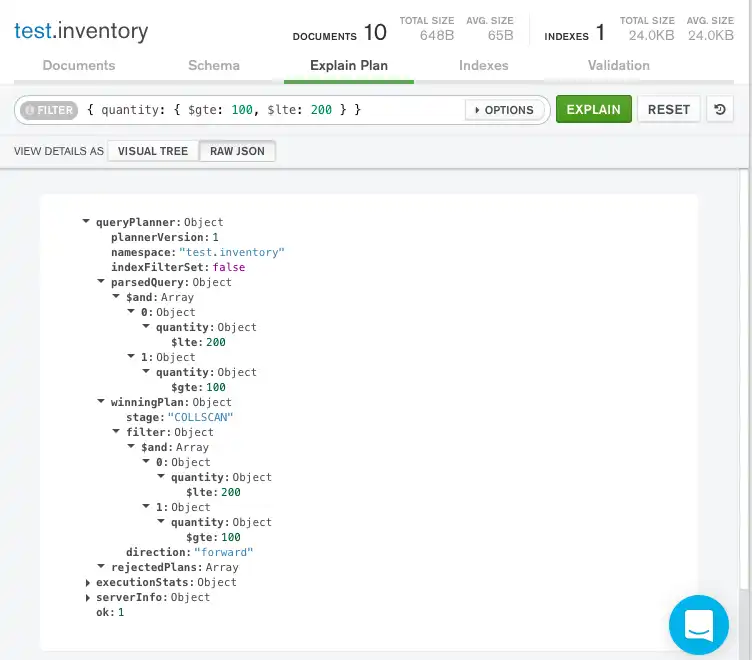
일치하는 문서 수와 검토된 문서 수의 차이는 효율성을 높이기 위해 쿼리에 인덱스를 사용하는 것이 도움이 될 수 있음을 시사할 수 있습니다.
인덱스가 있는 쿼리
quantity 필드에 대한 쿼리를 지원하려면 quantity 필드에 인덱스를 추가합니다.
db.inventory.createIndex( { quantity: 1 } )
쿼리 계획 통계를 보려면 explain() 메서드를 사용합니다.
db.inventory.find( { quantity: { $gte: 100, $lte: 200 } } ).explain("executionStats")
explain() 메서드는 다음 결과를 반환합니다.
{ queryPlanner: { ... winningPlan: { queryPlan: { stage: 'FETCH', inputStage: { stage: 'IXSCAN', keyPattern: { quantity: 1 }, ... } } }, rejectedPlans: [ ] }, executionStats: { executionSuccess: true, nReturned: 3, executionTimeMillis: 0, totalKeysExamined: 3, totalDocsExamined: 3, executionStages: { ... }, ... }, ... }
queryPlanner.winningPlan.queryPlan.inputStage.stage가IXSCAN을 표시해 인덱스를 사용함을 나타냅니다.executionStats.nReturned은(는)3을(를) 표시하여 우승한 쿼리 계획이 3개의 문서를 반환한다는 것을 나타냅니다.executionStats.totalKeysExamined가3을 표시해 MongoDB가 세 개의 인덱스 항목을 스캔했음을 나타냅니다. 검사한 키의 수는 반환된 문서 수와 일치합니다. 즉,mongod함수가 결과를 반환하기 위해 인덱스 키만을 검색했음을나타냅니다.mongod는 모든 문서를 스캔할 필요가 없었고 일치하는 문서 3개만을 메모리로 가져왔습니다. 그 결과 매우 효율적인 쿼리가 생성됩니다.executionStats.totalDocsExamined는3을 표시해 MongoDB가 문서 3개를 스캔했음을 나타냅니다.
test.inventorycollection의 Indexes 탭을 클릭합니다.Create Index를 클릭합니다.
Select a field name 드롭다운 메뉴에서
quantity을(를) 선택합니다.유형 드롭다운 메뉴에서
1 (asc)를 선택합니다.Create를 클릭합니다.
참고
인덱스 이름 필드를 비워두면 MongoDB Compass가 인덱스에 기본 이름을 생성합니다.
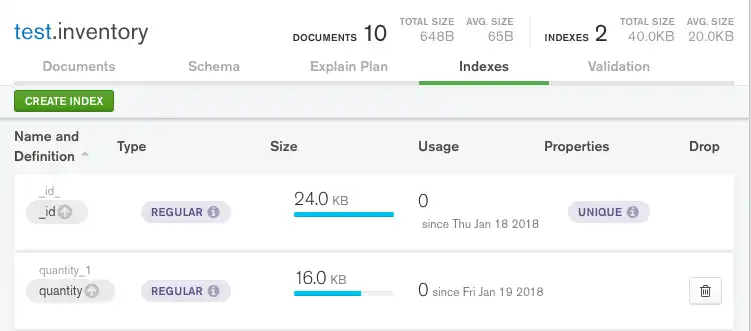
이제 Indexes 탭에서 새로 만든 인덱스를 볼 수 있습니다.
inventory 컬렉션에 대한 Explain Plan 탭으로 돌아가서 이전 단계의 쿼리를 다시 실행합니다.
{ quantity: { $gte: 100, $lte: 200 } }
MongoDB Compass는 다음과 같이 쿼리 계획을 표시합니다.
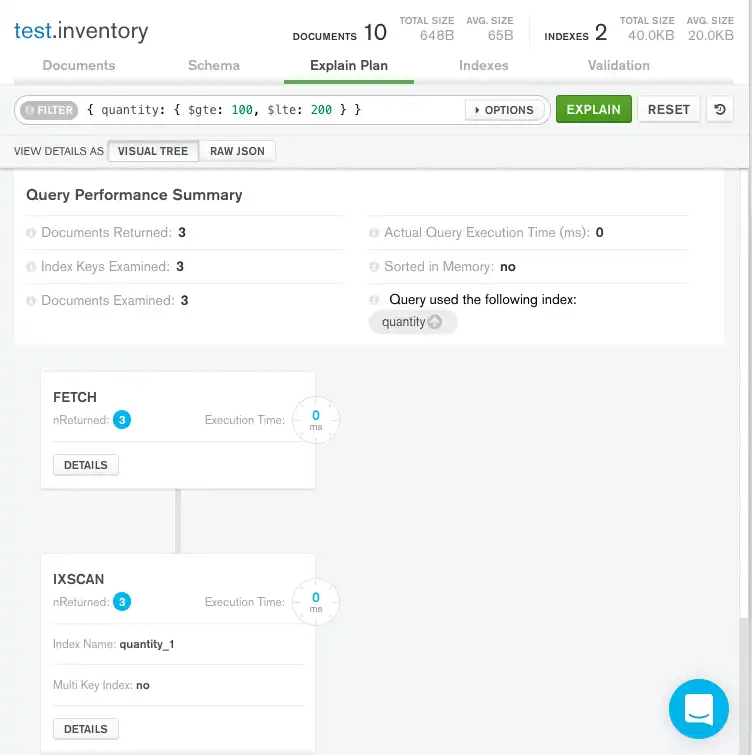
시각적 트리
Query Performance Summary은(는) 쿼리의 실행 통계를 보여줍니다.
Documents Returned 성공적인 쿼리 계획이 세 개의 문서를 반환한다는 것을 나타내기 위해
3을 표시합니다.Index Keys Examined 는
3을 표시하여 MongoDB가 세 개의 인덱스 항목을 스캔했음을 나타냅니다. 검사한 키의 수는 반환된 문서 수와 일치합니다. 즉,mongod는 결과를 반환하기 위해 인덱스 키만을 검색했습니다.mongod는 모든 문서를 스캔할 필요가 없었고 일치하는 문서 3개만을 메모리로 가져왔습니다. 그 결과 매우 효율적인 쿼리가 생성됩니다.Documents Examined
3을 표시하면 MongoDB가 세 개의 문서를 스캔했음을 나타냅니다.Query Performance Summary의 오른쪽에서 MongoDB Compass는 쿼리가
quantity인덱스를 사용했음을 보여줍니다.
Query Performance Summary 아래에서 MongoDB Compass는 쿼리 단계인
FETCH와IXSCAN을 표시합니다.IXSCAN은mongod가FETCH단계를 실행하고 문서를 검색하기 전에 쿼리를 만족시키기 위해 인덱스를 사용했음을 나타냅니다.
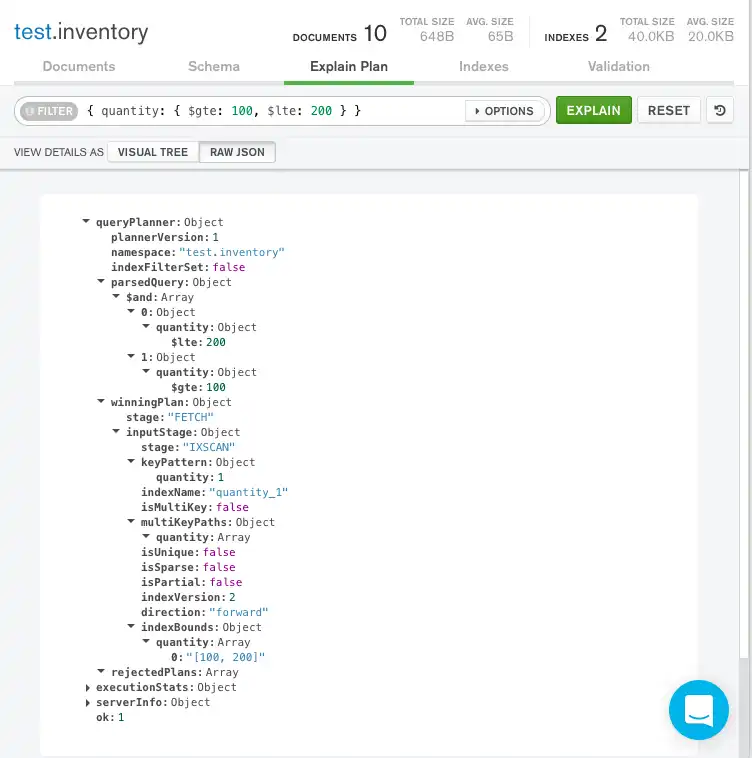
Raw JSON
쿼리 표시줄 아래의 Raw JSON을 클릭하여 원시 JSON 형식으로 설명 세부 정보를 볼 수도 있습니다.
인덱스가 없으면 쿼리는 10개 문서의 전체 컬렉션을 스캔하여 3개의 일치하는 문서를 반환합니다. 또한 쿼리는 각 문서 전체를 스캔하여 잠재적으로 해당 문서를 메모리로 가져와야 했습니다. 이로 인해 비용이 많이 들고 쿼리 작업이 느려질 수 있습니다.
인덱스를 사용하여 쿼리를 실행하면 3개의 인덱스 항목과 3개의 문서를 스캔하여 3개의 일치하는 문서를 반환하므로 매우 효율적인 쿼리가 됩니다.