Automatic Encryption
On this page
MongoDB supports automatically encrypting fields in read and write
operations when using Client-Side Field Level Encryption. You can perform automatic encryption
using mongosh and official MongoDB drivers which are
compatible with version 4.2 and later. For a complete list of official
compatible drivers with support for CSFLE, see Driver
Compatibility Compatibility.
How Encrypted Writes and Reads Work
The following diagrams show how the client application and driver write and read field-level encrypted data.
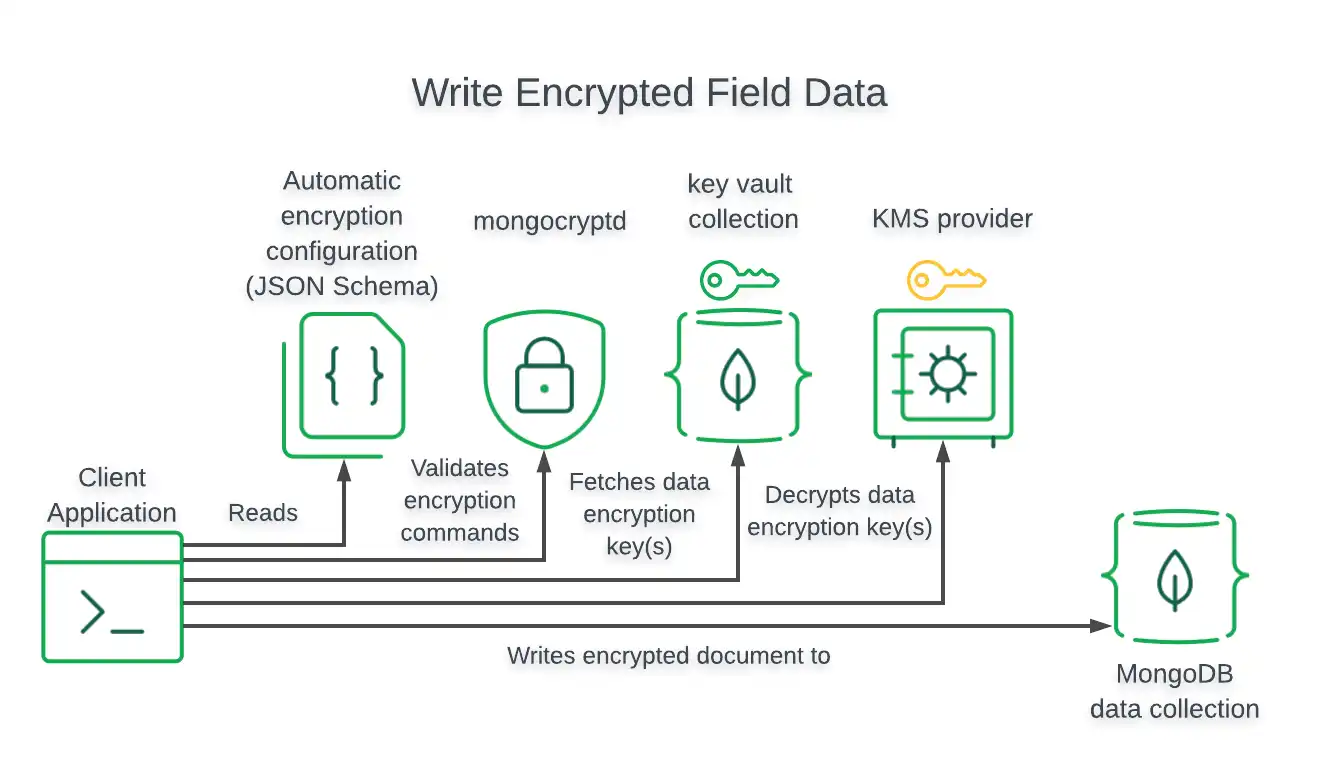
Encrypted Writes
For write operations, the driver encrypts field values prior to writing to the MongoDB database.
The following diagram shows the steps taken by the client application and driver to perform a write of field-level encrypted data:
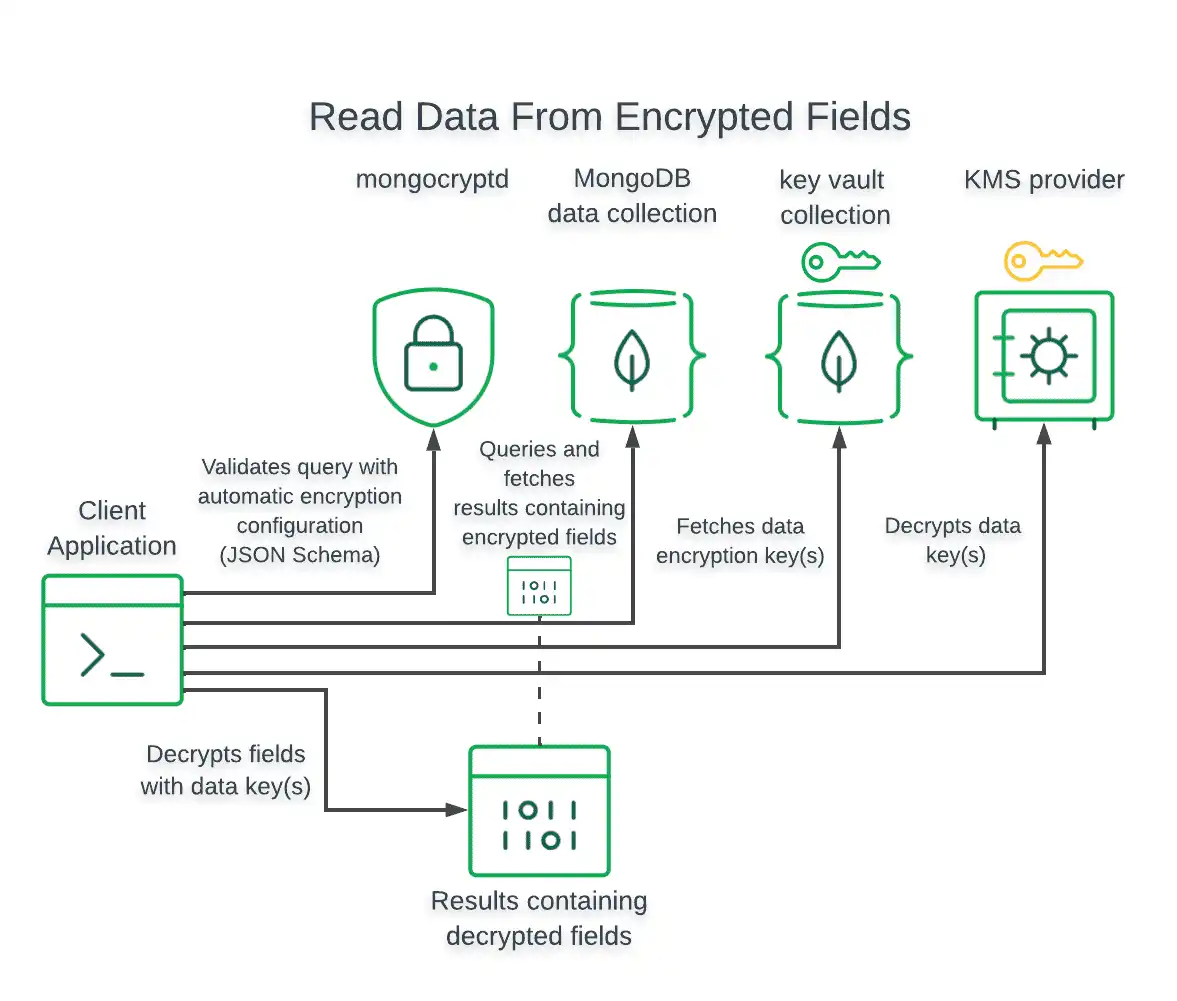
Encrypted Reads
For read operations, the driver encrypts field values in the query prior to issuing the read operation.
For read operations that return encrypted fields, the driver automatically decrypts the encrypted values only if the driver was configured with access to the Customer Master Key (CMK) and Data Encryption Keys (DEK) used to encrypt those values.
The following diagram shows the steps taken by the client application and driver to query and decrypt field-level encrypted data:
Enabling Automatic Client-Side Field Level Encryption
To enable automatic encryption, specify automatic encryption settings in
your client's MongoClient instance.
The following code snippets show how to create a client with automatic
encryption enabled in mongosh and MongoDB drivers:
var autoEncryptionOpts = { "keyVaultNamespace" : "<database>.<collection>", "kmsProviders" : { ... }, "schemaMap" : { ... } } cluster = Mongo( "<Your Connection String>", autoEncryptionOpts );
var clientSettings = MongoClientSettings.FromConnectionString(_connectionString); var autoEncryptionOptions = new AutoEncryptionOptions( keyVaultNamespace: keyVaultNamespace, kmsProviders: kmsProviders, schemaMap: schemaMap, extraOptions: extraOptions); clientSettings.AutoEncryptionOptions = autoEncryptionOptions; var client = new MongoClient(clientSettings);
autoEncryptionOpts := options.AutoEncryption(). SetKmsProviders(provider.Credentials()). SetKeyVaultNamespace(keyVaultNamespace). SetSchemaMap(schemaMap). SetExtraOptions(extraOptions) client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), options.Client().ApplyURI(uri).SetAutoEncryptionOptions(autoEncryptionOpts))
MongoClientSettings clientSettings = MongoClientSettings.builder() .applyConnectionString(new ConnectionString("mongodb://localhost:27017")) .autoEncryptionSettings(AutoEncryptionSettings.builder() .keyVaultNamespace(keyVaultNamespace) .kmsProviders(kmsProviders) .schemaMap(schemaMap) .extraOptions(extraOptions) .build()) .build(); MongoClient mongoClient = MongoClients.create(clientSettings);
const secureClient = new MongoClient(connectionString, { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true, monitorCommands: true, autoEncryption: { keyVaultNamespace, kmsProviders, schemaMap: patientSchema, extraOptions: extraOptions, }, });
fle_opts = AutoEncryptionOpts( kms_providers, key_vault_namespace, schema_map=patient_schema, **extra_options ) client = MongoClient(connection_string, auto_encryption_opts=fle_opts)
For more information on CSFLE-specific MongoClient settings,
see CSFLE-Specific MongoClient Options.
Server-Side Field Level Encryption Enforcement
MongoDB supports using schema validation to enforce encryption of specific fields in a collection. Clients performing automatic Client-Side Field Level Encryption have specific behavior depending on the database connection configuration:
If the connection autoEncryptionOpts
schemaMapobject contains a key for the specified collection, the client uses that object to perform automatic field level encryption and ignores the remote schema. At minimum, the local rules must encrypt those fields that the remote schema marks as requiring encryption.If the connection autoEncryptionOpts
schemaMapobject does not contain a key for the specified collection, the client downloads the server-side remote schema for the collection and uses it to perform automatic field level encryption.Important
Behavior Considerations
When
autoEncryptionOptsdoes not contain a key for the specified collection:The client trusts that the server has a valid schema with respect to automatic field level encryption.
The client uses the remote schema to perform automatic CSFLE only. The client does not enforce any other validation rules specified in the schema.
To learn how to set up server-side CSFLE enforcement, see Server-Side Schema Enforcement.