Technology stack
Before diving into the MERN stack, let's quickly understand what a technology stack is. A technology stack is a set of technologies you choose and use to build a web application, mobile application or similar applications. A good technology stack must give a seamless user experience as well as be scalable and cost-effective. A typical tech stack contains a frontend, backend and database and is known as a full technology stack.
Usually, the basic front-end or user interface technologies remain the same, i.e., HTML, CSS and JavaScript. Depending on the project requirements, you can use libraries and frameworks, like React or Angular, that are built upon these UI technologies.
Back-end consists of a server, where your application logic resides. You can write the application logic in one or more programming languages like JavaScript, Java, Python, or use frameworks like Django, Spring, Express.js. To execute the programs, your application needs a runtime like Node.js, JRE (Java Runtime Environment).
The database is the storage hub, where all the application related data is stored. You can choose to store your data in a tabular structure (using relational database systems), or using non-relational, also called NoSQL, such as document structure, graph structure and so on and select the database accordingly. Some examples of databases are MongoDB, Oracle, MySQL.
What is the MERN stack?
A technology stack can be custom (developers can choose the technologies depending on their project requirements) or pre-built (where the technologies have been pre-decided).
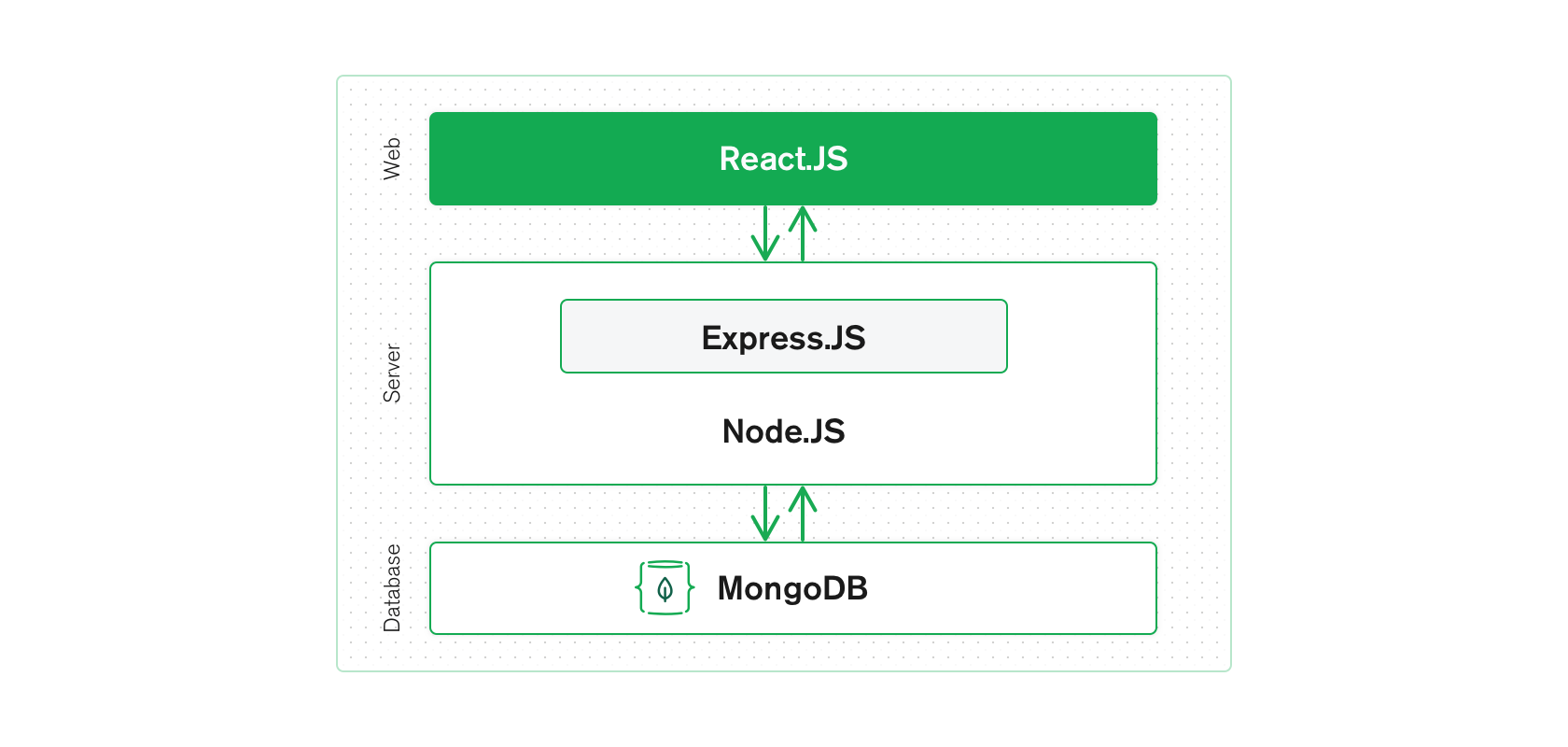
MERN is a pre-built technology stack based on JavaScript technologies. MERN stands for MongoDB, Express, React, and Node, after the four key technologies that make up the stack.
- MongoDB — document database
- Express(.js) — Node.js web framework
- React(.js) — a client-side JavaScript framework
- Node(.js) — the premier JavaScript web server (runtime)
Express and Node make up the middle (application) tier. Express.js is a server-side web framework, and Node.js is the popular and powerful JavaScript server platform. Regardless of which variant you choose, ME(RVA)N is the ideal approach to working with JavaScript and JSON, all the way through.
How does the MERN stack work?
The MERN architecture allows you to easily construct a three-tier architecture (front end, back end, database) entirely using JavaScript and JSON.
React.js front end
The top tier of the MERN stack is React.js, the declarative JavaScript framework for creating dynamic client-side applications in HTML. React lets you build complex interfaces through simple components, connect them to data on your back-end server, and render them as HTML.
React's strong suit is handling stateful, data-driven interfaces with minimal code and hassle, and it has all the features you'd expect from a modern web framework: great support for forms, error handling, events, lists, and more.
Express.js and Node.js server tier
The next level down is the Express.js server-side framework, running inside a Node.js server. Express.js bills itself as a “fast, unopinionated, minimalist web framework for Node.js,” and that is indeed exactly what it is. Express.js has powerful models for URL routing (matching an incoming URL with a server function), and handling HTTP requests and responses.
By making XML HTTP Requests (XHRs), GETs, or POSTs from your React.js front end, you can connect to Express.js functions that power your application. Those functions, in turn, use MongoDB's Node.js drivers, to access and update data in your MongoDB database.
MongoDB database tier
If your application stores any data (user profiles, content, comments, uploads, events, etc.), then you're going to want a database that's just as easy to work with as React, Express, and Node.js.
That's where MongoDB comes in: JSON documents created in your React.js front end can be sent to the Express.js server, where they can be processed and (assuming they're valid) stored directly in MongoDB for later retrieval. Again, if you're building in the cloud, you'll want to look at MongoDB Atlas. If you're looking to set up your own MERN stack, read on!
Example of a simple request/response using the MERN stack
A typical HTTP request (from a client) performs one of the 4 operations - POST, GET, PUT, DELETE corresponding to the four database operations - Create, Read, Update and Delete (CRUD) respectively. To cater to these requests, the Express.js provides request and response objects that store the required parameters. The HTTPrequest stores the data provided by the end user, and the HTTP response stores the data that is retrieved from the database.
With the MongoDB Node.js driver, you can easily connect your MongoDB deployments to the application in a few simple steps.
One of the most important features of MERN stack is that all the technologies store data in the same format.
The front-end layer, React, stores data as a JavaScript object, the backend (application) layer uses JavaScript code, and the data layer MongoDB stores data in BSON (Binary JavaScript ON) format. Express converts data between JS and JSON using the .json() method.
Node.js allows developers to write backend (server-side) application logic in JavaScript. Although Node.js provides core http modules, writing the same in Express provides a cleaner code experience. Express also provides powerful routing features to get the required data from the correct endpoint - another place where developers need not write explicit code for routing.
Since the code is written in the same language (JavaScript) from end-to-end, a lot of time that would otherwise go in conversions during transition from layer to layer, is saved.
Let us say a customer (client) wants to update his mobile number through an online portal. The frontend, built using React.js, would have a form where the user can enter the mobile number. React uses the "useState" hook to set the mobile number entered by the customer into the request parameter.
The Express.js code takes the mobile number from the http put request, maps it to the data model schema of the application, and applies the corresponding method (for example, findByIdAndUpdate()) to perform the update operation. The response is then sent over the http response object with a success/failure message.
A complete example is available on the MERN stack tutorial page.
MERN stack vs Full stack development
MERN stack is a type of full stack, where the technology layers are pre-defined. A full stack developer has a higher learning curve, as they need to be adept in multiple technologies, whereas a MERN stack developer needs to know only the corresponding technologies. Some prominent differences below will help you choose between a custom full stack and MERN stack, depending on your project requirements: