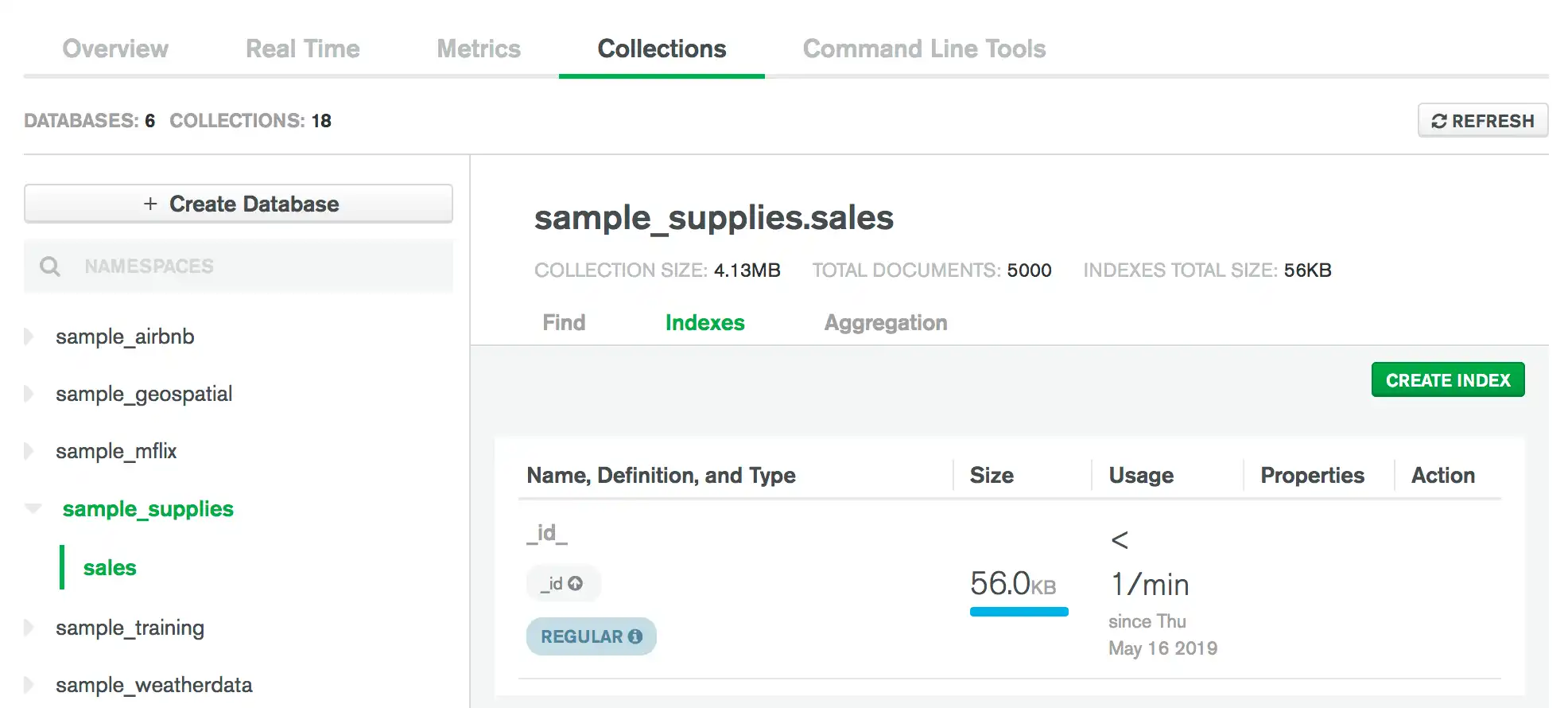
Você pode usar o Data Explorer para managed índices em suas collection.
Para interagir com dados na UI do Ops Manager:
Clique em Deployment na navegação à esquerda.
Selecione a implantação do MongoDB desejada.
Selecione a guia Data.
Funções obrigatórias
Para criar ou soltar índices, você deve ter acesso fornecido por pelo menos uma das seguintes funções:
Considerações
Por padrão, você pode ter até três construções de índice não contínuas simultâneas. Para saber mais, consulte Máximo de compilações simultâneas de índice.
Se você escolher construir índices de forma contínua, deve assegurar o seguinte:
Importante
A criação de um índice de forma contínua reduz a resiliência do cluster e aumenta o tempo de criação do índice. Recomendamos usar o uso de compilações de índice contínuo apenas quando as compilações de índice regulares não atenderem às suas necessidades.
Solicite construções de índice contínuas e não contínuas sequencialmente e não simultaneamente. Aguarde a conclusão de uma construção de índice em execução antes de solicitar outra construção de índice.
Se você precisar solicitar várias construções de índice contínuos, aguarde a conclusão da construção de índice contínuo em execução antes de solicitar outra construção de índice contínuo.
Para acompanhar a construção contínua de índices, veja o feed de atividades.
Para compilações de índices contínuos abortadas, você deve executar listIndexes em cada nó para verificar se o índice cancelado não existe mais. Caso contrário, o cluster pode permanecer em um estado inconsistente.
Visualizar índices
Na aba Collections, você pode visualizar informações de índice para uma coleção. Para visualizar as informações de índice de uma coleção:
Crie um índice
Dica
Ao criar índices, tenha em mente a proporção de leituras e gravações na collection de destino. Os índices têm um custo de desempenho, mas valem mais do que o custo para queries frequentes em grandes conjuntos de dados. Para saber mais sobre estratégias de indexação, consulte Estratégias de indexação.
Para criar um índice para uma collection através do Data Explorer:
Clique em Create Index.
No modal Create Index , insira o documento index key specification na caixa Fields :
{ <field1>: <index type>, ... }
Exemplo
Para criar um índice composto nos campos category (ordem crescente) e score (ordem decrescente), especifique o documento de especificação do índice:
{ category: 1, score: -1 }
Para obter mais informações sobre índices, consulte Índices.
(Opcional) Especifique as opções de índice.
{ <option1>: <value1>, ... }
Exemplo
Para definir a opção unique e um name para o novo índice, insira este documento:
{ unique: true, name: "myUniqueIndex" }
(Opcional) Defina as opções de Agrupamento.
O agrupamento permite que os usuários especifiquem regras específicas do idioma para comparação de strings, como regras para letras maiúsculas e acentos. O documento de agrupamento contém um campo locale que indica o código de localidade do ICUe pode conter outros campos para definir o comportamento do agrupamento.
Exemplo
O documento de opção de agrupamento a seguir especifica um valor de localidade de fr para um agrupamento de idioma francês:
{ "locale": "fr" }
Para revisar a lista de localidades suportadas pelo agrupamento do MongoDB, consulte a lista de idiomas e localidades. Para saber mais sobre as opções de compilação, incluindo quais estão habilitadas por padrão para cada localidade, consulte Agrupamento no manual do MongoDB.
(Opcional) Construa índices com compilações contínuas.
Aviso
Devido ao problema crítico SERVER-68925, as implantações do Ops Manager que usam certas versões do MongoDB Agent não devem executar compilações automatizadas de índice contínuo em clusters que executem as seguintes versões do MongoDB:
MongoDB 4.2.19-4.2.22
MongoDB 4.4.13-4.4.16
MongoDB 5.0.6-5.0.11
MongoDB 6.0.0-6.0.1
Você pode continuar a executar construções de índices contínuas manuais com segurança em seus clusters. Para executar construções contínuas e automatizadas de índices com segurança, atualize o MongoDB Agent para 12.0.11.7606 ou posterior ou atualize seus clusters para:
MongoDB 4.2.23 ou posterior
MongoDB 4.4.17 ou posterior
MongoDB 5.0.12 ou posterior
MongoDB 6.0.2 ou posterior
Importante
A criação de um índice de forma contínua reduz a resiliência do cluster e aumenta o tempo de criação do índice. Recomendamos usar o uso de compilações de índice contínuo apenas quando as compilações de índice regulares não atenderem às suas necessidades.
Considere que os índices contínuos devem atender a certas condições para serem bem-sucedidos. Para garantir que a criação do índice seja bem-sucedida, evite os seguintes padrões de design que geralmente acionam um loop de reinicialização:
A chave de índice excede o limite da chave de índice
O nome do índice já existe
Índice em mais de um campo de array
Índice na coleção que tem o número máximo de índices de texto
Índice de texto na coleção que tem o número máximo de índices de texto
Observação
O Data Explorer não oferece suporte à criação de índices de forma contínua para sistemas autônomos.
A construção de índices de forma contínua reduz o impacto no desempenho da construção de índices em conjuntos de réplicas e clusters fragmentados. Para manter a disponibilidade do cluster, o Ops Manager remove um nó do cluster de cada vez, começando com um secundário.
Depois de criar um índice de forma contínua, se o banco de MongoDB database for executado com um FCV menor que 4.2, ressincronize o banco de dados head para garantir que o banco de dados head leve em consideração o novo índice.
O Ops Manager cancela automaticamente a criação de índices contínuos que não são bem-sucedidos em todos os nós. Quando uma compilação de índice contínuo é concluída em alguns nós, mas falha em outros, o Ops Manager cancela a compilação e remove o índice de todos os nós nos quais foi criado com êxito.
No caso de um cancelamento de compilação de índice contínuo, o Ops Manager gera um evento de feed de atividade e envia um e-mail de notificação ao proprietário do projeto com as seguintes informações:
Nome do cluster no qual a criação do índice contínuo falhou
Namespace no qual a construção do índice contínuo falhou
Projeto que contém o cluster e o namespace
Organização que contém o projeto
Link para o evento da lista de atividades
Para saber mais sobre a reconstrução de índices, consulte Construir índices em conjuntos de réplicas.
Observação
As seguintes opções de índice são incompatíveis com a construção de índices de forma contínua:
O Ops Manager ignora estas opções se você especificá-las no painel Options.
Descarte um índice
Para descartar um índice de uma collection pelo Data Explorer:
Observação
Você não pode excluir o índice _id .