GridFS
On this page
Overview
In this guide, you can learn how to store and retrieve large files in MongoDB using the GridFS specification. GridFS splits large files into chunks and stores each chunk as a separate document. When you query GridFS for a file, the driver assembles the chunks as necessary. The driver implementation of GridFS is an abstraction that manages the operations and organization of the file storage.
Use GridFS if the size of your files exceeds the BSON document size limit of 16 MB. GridFS also helps you access files without loading the entire file into memory. To learn more about whether GridFS is suitable for your use case, see GridFS in the Server manual.
How GridFS Works
GridFS organizes files in a bucket, a group of MongoDB collections that contain the chunks of files and information describing them. The bucket contains the following collections:
chunks, which stores the binary file chunksfiles, which stores the file metadata
When you create a new GridFS bucket, the driver creates the preceding
collections. The default bucket name fs prefixes the collection names,
unless you specify a different bucket name. The driver creates the new GridFS
bucket during the first write operation.
The driver also creates an index on each collection to ensure efficient retrieval of the files and related metadata. The driver creates indexes if they do not already exist and when the bucket is empty. To learn more about GridFS indexes, see GridFS Indexes in the Server manual.
When storing files with GridFS, the driver splits the files into smaller
chunks, each represented by a separate document in the chunks collection.
It also creates a document in the files collection that contains
a file ID, file name, and other file metadata. The following diagram shows
how GridFS splits the uploaded files:
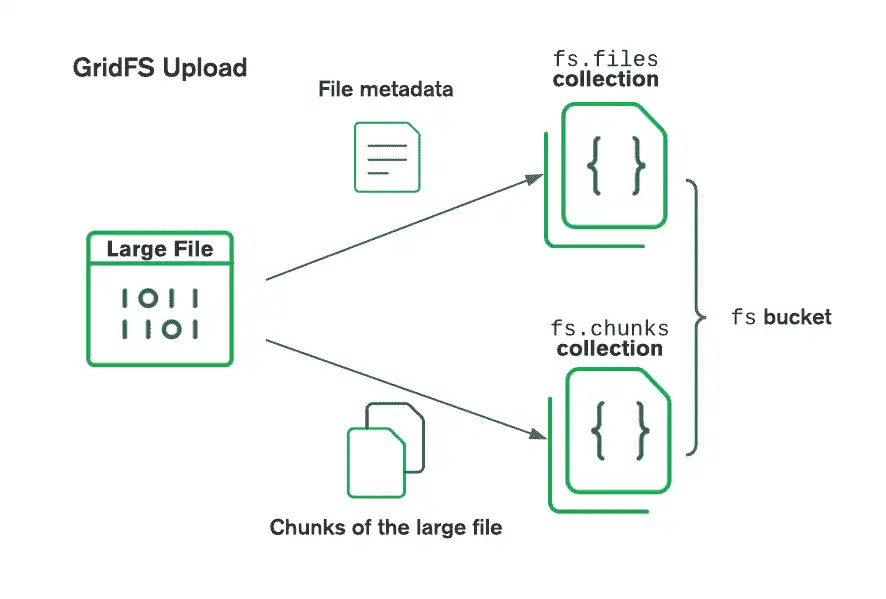
When retrieving files, GridFS fetches the metadata from the files
collection in the specified bucket then uses that information to reconstruct
the file from documents in the chunks collection. You can read the file
into memory or output it to a stream.
GridFS Operations
The following sections describe how to perform GridFS operations:
Create a GridFS Bucket
To store or retrieve files from GridFS, create a bucket or get a reference to
an existing bucket on a MongoDB database. To create a GridFSBucket instance,
call the GridFSBucket() method on a Database instance, as shown
in the following code:
db := client.Database("myDB") bucket := db.GridFSBucket()
Note
If a GridFS bucket already exists, the GridFSBucket() method returns a
reference to the bucket rather than instantiating a new one.
By default, the driver sets the name of the bucket to fs. To
create a bucket with a custom name, call the SetName() method
on a BucketOptions instance, as shown in the following code:
db := client.Database("myDB") bucketOpts := options.GridFSBucket().SetName("myCustomBucket") bucket := db.GridFSBucket(bucketOpts)
Upload Files
You can upload a file into a GridFS bucket by using one of the following methods:
UploadFromStream(), which reads from an input streamOpenUploadStream(), which writes to an output stream
For either upload process, you can specify configuration information by creating
an UploadOptions instance. To view a full list of options, see the
UploadOptions API documentation.
Upload with an Input Stream
To upload a file with an input stream, use the UploadFromStream() method
and include the following parameters:
File name
io.Readerinstance, including your opened file as a parameteroptsparameter to modify the behavior ofUploadFromStream()
The following code example reads from a file called file.txt,
creates an opts parameter to set file metadata, and uploads the
content to a GridFS bucket:
file, err := os.Open("home/documents/file.txt") uploadOpts := options.GridFSUpload().SetMetadata(bson.D{{"metadata tag", "first"}}) objectID, err := bucket .UploadFromStream( "file.txt", io.Reader(file), uploadOpts ) if err != nil { panic(err) } fmt.Printf("New file uploaded with ID %s", objectID)
New file uploaded with ID ...
Upload with an Output Stream
To upload a file with an output stream, use the OpenUploadStream() method
and include the following parameters:
File name
optsparameter to modify the behavior ofOpenUploadStream()
The following code example opens an upload stream on a GridFS bucket and sets
the number of bytes in each chunk in the options parameter. Then, it calls
the Write() method on the content of file.txt to write its content to
the stream:
file, err := os.Open("home/documents/file.txt") if err != nil { panic(err) } // Defines options that specify configuration information for files // uploaded to the bucket uploadOpts := options.GridFSUpload().SetChunkSizeBytes(200000) // Writes a file to an output stream uploadStream, err := bucket.OpenUploadStream("file.txt", uploadOpts) if err != nil { panic(err) } fileContent, err := io.ReadAll(file) if err != nil { panic(err) } var bytes int if bytes, err = uploadStream.Write(fileContent); err != nil { panic(err) } fmt.Printf("New file uploaded with %d bytes written", bytes) // Calls the Close() method to write file metadata if err := uploadStream.Close(); err != nil { panic(err) }
Retrieve File Information
You can retrieve file metadata stored in the files collection of the GridFS
bucket. Each document in the files collection contains the following
pieces of information:
File ID
File length
Maximum chunk size
Upload date and time
File name
metadatadocument that stores any other information
To retrieve file data, call the Find() method on a GridFSBucket
instance. You can pass a query filter as an argument to Find() to match
only certain file documents.
Note
You must pass a query filter to the Find() method. To retrieve all
documents in the files collection, pass an empty query filter to Find().
The following example retrieves the file name and length of documents in
which the length value is greater than 1500:
filter := bson.D{{"length", bson.D{{"$gt", 1500}}}} cursor, err := bucket.Find(filter) if err != nil { panic(err) } type gridFSFile struct { Name string `bson:"filename"` Length int64 `bson:"length"` } var foundFiles []gridFSFile if err = cursor.All(context.TODO(), &foundFiles); err != nil { panic(err) } for _, file := range foundFiles { fmt.Printf("filename: %s, length: %d\n", file.Name, file.Length) }
Download Files
You can download a GridFS file by using one of the following methods:
DownloadToStream(), which downloads a file to an output streamOpenDownloadStream(), which opens an input stream
Download a File to an Output Stream
You can download a file in a GridFS bucket directly to an output stream
by using the DownloadToStream() method. The DownloadToStream()
method takes a file ID and an io.Writer instance as parameters. The
method downloads the file with the specified file ID and writes it to the
io.Writer instance.
The following example downloads a file and writes to a file buffer:
id, err := primitive.ObjectIDFromHex("62f7bd54a6e4452da13b3e88") fileBuffer := bytes.NewBuffer(nil) if _, err := bucket.DownloadToStream(id, fileBuffer); err != nil { panic(err) }
Download a File to an Input Stream
You can download a file in a GridFS bucket to memory with an input
stream by using the OpenDownloadStream() method. The
OpenDownloadStream() method takes a file ID as a parameter and
returns an input stream from which you can read the file.
The following example downloads a file into memory and reads its contents:
id, err := primitive.ObjectIDFromHex("62f7bd54a6e4452da13b3e88") downloadStream, err := bucket.OpenDownloadStream(id) if err != nil { panic(err) } fileBytes := make([]byte, 1024) if _, err := downloadStream.Read(fileBytes); err != nil { panic(err) }
Rename Files
You can update the name of a GridFS file in your bucket by using the Rename()
method. Pass a file ID value and a new filename value as arguments to
Rename().
The following example renames a file to "mongodbTutorial.zip":
id, err := primitive.ObjectIDFromHex("62f7bd54a6e4452da13b3e88") if err := bucket.Rename(id, "mongodbTutorial.zip"); err != nil { panic(err) }
Delete Files
You can remove a file from your GridFS bucket by using the Delete() method.
Pass a file ID value as an argument to Delete().
The following example deletes a file:
id, err := primitive.ObjectIDFromHex("62f7bd54a6e4452da13b3e88") if err := bucket.Delete(id); err != nil { panic(err) }
Delete a GridFS Bucket
You can delete a GridFS bucket by using the Drop() method.
The following code example removes a GridFS bucket:
if err := bucket.Drop(); err != nil { panic(err) }
Additional Resources
To learn more about GridFS and storage, see the following pages in the Server manual:
API Documentation
To learn more about the methods and types mentioned in this guide, see the following API documentation: