Docs Home → Develop Applications → MongoDB Drivers → Node.js
Quick Start
On this page
This guide shows you how to create an application that uses the MongoDB Node.js driver to connect to a MongoDB cluster hosted on MongoDB Atlas. If you prefer to connect to MongoDB using a different driver or programming language, see our list of official drivers.
The Node.js driver is a library you can use to connect to and communicate with MongoDB.
MongoDB Atlas is a fully managed cloud database service that hosts your MongoDB servers. You can get started with your own free (no credit card required) MongoDB instance with this guide.
Follow the steps below to connect a sample Node.js application to a MongoDB instance on MongoDB Atlas.
Set up Your Project
Install Node and npm
Ensure you have Node.js v12 or later and npm (Node Package Manager) installed in your development environment.
For information on how to install Node.js and npm, see downloading and installing Node.js and npm.
Create the Project
First, in your shell, create a directory for your project:
mkdir node_quickstart
Then, navigate into that directory:
cd node_quickstart
Next, initialize your project:
npm init -y
Add MongoDB as a Dependency
Install the Node.js driver:
npm install mongodb@3.7
This command performs the following actions:
Downloads the
mongodbpackage and the dependencies it requiresSaves the package in the
node_modulesdirectoryRecords the dependency information in the
package.jsonfile
At this point, you are ready to use the Node.js driver with your application.
Create a MongoDB Cluster
Create a Free Tier Cluster in Atlas
Create a free tier MongoDB cluster on MongoDB Atlas to store and manage your data. MongoDB Atlas hosts and manages your MongoDB database in the cloud. Complete the Get Started with Atlas guide to set up a new Atlas account, a free tier cluster (a shared MongoDB instance) and load sample data into your cluster.
Connect to your Cluster
You can connect to your MongoDB cluster by providing a connection string which instructs the driver on where and how to connect. The connection string includes information on the hostname or IP address and port of your cluster, the authentication mechanism, user credentials when applicable, and other connection options.
To connect to an instance or cluster not hosted on Atlas, see Other Ways to Connect to MongoDB.
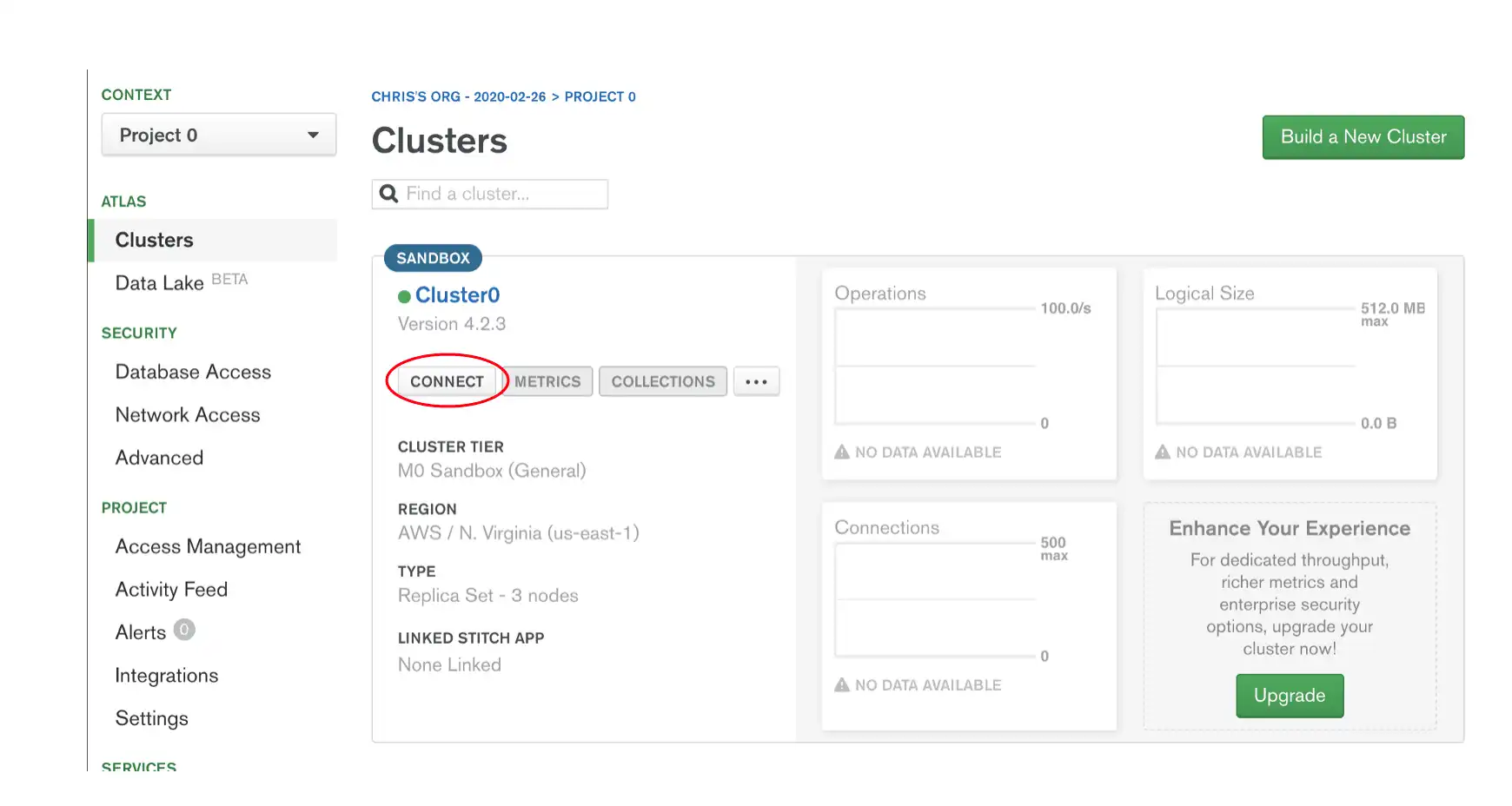
To retrieve your connection string for the cluster you created in the previous step, log into your Atlas account and navigate to the Database section and click the Connect button for the cluster that you want to connect to as shown below.
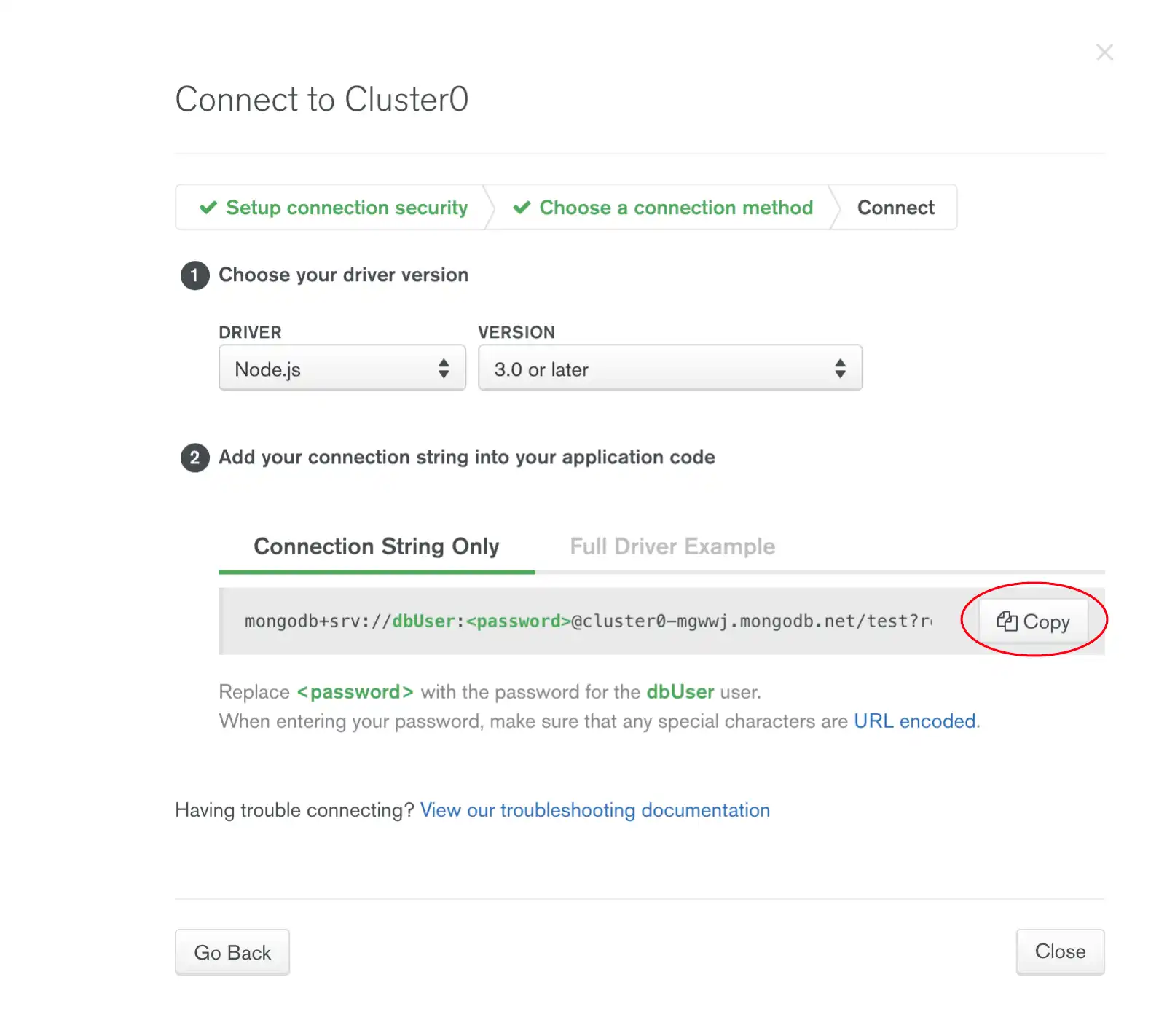
Proceed to the Connect Your Application section and select the Node.js driver. Select the Connection String Only tab and click the Copy button to copy the connection string to your clipboard as shown below.
Save your connection string to a safe location.
Connect to Your Application
Create your Node.js Application
Create a file to contain your application called index.js in your
project directory. Add the following code, assigning the uri
variable the value of your connection string.
const { MongoClient } = require("mongodb"); // Replace the uri string with your connection string. const uri = "mongodb+srv://<user>:<password>@<cluster-url>?retryWrites=true&writeConcern=majority"; const client = new MongoClient(uri, { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true, }); async function run() { try { await client.connect(); const database = client.db('sample_mflix'); const movies = database.collection('movies'); // Query for a movie that has the title 'Back to the Future' const query = { title: 'Back to the Future' }; const movie = await movies.findOne(query); console.log(movie); } finally { // Ensures that the client will close when you finish/error await client.close(); } } run().catch(console.dir);
Tip
The preceding code example assigns the MongoClient variable using
object destructuring,
introduced in Node.js v6. You can create an instance of a
MongoClient without using object destructuring as shown in the
following code:
const MongoClient = require("mongodb").MongoClient;
Run your Node.js Application
Run the application you created from the previous step from the command line:
node index.js
You should see the details of the retrieved movie document in the output:
{ _id: ..., plot: 'A young man is accidentally sent 30 years into the past...', genres: [ 'Adventure', 'Comedy', 'Sci-Fi' ], ... title: 'Back to the Future', ... }
If you encounter an error or no output, check whether you specified the proper connection string in the application code, and loaded the sample data set in your Atlas cluster.
At this point, you should have a working application that uses the Node.js driver to connect to your MongoDB instance, runs a query on the sample data, and prints out the result.
Next Steps
Learn how to read and modify data using the Node.js driver in our CRUD Operations guide or how to perform common operations in our Usage Examples.