您可以使用以下种方法查询 MongoDB 中的嵌入式文档:
您的编程语言的驱动程序。
MongoDB Atlas 用户界面。要了解更多信息,请参阅使用 MongoDB Atlas 查询嵌入式文档。
➤ 使用右上角的 Select your language(选择语言)下拉菜单,设置以下示例的语言或选择 MongoDB Compass。
此页面中的示例展示了使用 mongosh 中的 db.collection.find() 方法对嵌入式/嵌套文档执行的查询操作。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
本页面提供了使用 MongoDB Compass 对嵌套/嵌入文档执行查询操作的示例。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
本页提供的示例展示使用MongoDB C#驱动程序中的 MongoCollection.Find() 方法对嵌入式/嵌套文档进行查询操作。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
本页提供了使用MongoDB Go 驱动程序中的 Collection.Find 函数对嵌入式/嵌套文档进行查询操作的示例。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
本页提供了使用 com.mongodb.reactivestreams 对嵌入式/嵌套文档进行查询操作的示例。 MongoDB Java Reactive Streams 驱动程序中的客户端方法。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
本页提供了使用 com.mongodb 对嵌入式/嵌套文档进行查询操作的示例。 MongoDB Java同步驱动程序中的客户端方法。
提示
此驱动程序提供了 com.mongodb.client.model.Filters 辅助方法,以便于创建筛选器文档。此页面中的示例使用这些方法创建筛选器文档。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
本页提供了使用 motor.motor_asyncio.AsyncIOMotorCollection.find 方法在 Motor 驱动程序中对嵌入/嵌套文档进行查询操作的示例。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
本页提供了使用Collection.find()对嵌入式/嵌套文档进行查询操作的示例。MongoDB Node.js驱动程序中的方法。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
此页面中的示例展示了使用 MongoDB PHP 库中的 MongoDB\\Collection::find() 方法对嵌入/嵌套文档执行查询操作。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
pymongo.collection.Collection.find本页提供了使用PyMongo Python驱动程序中的 方法对嵌入式/嵌套文档进行查询操作的示例。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
本页提供了使用 MongoDB Ruby 驱动程序中的 Mongo::Collection#find() 方法对嵌入/嵌套文档进行查询操作的示例。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
本页提供了使用 .find()集合对嵌入式/嵌套文档进行查询操作的示例MongoDB Scala驱动程序中的方法。
此页面上的示例使用的是 inventory 集合。连接到 MongoDB 实例中的测试数据库,然后创建 inventory 集合:
db.inventory.insertMany( [ { item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }, { item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" }, { item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" }, { item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" }, { item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" } ]);
[ { "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": { "h": 14, "w": 21, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "A" }, { "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "status": "A" }, { "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": { "h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in" }, "status": "D" }, { "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": { "h": 22.85, "w": 30, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "D" }, { "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": { "h": 10, "w": 15.25, "uom": "cm" }, "status": "A" } ]
有关在 MongoDB Compass 中插入文档的说明,请参阅插入文档。
var documents = new[] { new BsonDocument { { "item", "journal" }, { "qty", 25 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 14 }, { "w", 21 }, { "uom", "cm" } } }, { "status", "A" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "notebook" }, { "qty", 50 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 8.5 }, { "w", 11 }, { "uom", "in" } } }, { "status", "A" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "paper" }, { "qty", 100 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 8.5 }, { "w", 11 }, { "uom", "in" } } }, { "status", "D" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "planner" }, { "qty", 75 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 22.85 }, { "w", 30 }, { "uom", "cm" } } }, { "status", "D" } }, new BsonDocument { { "item", "postcard" }, { "qty", 45 }, { "size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 10 }, { "w", 15.25 }, { "uom", "cm" } } }, { "status", "A" } }, }; collection.InsertMany(documents);
docs := []any{ bson.D{ {"item", "journal"}, {"qty", 25}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 14}, {"w", 21}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, {"status", "A"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "notebook"}, {"qty", 50}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 8.5}, {"w", 11}, {"uom", "in"}, }}, {"status", "A"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "paper"}, {"qty", 100}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 8.5}, {"w", 11}, {"uom", "in"}, }}, {"status", "D"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "planner"}, {"qty", 75}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 22.85}, {"w", 30}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, {"status", "D"}, }, bson.D{ {"item", "postcard"}, {"qty", 45}, {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 10}, {"w", 15.25}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, {"status", "A"}, }, } result, err := coll.InsertMany(context.TODO(), docs)
Publisher<Success> insertManyPublisher = collection.insertMany(asList( Document.parse("{ item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }") ));
collection.insertMany(asList( Document.parse("{ item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }"), Document.parse("{ item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }") ));
# Subdocument key order matters in a few of these examples so we have # to use bson.son.SON instead of a Python dict. from bson.son import SON await db.inventory.insert_many( [ { "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": SON([("h", 14), ("w", 21), ("uom", "cm")]), "status": "A", }, { "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": SON([("h", 8.5), ("w", 11), ("uom", "in")]), "status": "A", }, { "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": SON([("h", 8.5), ("w", 11), ("uom", "in")]), "status": "D", }, { "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": SON([("h", 22.85), ("w", 30), ("uom", "cm")]), "status": "D", }, { "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": SON([("h", 10), ("w", 15.25), ("uom", "cm")]), "status": "A", }, ] )
await db.collection('inventory').insertMany([ { item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' } ]);
$insertManyResult = $db->inventory->insertMany([ [ 'item' => 'journal', 'qty' => 25, 'size' => ['h' => 14, 'w' => 21, 'uom' => 'cm'], 'status' => 'A', ], [ 'item' => 'notebook', 'qty' => 50, 'size' => ['h' => 8.5, 'w' => 11, 'uom' => 'in'], 'status' => 'A', ], [ 'item' => 'paper', 'qty' => 100, 'size' => ['h' => 8.5, 'w' => 11, 'uom' => 'in'], 'status' => 'D', ], [ 'item' => 'planner', 'qty' => 75, 'size' => ['h' => 22.85, 'w' => 30, 'uom' => 'cm'], 'status' => 'D', ], [ 'item' => 'postcard', 'qty' => 45, 'size' => ['h' => 10, 'w' => 15.25, 'uom' => 'cm'], 'status' => 'A', ], ]);
db.inventory.insert_many( [ { "item": "journal", "qty": 25, "size": {"h": 14, "w": 21, "uom": "cm"}, "status": "A", }, { "item": "notebook", "qty": 50, "size": {"h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in"}, "status": "A", }, { "item": "paper", "qty": 100, "size": {"h": 8.5, "w": 11, "uom": "in"}, "status": "D", }, { "item": "planner", "qty": 75, "size": {"h": 22.85, "w": 30, "uom": "cm"}, "status": "D", }, { "item": "postcard", "qty": 45, "size": {"h": 10, "w": 15.25, "uom": "cm"}, "status": "A", }, ] )
client[:inventory].insert_many([ { item: 'journal', qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'notebook', qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'A' }, { item: 'paper', qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: 'in' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'planner', qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'D' }, { item: 'postcard', qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: 'cm' }, status: 'A' } ])
collection.insertMany(Seq( Document("""{ item: "journal", qty: 25, size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }"""), Document("""{ item: "notebook", qty: 50, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "A" }"""), Document("""{ item: "paper", qty: 100, size: { h: 8.5, w: 11, uom: "in" }, status: "D" }"""), Document("""{ item: "planner", qty: 75, size: { h: 22.85, w: 30, uom: "cm" }, status: "D" }"""), Document("""{ item: "postcard", qty: 45, size: { h: 10, w: 15.25, uom: "cm" }, status: "A" }""") )).execute()
使用点符号对嵌套字段进行查询
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档中的字段指定查询条件,请使用点符号 ("field.nestedField")。
注意
使用点表示法查询时,字段和嵌套字段必须放在引号内。
在嵌套字段上指定相等匹配项
以下示例会选择嵌套在 size 字段中的 uom 字段等于 "in" 的所有文档:
db.inventory.find( { "size.uom": "in" } )
将以下过滤器复制到 Compass 查询栏中,然后单击 Find:
{ "size.uom": "in" }
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("size.uom", "in"); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{{"size.uom", "in"}}, )
findPublisher = collection.find(eq("size.uom", "in"));
findIterable = collection.find(eq("size.uom", "in"));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.uom": "in"})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ 'size.uom': 'in' });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size.uom' => 'in']);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.uom": "in"})
client[:inventory].find('size.uom' => 'in')
findObservable = collection.find(equal("size.uom", "in"))
使用查询运算符指定匹配
除了相等过滤条件外,MongoDB 还提供各种查询操作符来指定过滤条件。使用 FilterDefinitionBuilder 方法创建过滤器文档。例如:
var builder = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter; builder.And(builder.Eq(<field1>, <value1>), builder.Lt(<field2>, <value2>));
除了相等条件外,MongoDB 还提供各种查询运算符来指定筛选条件。使用 com.mongodb.client.model.Filters 辅助方法,以便于创建筛选器文档。例如:
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), eq(<field3>, <value3>))
除了相等条件外,MongoDB 还提供各种查询运算符来指定筛选条件。使用 com.mongodb.client.model.Filters 辅助方法,以便于创建筛选器文档。例如:
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), eq(<field3>, <value3>))
除了相等条件外,MongoDB 还提供各种查询操作符来指定过滤条件。使用 com.mongodb.client.model.Filters_ 辅助方法促进过滤器文档的创建。例如:
and(gte(<field1>, <value1>), lt(<field2>, <value2>), equal(<field3>, <value3>))
以下查询将对嵌入到 size 字段中的 h 字段使用小于运算符 ($lt):
db.inventory.find( { "size.h": { $lt: 15 } } )
将以下过滤器复制到 Compass 查询栏中,然后单击 Find:
{ "size.h": { $lt: 15 } }
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Lt("size.h", 15); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"size.h", bson.D{ {"$lt", 15}, }}, })
findPublisher = collection.find(lt("size.h", 15));
findIterable = collection.find(lt("size.h", 15));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.h": {"$lt": 15}})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ 'size.h': { $lt: 15 } });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size.h' => ['$lt' => 15]]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.h": {"$lt": 15}})
client[:inventory].find('size.h' => { '$lt' => 15 })
findObservable = collection.find(lt("size.h", 15))
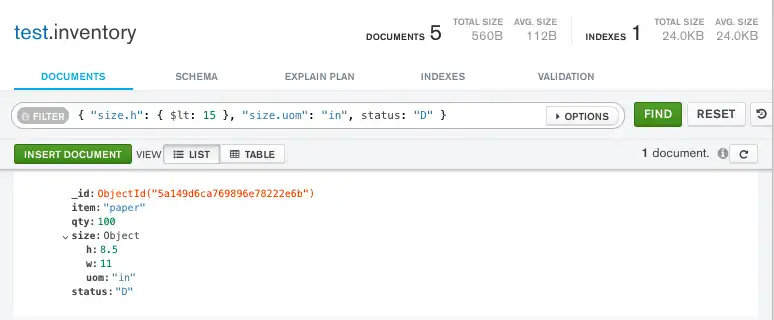
指定 AND 条件
以下查询选择嵌套字段 h 小于 15、嵌套字段 uom 等于 "in" 以及 status 字段等于 "D" 的所有文档:
db.inventory.find( { "size.h": { $lt: 15 }, "size.uom": "in", status: "D" } )
将以下过滤器复制到 Compass 查询栏中,然后单击 Find:
{ "size.h": { $lt: 15 }, "size.uom": "in", status: "D" }
var builder = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter; var filter = builder.And(builder.Lt("size.h", 15), builder.Eq("size.uom", "in"), builder.Eq("status", "D")); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"size.h", bson.D{ {"$lt", 15}, }}, {"size.uom", "in"}, {"status", "D"}, })
findPublisher = collection.find(and( lt("size.h", 15), eq("size.uom", "in"), eq("status", "D") ));
findIterable = collection.find(and( lt("size.h", 15), eq("size.uom", "in"), eq("status", "D") ));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.h": {"$lt": 15}, "size.uom": "in", "status": "D"})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ 'size.h': { $lt: 15 }, 'size.uom': 'in', status: 'D' });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find([ 'size.h' => ['$lt' => 15], 'size.uom' => 'in', 'status' => 'D', ]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size.h": {"$lt": 15}, "size.uom": "in", "status": "D"})
client[:inventory].find('size.h' => { '$lt' => 15 }, 'size.uom' => 'in', 'status' => 'D')
findObservable = collection.find(and( lt("size.h", 15), equal("size.uom", "in"), equal("status", "D") ))
匹配嵌入式/嵌套文档
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用查询过滤器文档 { <field>: <value> },其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用查询过滤器文档 { <field>: <value> },其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
要在嵌入/嵌套文档的字段上指定相等条件,请使用 Eq 方法构造一个过滤器:
Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq(<field>, <value>)
<value> 是要匹配的文档。
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用过滤器文档 eq( <field1>, <value>),其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用过滤器文档 eq( <field1>, <value>),其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用查询过滤器文档 { <field>: <value> },其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用查询过滤器文档 { <field>: <value> },其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用查询过滤器文档 [ <field> => <value> ],其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用查询过滤器文档 { <field>: <value> },其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用查询过滤器文档 { <field> => <value> },其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
要对嵌入式/嵌套文档的字段指定相等条件,请使用过滤器文档 equal( <field1>, <value> ),其中 <value> 是要匹配的文档。
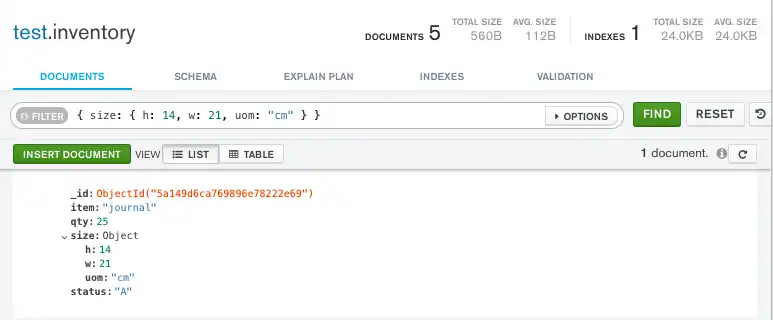
例如,以下查询会选择字段 size 等于文档 { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } 的所有文档:
db.inventory.find( { size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } } )
将以下过滤器复制到 Compass 查询栏中,然后单击 Find:
{ size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: "cm" } }
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("size", new BsonDocument { { "h", 14 }, { "w", 21 }, { "uom", "cm" } }); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"size", bson.D{ {"h", 14}, {"w", 21}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, })
FindPublisher<Document> findPublisher = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }")));
FindIterable<Document> findIterable = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' }")));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size": SON([("h", 14), ("w", 21), ("uom", "cm")])})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' } });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size' => ['h' => 14, 'w' => 21, 'uom' => 'cm']]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size": {"h": 14, "w": 21, "uom": "cm"}})
client[:inventory].find(size: { h: 14, w: 21, uom: 'cm' })
var findObservable = collection.find(equal("size", Document("h" -> 14, "w" -> 21, "uom" -> "cm")))
警告
MongoDB 不建议对嵌入式文档进行比较,因为这些操作需要与指定的 <value> 文档完全匹配,包括字段顺序。
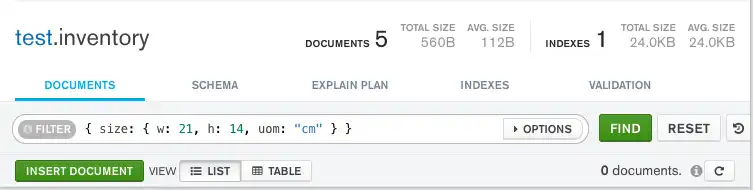
例如,以下查询不会匹配 inventory 集合中的任何文档:
db.inventory.find( { size: { w: 21, h: 14, uom: "cm" } } )
var filter = Builders<BsonDocument>.Filter.Eq("size", new BsonDocument { { "w", 21 }, { "h", 14 }, { "uom", "cm" } }); var result = collection.Find(filter).ToList();
cursor, err := coll.Find( context.TODO(), bson.D{ {"size", bson.D{ {"w", 21}, {"h", 14}, {"uom", "cm"}, }}, })
findPublisher = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ w: 21, h: 14, uom: 'cm' }")));
findIterable = collection.find(eq("size", Document.parse("{ w: 21, h: 14, uom: 'cm' }")));
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size": SON([("w", 21), ("h", 14), ("uom", "cm")])})
const cursor = db.collection('inventory').find({ size: { w: 21, h: 14, uom: 'cm' } });
$cursor = $db->inventory->find(['size' => ['w' => 21, 'h' => 14, 'uom' => 'cm']]);
cursor = db.inventory.find({"size": {"w": 21, "h": 14, "uom": "cm"}})
client[:inventory].find(size: { h: 21, w: 14, uom: 'cm' })
findObservable = collection.find(equal("size", Document("w" -> 21, "h" -> 14, "uom" -> "cm")))
当与不使用有序数据结构来表达查询的驱动程序一起使用时,对嵌入式文档进行比较的查询可能会导致不可预测的行为。
使用 MongoDB Atlas 查询嵌入式文档
本部分的示例使用的是示例电影数据集。要了解如何将示例数据集加载到您的 MongoDB Atlas 部署中,请参阅加载示例数据。
要在 MongoDB Atlas 中查询嵌入文档,请按照以下步骤操作:
在 MongoDB Atlas 用户界面中,转到您项目的 Clusters(集群)页面。
如果尚未显示,请从导航栏上的 Organizations 菜单中选择包含所需项目的组织。
如果尚未显示,请从导航栏的 Projects 菜单中选择您的项目。
在侧边栏中,单击 Database 标题下的 Clusters。
会显示集群页面。
其他查询教程
有关其他查询示例,请参阅: